Lasius flavus
| Lasius flavus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Lasiini |
| Genus: | Lasius |
| Section: | flavus clade |
| Species group: | flavus |
| Species: | L. flavus |
| Binomial name | |
| Lasius flavus (Fabricius, 1782) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Lasius flavus is hypogeic, seldom occurring above ground, and feeding on small insects and the exudate of subterranean root feeding aphids. It occurs in grasslands and at forest margins, nesting in the soil and under stones. (Japanese Ant Image Database) In Greece it prefers shadow mountain forests growing on high altitudes. In Achaia and Aetolia-Acarnania, it was observed mostly in fir forests; single records come from mixed chestnut and fir forest and mountain pasture (Borowiec & Salata, 2021).
| At a Glance | • Polygynous |
| Common Name | |
|---|---|
| キイロケアリ | |
| Translation: | Kiiro-ke-ari |
| Language: | Japanese |
Photo Gallery
Identification
Clear yellow to brownish yellow. Body hairs on dorsum of gaster and alitrunk long; appendages and body covered with more or less thick adpressed pubescence, more dilute on head. No erect hairs on tibiae, scapes or genae. Scale thin in side view, low and broad in front view with dorsal margin mildly convex straight or in larger specimens occasionally emarginate. Size very variable in North European populations. Length: 2.2-4.8 mm (Europe: Collingwood 1979).
Keys including this Species
- Key to Lasius Palaearctic workers
- Key to Lasius males
- Key to Lasius queens
- Key to Metalasius and Lasius of the subgenus Cautolasius of Greece
Distribution
This species is rare in southern parts of Japan, but it is found commonly in northern regions such as Hokkaido and the Tohoku district. In the Kanto district it commonly occurs in mountainous regions, and there are a few lowland records (Japanese Ant Image Database).
The Reinig Line faunal divide separates East Siberian, Inner Mongolian, Chinese and Tibetan species from those of Central Siberia, West Siberia and the Turanian region (DE LATTIN, 1967). In ants, the Reinig Line is crossed only by a cold resistant species including Camponotus herculeanus, Formica exsecta, Formica gagatoides, Formica lugubris, Formica manchu, Formica picea, Formica pisarskii, Formica uralensis, Lasius flavus, Leptothorax acervorum and Tetramorium sibiricum (DLUSSKY, 1967; FRANCOEUR, 1983; SEIFERT, 2000, 2021a, 2021b).
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 70.377854° to 28.814°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Palaearctic Region: Albania, Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Balearic Islands, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canary Islands, Channel Islands, China, Croatia, Czechia, Democratic Peoples Republic of Korea, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iberian Peninsula, Iran, Italy, Japan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mongolia, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, North Macedonia, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Türkiye, Turkmenistan, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
This name had long been applied to a morphologically similar North American form that is now know as Lasius aphidicola (Schär et al. 2018).
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
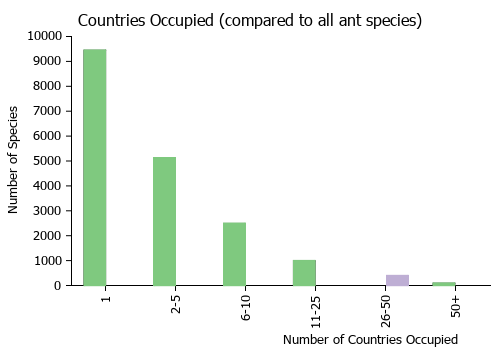
|
Habitat
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - In Greece, it is one of the least thermophilic species of the genus Lasius, it prefers mountain and shady forests. Most records are from coniferous forests especially fir forests) but it was noted also from mountain deciduous forests, stream valleys in deciduous forests, pastures with mixed forests, roadsides in coniferous forests, mixed forests close to parkings and alpine pastures with shrubs. Most records are from 800 to 1720 m a. s. l., only in northern Greece it was noted from 100 to 700 m.
Biology
Nests under stone, rarely in stable soil mound cemented by the dense root turf made of diverse plants.
Wilson (1955) - The nesting habits and habitat preferences of flavus are subject to marked geographic variation. In Germany, Gosswald (1932) found the species to be highly adaptable, occupying moist forest floors, forest borders, hedgerows, grassy paths, cultivated areas but does not nest in gardens. In a random field sample, Gosswald recorded 835 colonies under stones, usually in dry situations, 300 in mounds, mostly in meadows, and 30 in dead tree trunks in woodland. The mounds reach their largest size in swampy areas, and may exceed 60 cm. in height. Gosswald judged this species to be more adaptable, although not more abundant, than Lasius niger. He encountered 6 colonies that he determined as "myops", all under rocks in open, dry ground. It sounds likely that these were depauperate colonies living in a habitat affording only marginal existence.
Many other authors have made similar observations concerning the diverse nesting habits of flavus in northern and central Europe. O'Rourke (1950) found it in Ireland mostly in dry, sunny situations with fine soil, but never encountered it in marshes or in rotting wood in forests. Skwarra (1929) found it to be a very successful ant in the Zehlau Moor of East Prussia, exceeded in abundance there only by Lasius niger, she notes the general preferences of this species for open, moist, grassy land, in fields, marshes, along the shores of inland lakes and ponds, and on riverbanks.
The mounds which the European flavus builds have been described in the literature many times. In Switzerland they occur mostly on eastern and southern mountain slopes, tending to increase in height and size with elevation (Wheeler, Forel, et al.). They are typically elongate in shape under these conditions, with the long axis east-west and the east face precipitous. According to Linder (1908) this peculiar shape is caused by the ants inhabiting and building only in the east end of the mound.
In southern Europe, in the lowlands at least, the mound-building habit is lost, and the species nests almost exclusively under stones. Zimmermann (1934), for instance, found it limited to this latter nesting site in the islands around the Quarnerolo. At Miao T'ai Tze, Shensi, China, W. L. Brown (pers. commun.) found flavus nesting under stones.
European observers are in agreement that flavus is completely subterranean. Its mounds ordinarily lack external openings and workers are rarely seen above the ground. It has been generally assumed that the main food source of this species consists of the secretions of Homoptera maintained in the nests (cf. Eidmann, 1926), but food habits have never been well investigated. The utilization of some amount of insect food seems likely. Donisthorpe (1927, p. 258) mentions the presence of insect remains in flavus galleries under stones, and Richards (1953, p. 128) has observed flavus workers dismembering a caterpillar on top of a mound.
The mass of published data on nuptial flights by this species in Europe has been well summarized by Donisthorpe (1927). The flights occur in the late afternoon from July to September and predominantly in August. They are often concurrent with flights of niger. Winged forms are found in the nests from June to October.
Seifert (2020) - Achieves in extensively managed pastures of southern England (Waloff & Blackith 1962) and southern Germany (Seifert 2017) the largest biomass known for any ant species worldwide, with estimates of 160 kg fresh weight / ha in the first and of 145 kg in the second study. Seven tons of soil material are here transported to surface per ha and year by a single ant species – the consequences on drainage and aeration of soils are considerable.
Collingwood (1979) - This species is very widely distributed and one of the most abundant in North Europe where it is a characteristic earth mound builder in pastures and along the periphery of woodlands but also nesting under stones in rocky areas. Colonies are started by one or more queens with primary pleometrose quite frequent. In North Europe nests in exposed places and in northern extremity of its distribution, L.flavus exhibits a wide range of worker size. On warm sites in southern areas usually in sandy lowland heath, worker size is small and much less variable. Eye ommatidium number is correlated with size and series of small workers with eyes with low ommatidium number are sometimes referred to Lasius myops Forel. However, queen size is constant regardless of worker size. L. myops is therefore regarded as a synonym of L.flavus. Individual nests may contain several thousand individuals and favourable nest sites, e. g. pasture sloping with a southern aspect, may be crowded with mound nests. This species, as with Lasius niger, tends to swarm on the same day in any one area and in years of abundant production of sexuals huge mating swarms may occur during late July or August. This species is hypogoeic, seldom occurring above ground, feeding on small insects and the exudate of subterranean root feeding aphids.
Mixed Nests
Kvifte and Soule (2017) - Lasius flavus and Formica lemani were found in a plesiobiotic association in a heathland in western Norway. The colonies were found in chambers under rocks, with both larvae and pupae of both species present.
This is the first confirmed case of F. lemani in a plesiobiontic relationship with another ant species, providing further evidence for Collingwood’s (1979) claim that the habits of F. lemani are similar to Formica fusca – the most frequently recorded plesiobiont in the Palearctic region (Kaniszai et al., 2013). Workers of Formica lemani and Lasius flavus differ markedly in size and foraging behaviour. Whereas F. lemani is a free-living and active predacious, aphidicolous and nectarivorous species, L. flavus is mostly subterranean and feeds on smaller arthropods and honeydew from root feeding aphids (Collingwood, 1979; Douwes et al., 2012). The resources exploited by each species thus show little overlap, permitting coexistence without competition. This follows the general pattern outlined for plesiobiontic relationships by Kanizsai et al. (2013). Colony sizes of the two species are listed in the literature as a few hundred to a few thousand for F. lemani and up to 100 000 workers for L. flavus (Douwes et al., 2012).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formica aquilonia (a xenobiont) in Finland (Czechowski, 2004; Kanizsai et al., 2013) (Different successional series of rocky habitats. Mound of Formica aquilonia.).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formica cunicularia (a xenobiont) in United Kingdom (Kanizsai et al., 2013; Morley, 1945) (Foreshore. Under stone).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formica fusca (a xenobiont) in Finland (Czechowski, 2004; Kanizsai et al., 2013) (Different successional series of rocky habitats. In rock crevice).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formica fusca (a xenobiont) in Italy (Balzani et al., 2022).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formica fuscocinerea (a xenobiont) in Poland (Czechowski & Czechowska, 2000; Kanizsai et al., 2013) (Grassy mountain slope. Under stone.).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Lasius niger (a xenobiont) in Finland, United Kingdom (Czechowski, 2004; Kanizsai et al., 2013; Morley, 1945) (Rocky outcrop; shore meadow, foreshore. In rock crevice/under stone.).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Lasius platythorax (a xenobiont) in Finland (Czechowski, 2004; Kanizsai et al., 2013) (Different successional series of rocky habitats. In rock crevice/under stone/overgrown soil.).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Myrmica ruginodis (a xenobiont) in Italy (Balzani et al., 2022).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Myrmica scabrinodis (a xenobiont) in United Kingdom (Kanizsai et al., 2013; Morley, 1945) (Foreshore. Under stone.).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Tetramorium caespitum (a xenobiont) in Finland (Czechowski, 2004; Kanizsai et al., 2013) (Different successional series of rocky habitats. Under stone.).
Life History Traits
- Colony founding: claustral independent (pleometrotic)
Flight Period
| X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Source: antkeeping.info.
- Check details at Worldwide Ant Nuptial Flights Data, AntNupTracker and AntKeeping.
 Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
This species is a host for the temporary parasites Lasius carniolicus, Lasius mixtus and Lasius orientalis.
Khaustov 2015 (abstract): Twenty four species of pygmephoroid mites (Acari: Pygmephoroidea: Neopygmephoridae, Scutacaridae, Microdispidae) are recorded from the ant Lasius flavus (Fabricius) or from its nests from Western Siberia and Crimea. Four of them of the genus Scutacarus Gros, 1845 (Acari: Scutacaridae), S. insolitus sp. nov., S. heterotrichus sp. nov., S. moseri sp. nov. and S. sibiriensis sp. nov. are described as new for science. Four species of scutacarid mites are recorded for the first time in Russia. The comparison of pygmephoroid mite communities associated with Lasius flavus from Crimean and West Siberian populations and notes on phoresy of pygmephoroid mites on ants are provided.
Other Arthropods
- Arroyo et al. (2015) studied the diversity of mites living in meadow nests of Lasius flavus in Ireland.
- This species is a mutualist for the aphid Forda marginata (a trophobiont) (Cockerell, 1903; Saddiqui et al., 2019).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon buccatus (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon buccatus (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the phorid fly Pseudacteon formicarum (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a prey for the Microdon fly Microdon sp. (a predator) (Quevillon, 2018).
Fungi
- This species is a host for the fungus Aegeritella tuberculata (a pathogen) (Espadaler & Santamaria, 2012).
Mites
- This species is a host for the mite Imparipes obsoletus (a parasite) (Khaustov, 2015) (ectoparasite).
- This species is a host for the mite Petalomium carelitschensis (a parasite) (Khaustov, 2015) (ectoparasite).
- This species is a host for the mite Scutacarus longisetus (a parasite) (Khaustov, 2015) (ectoparasite).
Nematodes
- This species is a host for the nematode Oscheius dolichura (a parasite) (Quevillon, 2018) (multiple encounter modes; indirect transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the nematode Oscheius dolichura (a parasite) (Janet, 1893; Wahab, 1962).
- This species is a host for the nematode Pheromermis villosa (a parasite) in Austria (Kaiser, 1986a, 1986b).
- This species is a host for the nematode "Mermis" (a parasite) in England (Oxford, Cornwal) (Crawley & Baylis, 1921).
- This species is a host for the nematode Pheromermis myrmecophila (a parasite) in Ireland (O'Rourke, 1946; O’Grady & Breen, 2011; Laciny, 2021).
- This species is a host for the nematode Mermithidae (unspecified "Mermix") (a parasite) in Germany (Wuerzburg) (Gösswald, 1938; Laciny, 2021).
Life History Traits
- Queen number: monogynous (Waloff, 1957; Frumhoff & Ward, 1992)
- Queen mating frequency: multiple (Waloff, 1957; Frumhoff & Ward, 1992)
Castes
Worker
Queen
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0173149. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
    
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0173168. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Male
Images from AntWeb
     
| |
| Male (alate). Specimen code casent0173150. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
     
| |
| Male (alate). Specimen code casent0173169. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- flavus. Formica flava Fabricius, 1782: 491 (w.) EUROPE. Latreille, 1798: 42 (q.m.); Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1953c: 152 (l.); Hauschteck, 1962: 219 (k.); Imai, 1966: 120 (k.). Combination in Lasius: Mayr, 1861: 50; Emery, 1925b: 231; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1929b: 36; in Donisthorpea: Donisthorpe, 1915d: 216; in Formicina: Emery, 1916b: 241; in Acanthomyops: Forel, 1916: 460; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1927e: 187; in Lasius (Chthonolasius): Ruzsky, 1914a: 59; in Chthonolasius: Ruzsky, 1925a: 288; Ruzsky, 1936: 90; in Lasius (Cautolasius): Wilson, 1955a: 112. Senior synonym of ruficornis: Roger, 1862c: 285; of ibericus and material of the unavailable name sancho referred here: Wilson, 1955a: 112; Seifert, 1990: 12; of apennina, brevicornis, fuscoides, helvus, microps (and its junior synonym claripennis), morbosa, odoratus, olivacea: Wilson, 1955a: 112. See also: Bernard, 1967: 359; Kutter, 1977c: 229; Collingwood, 1979: 96; Yamauchi, 1979: 160; Kupyanskaya, 1990: 222; Atanassov & Dlussky, 1992: 241.
- brevicornis. Lasius brevicornis Emery, 1893i: 639, pl. 22, fig. 22 (w.q.m.) U.S.A. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- fuscoides. Lasius flavus var. fuscoides Ruzsky, 1902e: 16 (w.) RUSSIA. Combination in L. (Chthonolasius): Ruzsky, 1914a: 61; in Chthonolasius: Ruzsky, 1925a: 288; in Acanthomyops: Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1927e: 187. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- odoratus. Lasius flavus var. odoratus Ruzsky, 1905b: 282 (w.) RUSSIA. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- claripennis. Lasius (Formicina) flavus subsp. claripennis Wheeler, W.M. 1917a: 527 (w.q.m.) CANADA. Junior synonym of microps: Creighton, 1950a: 422.
- microps. Lasius (Formicina) brevicornis var. microps Wheeler, W.M. 1917a: 526 (w.) U.S.A. Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1953c: 152 (l.). Combination in L. (Chthonolasius): Creighton, 1950a: 422. Subspecies of brevicornis: Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, E.W. 1944: 253; of flavus: Creighton, 1950a: 422. Senior synonym of claripennis: Creighton, 1950a: 422. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- morbosa. Formicina flava var. morbosa Bondroit, 1918: 28 (w.q.) FRANCE. Junior synonym of flavoides: Emery, 1925b: 231; of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- apennina. Lasius (Chthonolasius) umbratus var. apennina Menozzi, 1925d: 34 (w.) ITALY. Menozzi, 1932a: 8 (q.m.). Subspecies of flavus: Menozzi, 1932a: 8. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- ibericus. Lasius (Chthonolasius) umbratus st. ibericus Santschi, 1925g: 349, fig. 2 (w.) SPAIN. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 112.
- olivacea. Lasius (Lasius) flavus var. olivacea Karavaiev, 1926e: 194 (w.) CAUCASUS. Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 113.
- helvus. Lasius helvus Cook, 1953: 326, figs. (w.) U.S.A. [Also spelled helveolus, on p. 327.] Junior synonym of flavus: Wilson, 1955a: 113.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Wilson (1955) - Mandibular dentition follows certain recognizable trends specific at least for the subgenus. In large specimens from northern Europe there are commonly four basal teeth, with either the second or third from the base frequently reduced in size. As body size decreases the common basal tooth number becomes three and then two; in the latter case the median tooth is frequently reduced. Superimposed on this allometric variation is the frequent, non-allometric loss of the second intercalary tooth. Clypeus with a well defined median carina, which tends to become obsolescent in small workers. Anterior border of median clypeal lobe broadly and evenly rounded. Head tending to be more massive relative to body than in all other members of the genus with the exception of L. brunneus. Color highly variable, from straw yellow to dark yellowish brown. Minor workers are nearly aways clear yellow, medias show various degrees of light infuscation, and very large workers (found in northern Eurasia only) are often deeply infuscated.
Worker and queen. In the eastern United States, where Lasius flavus occurs sympatrically with Lasius nearcticus, it can be separated from this and other Cautolasius by a host of characters, but elsewhere these are subject to much geographic variation and tend to break down and lose their diagnostic value. Only one character has been found which will consistently separate all Nearctic and Palaearctic flavus populations from Lasius nearcticus (no. 1 below).
(1) Maxillary palp segment V as long as segment VI or longer.
(2) A much weaker character is found in the petiolar outline. In flavus the dorsal margin in frontal view is usually emarginated to flat, while in the majority of nearcticus it is convex.
(3) In addition, flavus can be separated from the related species Lasius fallax and Lasius talpa by the following character: scapes and outer tibial surfaces lacking standing hairs.
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - Polymorphic, HL 0.674-0.953, HW 0.603-0.952, ML 0.76-1.14. Scape moderately elongate, SL 0.556-0.800. Color. Whole body including appendages pale yellow . Structure and setation. Head from slightly longer than wide to as long as wide, sides rounded, occipital margin straight to slightly concave. Eyes small, head length 6.0-7.2 times the maximum diameter of eye. Whole frontal head covered with moderately long, appressed and dense pubescence and sparse, long, erected setae. Occipital part of head with 6-8 long erected setae. Gena and underside of head lacking erected setae. Mesosomal dorsum with several long erected setae, length of the longest seta 0.143. Below propodeal spiracle no erected setae. Masticatory border of mandibles with 5-6 teeth. Antennal scapi with short appressed and slightly decumbent pubescence, erected setae absent onwhole anterior and dorsal surface. Hind tibiae lacking erected setae on external surface. Ventral surface of fore femora with up to two erected setae, od mid- and hind femora lacking erected setae, anterior surface of fore coxa with few long erected setae. Pubescence on the whole body and appendages very dense and whitish. Pubescence of clypeus sparse, not covering Clypeus. Surface of gastral tergites with microsculpture but shiny, first gastral tergite in central part with sparse, long erected setae. Propodeum in lateral view moderately high, slightly conical, metanotal groove deep.
Queen
see Wilson, in previous section, for "worker and queen"
Male
Wilson (1955) - Isolated individuals cannot be separated with certainty from other members of the subgenus.
(1) The subgenital plate tends to be subquadrate, with a protruding posteromedian setiferous area. This character will separate a majority of series from Lasius nearcticus.
(2) The outer femoral surfaces in Lasius flavus are ordinarily bare of standing hairs, separating this species from Lasius fallax and doubtfully from Lasius talpa.
Mandible form highly variable, ranging from the presumably primitive Lasius pallitarsis type to the Lasius niger type. The variation is partly allometric, i.e. the largest males usually have the pallitarsis type, while the smallest males always have the niger type or some degenerate modification of it.
Karyotype
- See additional details at the Ant Chromosome Database.
 Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- n = 15, 2n = 30 (Switzerland) (Hauschteck, 1962; Hauschteck-Jungen & Jungen, 1983).
References
- Arroyo, J., A. O'Grady, H. Vance, and T. Bolger. 2015. The mite (Acari: Oribatida, Mesostigmata) assemblages associated with Lasius flavus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) nests and surrounding soil in an Irish grassland. Biology and Environment-Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy. 115B:17-28. doi:10.3318/bioe.2015.03
- Atanassov, N.; Dlussky, G. M. 1992. Fauna of Bulgaria. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Fauna Bûlg. 22: 1-310 (page 241, see also)
- Baer, B. 2011. The copulation biology of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 14: 55-68.
- Balzani, P., Frizzi, F., Masoni, A., Santini, G. 2022. The effect of the introduced Red Wood Ant Formica paralugubris on the frequency of ant nests and first plesiobiotic association between Myrmica ruginodis (Nylander, 1846) and Lasius flavus (Fabricius, 1782). Sociobiology 69(4), e7901 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v69i4.7901).
- Bartz, S.H., Holldobler, B. 1982. Colony founding in Myrmecocystus mimicus Wheeler (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and the evolution of foundress associations. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 10, 137-147 (doi:10.1007/bf00300174).
- Berkelhamer, R.C. 1980. Reproductive strategies in ants: A comparison of single-queened versus multiple-queened species in the subfamily Dolichoderinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
- Bernadou, A., Fourcassié, V., Espadaler, X. 2013. A preliminary checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Andorra. ZooKeys 277, 13–23 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.277.4684).
- Bernard, F. 1967a [1968]. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp. (page 359, see also)
- Boomsma, J.J., Leusink, A. 1981. Weather conditions during nuptial flights of four European ant species. Oecologia 50, 236–241. (doi:10.1007/bf00348045).
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2021. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Western Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 30: 1-23 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.5571258).
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. A monographic review of ants of Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Vol. 1. Introduction and review of all subfamilies except the subfamily Myrmicinae. Part 1: text. Natural History Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum 1: 1-297.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Thassos Island, Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 31 (online 2): 1-15 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.6123287).
- Borowiec, L., van Delft, J.P.L., van Delft, J.J.C.W., Salata, S. 2023. Five ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) new to the Greek fauna with notes on ants from Greek Thrace. Annales of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 32 (online 008), 1-13 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.10101028).
- Boudinot, B.E., Borowiec, M.L., Prebus, M.M. 2022. Phylogeny, evolution, and classification of the ant genus Lasius, the tribe Lasiini and the subfamily Formicinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Systematic Entomology 47, 113-151 (doi:10.1111/syen.12522).
- Bračko, G. 2019. New data on the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Azerbaijan. Caucasian Entomological Bulletin 15, 165–175 (doi:10.23885/181433262019151-165175).
- Bracko, G., Wagner, H.C., Schulz, A., Gioahin, E., Maticic, J., Trantnik, A. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10: 10-24.
- Cantone S. 2017. Winged Ants, The Male, Dichotomous key to genera of winged male ants in the World, Behavioral ecology of mating flight (self-published).
- Carroll, T.M. 2011. The ants of Indiana (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). M.S. thesis, Purdue University.
- Collingwood, C. A. 1979. The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Fauna Entomol. Scand. 8: 1-174 (page 96, see also)
- Crawley, W.C., Baylis, H.A. 1921. Mermis parasitic on ants of the genus Lasius. Journal of the Royal Microscopy Society 257: 353–72 (doi:10.1111/j.1365-2818.1921.tb01370.x).
- Csősz, S., Báthori, F., Gallé, L., Lőrinczi, G., Maák, I., Tartally, A., Kovács, É., Somogyi, A.Á., Markó, B. 2021. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: Survey of ant species with an annotated synonymic inventory. Insects 16;12(1):78 (doi:10.3390/insects12010078).
- Csosz, S., Marko, B., Galle, L. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Cushing, P.E. 2012. Spider-ant associations: An updated review of myrmecomorphy, myrmecophily, and myrmecophagy in spiders. Psyche: A Journal of Entomology 2012, 1–23 (doi:10.1155/2012/151989).
- Czechowski, W. 2004. Scarcity of sites suitable for nesting promotes plesiobiosis in ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomologica Fennica 15(4). 211–218.
- Czechowski, W., Czechowska, W. 2000. Formica cinerea fuscocinerea For. in the Pieniny Mts, its untypical habitat and plesiobiosis with Lasius flavus (F.) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Fragmenta Faunistica 43, 131–133
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A., Czechowska, W. 2002. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Poland. MIZ PAS Warsaw.
- Davis, T. 2009. The ants of South Carolina (thesis, Clemson University).
- de Bekker, C., Will, I., Das, B., Adams, R.M.M. 2018. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and their parasites: effects of parasitic manipulations and host responses on ant behavioral ecology. Myrmecological News 28: 1-24 (doi:10.25849/myrmecol.news_028:001).
- Dekoninck, W., Ignace, D., Vankerkhoven, F., Wegnez, P. 2012. Verspreidingsatlas van de mieren van België. Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 148: 95-186.
- Del Toro, I., Robbons, R.R., Pelini, S.L. 2012. The little things that run the world revisited: a review of ant-mediated ecosystem services and disservices (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 17: 133-146.
- Depa, L. 2006. Weather conditions during nuptial flight of Manica rubida (LATREILLE, 1802) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in southern Poland. Myrmecological News 9: 27-32.
- Donisthorpe, H. 1915f. British ants, their life-history and classification. Plymouth: Brendon & Son Ltd., xv + 379 pp. (page 216, Combination in Donisthorpea)
- Emery, C. 1916a [1915]. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 47: 79-275 (page 241, Combination in Formicina)
- Emery, C. 1925d. Hymenoptera. Fam. Formicidae. Subfam. Formicinae. Genera Insectorum 183: 1-302 (page 231, Combination in Lasius)
- Espadaler, X., Santamaria, S. 2012. Ecto- and Endoparasitic Fungi on Ants from the Holarctic Region. Psyche Article ID 168478, 10 pages (doi:10.1155/2012/168478).
- Fabricius, J. C. 1782 [1781]. Species insectorum exhibentes eorum differentias specificas, synonyma, auctorum loca natalia, metamorphosin adiectis observationibus, descriptionibus. Tome I. Hamburgi et Kilonii [= Hamburg and Kiel]: C. E. Bohn, 552 pp. (page 491, worker described)
- Forel, A. 1916. Fourmis du Congo et d'autres provenances récoltées par MM. Hermann Kohl, Luja, Mayné, etc. Rev. Suisse Zool. 24: 397-460 (page 460, Combination in Acanthomyops)
- García, F., Cuesta-Segura, A.D., Espadaler, X. 2024. Myrmica babiensis sp. nov. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), a new social parasite from the NW Iberian Peninsula. Annales Zoologici 74(1), 113-127 (doi:10.3161/00034541anz2024.74.1.006).
- Glaser, F. 2016. Artenspektrum, Habitatbindung und naturschutzfachliche Bedeutung von Ameisen (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) am Stutzberg (Vorarlberg, Österreich). inatura – Forschung 34: 26 S.
- Gösswald, K. 1938. Über bisher unbekannte, durch den Parasitismus der Mermithiden (Nemat.) verursachte Formveränderungen bei Ameisen. Parasitology Research 10: 138-152.
- Haelewaters, D., Boer, P., Noordijk, J. 2015. Studies of Laboulbeniales (Fungi, Ascomycota) on Myrmica ants: Rickia wasmanniii in the Netherlands. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 44, 39–47 (doi:10.3897/jhr.44.4951).
- Hauschteck, E. 1962. Die Chromosomen einiger in der Schweiz vorkommender Ameisenarten. Vierteljahrsschr. Naturforsch. Ges. Zür. 107: 213-220 (page 219, karyotype described)
- Hisasue, Y. 2019. Ants collected from Akita Prefecture (Japan) in August 2017. ARI 40: 15-18.
- Imai, H. T. 1966b. The chromosome observation techniques of ants and the chromosomes of Formicinae and Myrmicinae. Acta Hymenopterol. 2: 119-131 (page 120, karyotype described)
- Imai, H.T., Kihara, A., Kondoh, M., Kubota, M., Kuribayashi, S., Ogata, K., Onoyama, K., Taylor, R.W., Terayama, M., Yoshimura, M., Ugawa, Y. 2003. Ants of Japan. 224 pp, Gakken, Japan.
- Ivanov, K. 2019. The ants of Ohio (Hymenoptera, Formicidae): an updated checklist. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 70: 65–87 (doi:10.3897@jhr.70.35207).
- Janet, M.-Ch. 1893. Sur les n´ematodes des glandes pharyngiennes des fourmis (Pelodera sp.). Comptes Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences 117: 700–703.
- Kaiser, H. 1986. Morphologische Analyse des Ameisen-Parasitioden Pheromermis villosa n. sp. (Nematoda, Mermithidae). Mitteilungen des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins fur Steiermark 116: 269–294.
- Kaiser, H. 1986. Über Wechselbeziehungen zwischen Nematoden (Mermithidae) und Ameisen. Zoologischer Anzeiger 217: 156-177.
- Kanizsai, O. 2014. Forms and background factors of the coexistence between colonies of Formica fusca and Camponotus vagus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in forest steppe habitats. Ph.D. thesis, University of Szeged.
- Kanizsai, O., Lőrinczi, G., Gallé, L. 2013. Nesting associations without interdependence: A preliminary review on plesiobiosis in ants. Psyche 2013, 238602 (doi:10.1155/2013/238602).
- Karaman, C., Kiran, K. 2022. Additional records of parasitic Camponotus Mayr (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species from Turkey with queen description of Camponotus ruseni Karaman, 2012. Zoology in the Middle East 68(2), 156–164 (doi:10.1080/09397140.2022.2051918).
- Khaustov, A. A. 2015. Myrmecophilous pygmephoroid mites (Acari: Pygmephoroidea) associated with Lasius flavus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Russia. Zootaxa. 4044:345-370.
- Khaustov, A.A. 2015. Myrmecophilous pygmephoroid mites (Acari: Pygmephoroidea) associated withLasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Western Siberia, Russia. International Journal of Acarology 42(2): 92–105 (doi:10.1080/01647954.2015.1124921).
- Kim, G., Lyu, D. 2012. Distribution of Ants (Insecta, Hymenoptera) in Chiaksan Mountain, Prov. Gangweon, Korea. Journal of Korean Nature 5, 127–129 (doi:10.7229/jkn.2012.5.2.127).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C. 2020. Additions to the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoosystema 42(18), 285-329 (doi:10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a18).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C., Heinze, J. 2021. First record of the inquiline ant Leptothorax kutteri Buschinger, 1965 from Turkey. Sociobiology 68, e7224 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v68i3.7224).
- Kirchmair, G., Friess, T. et al. 2017. Zoologischer Bericht vom Tag der Biodiversität 2017 im Naturpark Südsteiermark. Mitteilungen des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereines für Steiermark 147: 99–134.
- Kupyanskaya, A. N. 1990a. Ants of the Far Eastern USSR. Vladivostok: Akademiya Nauk SSSR, 258 pp. (page 222, see also)
- Kutter, H. 1977c. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Insecta Helv. Fauna 6: 1-298 (page 229, see also)
- Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, N. N. 1927e. Contributions to the knowledge of the myrmecology of Turkestan. III. Rus. Entomol. Obozr. 21: 186-196 (page 187, Combination in Acanthomyops)
- Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, N. N. 1929b. Die Ameisenfauna Daghestans. Zool. Anz. 83: 34-45 (page 36, Combination in Lasius)
- Kvifte, G. M., T. A. Legoy, and J. Soule. 2017. The Plesiobiontic Association of Formica lemani Bondroit with Lasius flavus (Fabricius) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Norway. Sociobiology. 64:366-368. doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v64i3.1030
- Laciny, A. 2017. Evidence of mermithism in a gyne of Lasius niger (Linnaeus, 1758) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Burgenland, Austria. Zeitschrift der Arbeitsgemeinschaft Österreichischer Entomologen 69: 131–138.
- Laciny, A. 2021. Among the shapeshifters: parasite-induced morphologies in ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) and their relevance within the EcoEvoDevo framework. EvoDevo 12, 2 (doi:10.1186/s13227-021-00173-2).
- Latreille, P. A. 1798. Essai sur l'histoire des fourmis de la France. Brive: F. Bourdeaux, 50 pp. (page 42, queen, male described)
- Liu, C., Fischer, G., Hita Garcia, F., Yamane, S., Liu, Q., Peng, Y.Q., Economo, E.P., Guénard, B., Pierce, N.E. 2020. Ants of the Hengduan Mountains: a new altitudinal survey and updated checklist for Yunnan Province highlight an understudied insect biodiversity hotspot. ZooKeys 978, 1–171 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.978.55767).
- MacGown, J.A., Booher, D., Richter, H., Wetterer, J.K., Hill, J.G. 2021. An updated list of ants of Alabama (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with new state records. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 147: 961-981 (doi:10.3157/061.147.0409).
- Mayr, G. 1861. Die europäischen Formiciden. Nach der analytischen Methode bearbeitet. Wien: C. Gerolds Sohn, 80 pp. (page 50, Combination in Lasius)
- Meurville, M.-P., LeBoeuf, A.C. 2021. Trophallaxis: the functions and evolution of social fluid exchange in ant colonies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 31: 1-30 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_031:001).
- Mokadam, C. 2021. Native and non-native ant impacts on native fungi (M.A. thesis, Buffalo State University).
- Morley, D.W. 1945. Observations on some plesiobiotic colonies of ants (Hymenoptera), with notes on some other mixtobiotic colonies. Proceedings of the Royal Entomological Society of London 20, 1–4.
- Nemet, E., Czekes, Z., Tausan, I., Marko, B. 2012. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the Cefa Nature Park (North-Western Romania). Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica Biologia 20, 61-72.
- O’Grady, A., Breen, J. 2011. Observations on mermithid parasitism (Nematoda: Mermithidae) in two species of Lasius ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Journal of Natural History 45: 2339-2345 (doi:10.1080/00222933.2011.596634).
- O’Rourke, B.S. 1946. The occurrence of three mermithogynes at Roundstone, Connemara, with notes on the ants of the area. Entomological Record 58: 65-70.
- Parmentier, T. 2020. Guests of Social Insects. In: Encyclopedia of Social Insects (doi:10.1007/978-3-319-90306-4_164-1).
- Parmentier, T., Gaju-Ricart, M., Wenseleers, T., Molero-Baltanás, R. 2021. Chemical and behavioural strategies along the spectrum of host specificity in ant-associated silverfish. Research Square (doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1108003/v1).
- Perfilieva, K.S. 2021. Distribution and differentiation of fossil Oecophylla (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species by wing imprints. Paleontological Journal 55(1), 76–89 (doi:10.1134/s003103012101010x).
- Phillips, A.L., Attewell, P. J. 2011. An occurrence of Lasius sabularum (Bondroit, 1918) and Lasius umbratus (Nylander, 1846) within the same nest in Lincolnshire, England. BWARS Newsletter Autumn 2011:22-24.
- Purkart, A., Kollár, J., Goffová, K. 2019. Fauna of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of selected sand habitats in Podunajsko Region, Slovakia. Naturae Tutela 23(1): 101-111.
- Radchenko, A.G., Fisher, B.L., Esteves, F.A., Martynova, E.V., Bazhenova, T.N., Lasarenko, S.N. 2023. Ant type specimens (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the collection of Volodymyr Opanasovych Karawajew. Communication 1. Dorylinae, Poneromorpha and Pseudomyrmecinae. Zootaxa, 5244(1), 1–32 (doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5244.1.1).
- Rericha, L. 2007. Ants of Indiana. Indiana Department of Natural Resources, 51pp.
- Roger, J. 1862c. Synonymische Bemerkungen. 1. Ueber Formiciden. Berl. Entomol. Z. 6: 283-297 (page 285, Senior synonym of ruficornis)
- Ruzsky, M. 1914a [1913]. Myrmekologische Notizen. Arch. Naturgesch. (A)79(9 9: 58-63 (page 59, Combination in Lasius (Chthonolasius))
- Ruzsky, M. 1925a. Material on the fauna of the spa "Karachinskoe Ozero". Izv. Tomsk. Gos. Univ. 75: 283-290 (page 288, Combination in Chthonolasius)
- Ruzsky, M. 1936. Ants of the Transbaikal region. Tr. Biol. Nauchn.-Issled. Inst. Tomsk. Gos. Univ. 2: 89-97 (page 90, Combination in Chthonolasius)
- Salata, S., Borowiec, L., Trichas, A. 2020. Review of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Crete, with keys to species determination and zoogeographical remarks. Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum No 12: 5–296 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.3738001).
- Santamaria, S., Espadaler, X. 2015. Rickia lenoirii, a new ectoparasitic species, with comments on world Laboulbeniales associated with ants. Mycoscience 56, 224–229 (doi:10.1016/j.myc.2014.06.006).
- Schar, S., Talavera, G., Espadaler, X., Rana, J.D., Andersen, A.A., Cover, S.P., Vila, R. 2018. Do Holarctic ant species exist? Trans-Beringian dispersal and homoplasy in the Formicidae. Journal of Biogeography 2018:1–12 (doi:10.1111/jbi.13380).
- Schifani, E., Csősz, S., Viviano, R., Alicata, A. 2021. Ant diversity on the largest Mediterranean islands: on the presence or absence of 28 species in Sicily (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natural History Sciences 8, 55–70 (doi:10.4081/nhs.2021.532).
- Schifani, E., Nalini, E., Gentile, V., Alamanni, F., Ancona, C., Caria, M., Cillo, D., Bazzato, E. 2021. Ants of Sardinia: An updated checklist based on new faunistic, morphological and biogeographical notes. Redia 104, 21–35 (doi:10.19263/redia-104.21.03).
- Seifert, B. 1990. Supplementation to the revision of European species of the ant subgenus Chthonolasius Ruzsky, 1913 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Doriana 6(2 271: 1-13 (page 12, Senior synonym of ibericus, and material of the unavailable name sancho referred here.)
- Seifert, B. 2021. Surviving the winter: Tetramorium sibiricum n. sp., a new Central Siberian ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Osmia 9, 15–24 (doi:10.47446/osmia9.3).
- Siddiqui, J. A., Li, J., Zou, X., Bodlah, I., Huang, X. 2019. Meta-analysis of the global diversity and spatial patterns of aphid-ant mutualistic relationships. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 17: 5471-5524 (doi:10.15666/aeer/1703_54715524).
- Snegovaya, N., Shigayev, C. 2021. A checklist of the ants (Insecta, Formicidae) of Azerbaijan Republic. Iranian Journal of Animal Biosystematics 17(2): 179-207 (doi:10.22067/ijab.2022.67343.1000).
- Sondej, I., Domisch, T. 2024. Impact of large-scale fire and habitat type on ant nest density and species abundance in Biebrza National Park, Poland. Forests 151, 123 (doi:10.3390/f15010123).
- Stukalyuk, S., Goncharenko, I. 2020. SHIFT IN THE STRUCTURE OF Lasius flavus (HYMENOPTERA, FORMICIDAE) NEST COMPLEXES UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS. Serangga 25(3): 160-178.
- Stukalyuk, S., Radchenko, Y., Gonchar, O., Akhmedov, A., Stelia, V., Reshetov, A., Shymanskyi, A. 2021. Mixed colonies of Lasius umbratus and Lasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae): when superparasitism may potentially develop into coexistence: a case study in Ukraine and Moldova. Halteres 12, 25–48 (doi:10.5281/zenodo.5753121).
- Vatanparast, M., Park, Y. 2021. Comparative RNA-Seq analyses of Solenopsis japonica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) reveal gene in response to cold stress. Genes 12, 1610 (doi:10.3390/genes12101610).
- Wahab, A. 1962. Untersuchungen uber Nematoden in den drusen des kopfes der Ameisen (Formicidae). Zeitschrift fur Morphologie und Okologie der Tiere 52: 33–92.
- Waloff, N. 1957. The effect of the number of queens of the ant Lasius flavus (Fab.) (Hym., Formicidae) on their survival and on the rate of development of the first brood. Insectes Sociaux 4(4), 391–408 (doi:10.1007/bf02224159).
- Wegnez, P. 2017. Découverte de Myrmica lobicornis Nylander, 1846 et Lasius jensi Seifert, 1982, deux nouvelles espèces pour le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie153, 46–49.
- Wheeler, G. C.; Wheeler, J. 1953c. The ant larvae of the subfamily Formicinae. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 46: 126-171 (page 152, larva described; Senior synonym of ibericus, and material of the unavailable name sancho referred here; Senior synonym of apennina, brevicornis, fuscoides, helvus, microps (and its junior synonym cleripennis), morbosa, odoratus and olivacea)
- Wiezik, M., Svitok, M., Wieziková, A., Dovčiak, M. 2013. Shrub encroachment alters composition and diversity of ant communities in abandoned grasslands of western Carpathians. Biodiversity and Conservation 22, 2305–2320 (doi:10.1007/s10531-013-0446-z).
- Yamauchi, K. 1979 [1978]. Taxonomical and ecological studies on the ant genus Lasius in Japan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). I. Taxonomy. Sci. Rep. Fac. Educ. Gifu Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 6: 147-181 (page 160, see also)
- Zhang, X., Xin, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., HaitaoWu. 2021. Effects of ant colonies on molecular characteristics of dissolved organic matter in peatland soils, Northeast China. Applied Soil Ecology 171, 104298 (doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104298).
- Zhu, W., Wu, L., Duan, L., Xu, S. 2022. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in northern Shaanxi Province, China, with one new species of genus Proformica Ruzsky, 1902, Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 25, 101875 (doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2022.101875).
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Acosta, F. J., M. D. Martínez Ibáñez, and M. A. Morales. "Contribución al conocimiento de la mirmecofauna del encinar peninsular. I." Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 6 (2) (1983): 379-391.
- Agosti, D. and C.A. Collingwood. 1987. A provisional list of the Balkan ants (Hym. Formicidae) and a key to the worker caste. I. Synonymic list. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, 60: 51-62
- Aktaç, N.. "Studies on the myrmecofauna of Turkey I. Ants of Siirt, Bodrum and Trabzon." Istanbul Universitesi Fen Fakultesi Mecmuasi. Seri B 41 (1977): 115-135.
- Aldawood AS, Sharaf MR (2011) Monomorium dryhimi sp. n., a new ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the M. monomorium group from Saudi Arabia, with a key to the Arabian Monomorium monomorium-group. ZooKeys 106: 4754. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.106.139
- Alinvi, O., J. Bohlin and J. P. Ball. 2008. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Interspecific competition among ants in the boreal forest: Testing predictions from a linear hierarchical competition model. Insectes Sociaux 55(1):1-11.
- Andoni V. 1977. Kontribut mbi Himenopteret e familjes Formicidae te vendit tone. Buletini I Shkencave te Natyres 31(2): 93-101.
- Anonymous. A list of ants collected at Bandai, Fukushima Prefecture by the members of the Myrmecological Society of Japan in 1992. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 18: 31
- AntArea. Accessed on February 5th 2014 at http://antarea.fr/fourmi/
- Antarea (Personal Communication - Rumsais Blatrix- 27 April 2018)
- Antonov I. A. 2013. Ant Assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Cities of the Temperate Zone of Eurasia. Russian Journal of Ecology 44(6): 523526.
- Arnan X., M. Gracia, L. Comas, and J. Retana. 2009. Forest management conditioning ground ant community structure and composition in temperate conifer forests in the Pyrenees Mountains. Forest Ecology and Management 258(2): 5159.
- ArtDatabanken Bugs (via GBIG)
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2011. List of species collected during the Taxomara Lisboa 2011. Iberomyrmex 3: 30-31.
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2014. List of species collected during the Taxomara 2014 Oviedo. Iberomyrmex 6: 23-24.
- Assing V. 1989. Die Ameisenfauna (Hym.: Formicidae) nordwestdeutscher Calluna-Heiden. Drosera 89: 49-62.
- Azuma M. 1951. On the Myrmecological fauna of Osaka Prefecture, Japan with description of new species (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). Hyogo Biology 1(5): 1-5.
- Azuma M. 1955. A list of ants (Formicidae) from Hokkaido Is. Hyogo Biology 3:79-80.
- Babik H. 2011. Ants of Botanical and Zoological Gardens of Warsaw (Poland). Entomologica romanica 16: 53.
- Babik H., C. Czechowski, T. Wlodarczyk, and M. Sterzynska. 2009. How does a strip of clearing affect the forest community of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)? Fragmenta Faunistica 52(2): 125-141?
- Banert P, and B. Pisarski. 1972. Mrówki (Formicidae) Sudetów. Fragmenta Faunistica (Warsaw) 18: 345-359.
- Baroni Urbani C. 1968. Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. V. Aspetti ecologici della Riviera del M. Cònero. Boll. Zool. 35: 39-76.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1976. A Numerical Analysis of the Distribution of British Formicidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata). Verhandlungen der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Basel 85: 51-91.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1977. The zoogeography of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Northern Europe. Acta Zoologica Fennica 152: 1-34.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Catalogo delle specie di Formicidae d'Italia (Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia X)." Memorie della Società Entomologica Italiana Volume 50 (1971): 5-287.
- Barrett K. E. 1967. Ants in South Brittany. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 79:112-116.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968. Ants in western France. Entomologist 101: 153-155.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968b. The distribution of ants in central southern England. Transactions of the Society for British Entomology 17: 235-250.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1970. Ants in France, 1968-69. Entomologist 103: 270-274.
- Baugnee J. Y. 2003. Camponotus piceus (Leach, 1825), fourmi nouvelle pour la faune belge decouverte dans le parc naturel Viroin-Hermeton (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin S. R. B. E./K. B. V. E. 139: 219-225.
- Behr D., S. Lippke, and K. Colln. 1996. Zur kenntnis der ameisen von Koln (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Decheniana-Beihefte (Bonn) 35: 215-232.
- Behr D., and K. Colln. 1993. Zur ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) von Gonnersdorf (Kr. Daun). Dendrocopos 20: 148-160.
- Bernadou A., V. Fourcassié, and X. Espadaler. 2013. A preliminary checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Andorra. Zookeys 277: 13-23.
- Bernadou A., X. Espadaler, A. Le Goff, and V. Fourcassie. 2015. Ant community organization along elevational gradients in a temperate ecosystem. Insect. Soc. 62:5971
- Bernadou, A., G. Latil, V. Fourcassié, and X. Espadaler. "Les formigues de la Vall del Madriu-Perafita-Claror : diversitat i distribució." Hàbitats, 13 (2006): 10-21.
- Bernard F. 1973. Tendances calcicoles ou silicicoles chez les fourmis méditerranéennes. Pp. 16-21 in: International Union for the Study of Social Insects. Congress 1973. Proceedings IUSSI VIIth International Congress, London, 10-15 September, 1973. Southampton: University of Southampton, vi + 418 pp.
- Bernard F. 1975. Rapports entre fourmis et vegetation pres des Gorges du Verdon. Annales du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Nice 2: 57-79.
- Bernard F. 1978. Fourmis et milieu dans le massif des Maures. Vie et Milieu. Série C. Biologie Terrestre 27: 83-118.
- Bezdecka P. 1996. The ants of Slovakia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomofauna carpathica 8: 108-114.
- Bezdeckova K., and P. Bezdecka. 2009. Nejvetsi polykalicka kolonie Formica foreli (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) y Ceské republice. Acta rerum naturalium 7: 121126.
- Blacker N. C. 1989. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the Gower Peninsula, West Glamorgan, South Wales. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 101: 261-266.
- Blacker N. C. and C. A. Collingwood. 2002. Some significant new records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Salisbury area, south Wiltshire, England, with a key to the British species of Lasius. British Journal of Entomology and Natural History 15: 25-46
- Blatrix R., C. Lebas, C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, P. Pimenta, and D. Morichon. 2016. Vegetation cover and elevation drive diversity and composition of ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in a Mediterranean ecosystem. – Myrmecological News 22: 119-127.
- Blinova S. V. 2011. Changes in the Ant Assemblage of PineBirch Forest upon Removal of the Nests of Dominant Species. Russian Journal of Ecology 42(6): 525528.
- Boer P. 2019. Species list of the Netherlands. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/specieslist.html
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. Van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten (Amsterdam) 63: 54-58.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten 63(3): 54-57.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. List of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Belgium and The Netherlands, their status and Dutch vernacular names. Entomologische Berichten 63 (3): 54-58.
- Bonaric J. C. 1971. Contribution a l'etude systematique et ecologique des formicides du Bas-Languedoc. PhD thesis Universite des sciences et techniques du Languedoc, 175 pages.
- Bonaric J. C. 1971. Étude systématique et ecologique des fourmis de lHérault (fin). Ann. Soc. Hortic. Hist. Nat. Hérault 111: 169-176.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2012. Ants of Greece - Checklist, comments and new faunistic data (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus 23(4): 461-563.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2017. Ants of the Peloponnese, Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Polish Journal of Entomology 86: 193-236.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2018. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Euboea Island, Central Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 27(5): 1-15.
- Bracko G., K. Kiran, C. Karaman, S. Salata, and L. Borowiec. 2016. Survey of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Greek Thrace. Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e7945. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e7945
- Bracko, G. 2006. Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) of Croatia. Acta Entomologica Slovenica 14(2): 131-156.
- Bracko, G.. "Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Croatia." Acta Entomologica Slovenica Vol 14 st (2006): 131-156.
- Brangham A. N. 1938. Additions to the wild fauna and flora of the Royal Botanic gardens, Kew: XVIII. Bulletin of Miscellaneous Information (Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew), 9: 390-396.
- Braschler, B. and B. Baur. 2005. Experimental Small-Scale Grassland Fragmentation Alters Competitive Interactions among Ant Species. Oecologia 143(2):291-300
- Cagniant, H.. "Deuxième liste de fourmis d'Algérie, récoltées principalement en forêt (Deuxième partie)." Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse 106 (1970): 28-40.
- Cagniant, H.. "Étude de fourmis récoltées par le Professeur H. Janetschek dans la Sierra Nevada." Bulletin de la Société d' Histoire naturelle de l' Afrique du Nord 52 (1961): 104-117.
- Cagniant, H.. "Étude de quelques fourmis marocaines. Statistique provisoire des Formicidae du Maroc." Bulletin de la Société d' Histoire naturelle de l' Afrique du Nord 53 (1964): 83-118.
- Cagniant, H.. Les peuplements de fourmis des forêts algériennes: écologie, biocénotique, essai biologique. Universite de Toulouse, 1973.
- Callot H., and A. Astric. 2011. Liste de référence des Fourmis d'Alsace. 7 p. Version mise à jour au 23/03/2013. http://sites.estvideo.net/sae/ consultation du 27 January 2014.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J. 1990. Etude Systematique de la Myrmecofaune Corse (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), deuxieme partie. Bull. Mus. Natn. Hist. Nat. Paris. 4eme serie 12, section A(2): 415-442.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and M. Prost. 1991. Fourmis de la Côte-d'Or présentes dans les collections du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Dijon. Bulletin Scientifique de Bourgogne 44: 53-72.
- Casevitz-Weulersse, J.. "Contribution a la connaisance des fourmis de la Corse (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." These de Doctorat Museum Nat (1989): 379pp.
- Chen P., Y. Su, S. S. Rao, Y. F. Long, and C. H. Du. 2012. Study on the ant diversity in different Illicium verum stands. Journal of West China Forestry Science 41(1): 60-68.
- Chen Y., C. W. Luo, H. W. Li, Y. J. Liu, H. F. Zheng, and F. C. Yang. 2013. Investigation of ant species and distribution on Wuliang Mountain. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences 42(5): 118-122.
- Cheng D., Z. Chen, and S. Zhou. 2015. An analysis on the ant fauna of Jinzhongshan Nature Reserve in Gunagxi, China. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 33(3): 129.137.
- Cherix D., and S. Higashi. 1979. Distribution verticale des fourmis dans le Jura vaudois et recensement prelimaire des bourdons (Hymenoptera, Formicidae et Apidae). Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sc. Nat. 356(74): 315-324.
- Choi B.-M. 1987. Taxonomic study on ants (Formicidae) in Korea (1). On the genus Monomorium. Journal of the Institute of Science Education (Cheongju National Teachers' College) 11:17-30.
- Choi B.M. 1985. Study on distribution of ants (Formicidae) from Korea (1). Formic fauna in Mt. Songni. Cheongju Sabom Taehak Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National Teachers' College) 22:401-437.
- Choi B.M. 1986. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea. Journal of Chongju National Teacher College 23: 317-386.
- Choi B.M. 1996. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (15) -Ant fauna islands Ullungdo and Dokdo. Journal of Chongju National University of Education 33: 201-219.
- Choi B.M. 1997. Distribution of Ants (Formicidae) in Korea (18). Ants Fauna in island Paekryongdo and Taechongdo. Journal of Chongju National University of Education 34: 119-138.
- Choi B.M., Bang, J.R. 1992. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (9). Ant fauna in Mt. Togyusan. Korean Journal of Applied Entomology 31:101-112.
- Choi B.M., K. Ogata, and M. Terayama. 1993. Comparative studies of ant faunas of Korea and Japan. 1. Faunal comparison among islands of Southern Korean and northern Kyushu, Japan. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Japan 48(1): 37-49.
- Choi B.M., Kim, C.H., Bang, J.R. 1993. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (13). A checklist of ants from each province (Do), with taxonomic notes. Cheongju Sabom Taehakkyo Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National University of Education) 30: 331-380.
- Choi B.M., and H.S. Lee. 1999. Studies on the distribution ants in Korea (21) - Ant fauna in Kwanaksan. Korean J. Soil Zoology 4(1): 1-4.
- Choi B.M., and J. R. Bang. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (12): the analysis of ant communities in 23 islands. Journal of Cheongju National University of Education 30:317-330.
- Colindre L. 2015. Les fourmis en Picardie: bilan 2014 (Hymenoptera/ Formicidae). Entomologiste Picard 26, 15 pages.
- Colindre L. 2017. Richess et utilite du cortege de fourmis en foret d'Ermenonville, Oise, Region Hauts-de-France. Association des Entomologistes de Picardie. 19 pages.
- Collingwood C. A. 1951. The distribution of ants in north-west Scotland. Scottish Naturalist 63: 45-49
- Collingwood C. A. 1951. The distribution of ants in north-west Scotland. Scottish Naturalist 63: 45-49.
- Collingwood C. A. 1955. Ants in S.W. Scotland. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 67: 11-12.
- Collingwood C. A. 1956. Ant hunting in France. Entomologist 89: 106-108.
- Collingwood C. A. 1961. Ants in the Scottish Highlands. Scotish Naturalist 70: 12-21.
- Collingwood C. A. 1971. A synopsis of the Formicidae of north Europe. Entomologist 104: 150-176
- Collingwood C. A. 1981. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Korea, 2. Folia Entomologica Hungarica 42(34): 25-30.
- Collingwood C. A., and J. E. Satchell. 1956. The ants of the South Lake District. Journal of the Society for British Entomology 5: 159-164.
- Collingwood C., and A. Prince. 1998. A guide to ants of continental Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia. Suplemento 5: 1-49.
- Collingwood C.A. 1955. Ants in S.W. Scotland. Entomol.Rec. 67: 11-12
- Collingwood C.A. 1957. The Species of Ants of the Genus Lasius in Britain. Journal of the Society for British Entomology. 5: 204-214
- Collingwood C.A. 1959. Ants in the Scottish Highlands. The Scottish Naturalist. 70: 12-21
- Collingwood C.A. 1959. Scandinavian Ants. Entomol. Rec. 71: 78-83
- Collingwood C.A. 1961. New Vice-County Records for British Ants. Entomologist. 73: 90-93
- Collingwood C.A. and Satchell J.E. 1956. The Ants of the South Lake District. Journal of the Society for British Entomology. 5: 159-164
- Collingwood, C. A. 1958b. A key to the species of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) found in Britain. Trans. Soc. Br. Entomol. 13: 69-96
- Collingwood, C. A. 1964. The Identification of British Ants (Hym. Formicidae). Transactions of the Society for British Entomology. 16:93-121.
- Collingwood, C. A. 1974. A revised list of Norwegian ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Norsk Entomologisk Tidsskrift 21: 31-35.
- Collingwood, C. A., and I. H. H. Yarrow. "A survey of Iberian Formicidae." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 44 (1969): 53-101.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark." Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 8 (1979): 1-174.
- Collingwood, C.A. 1958. A survey of Irish Formicidae. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy 59B:213-219
- Consani M., and P. Zangheri. 1952. Fauna di Romagna. Imenotteri - Formicidi. Memorie della Societa Entomologica Italiana 31: 38-48.
- Csosz S., B. Marko, K. Kiss, A. Tartally, and L. Galle. 2002. The ant fauna of the Ferto-Hansag National Park (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Mahunka, S. (Ed.): The fauna of the Fert?-Hanság National Park. Hungarian Natural History Museum, Budapest, pp. 617-629.
- Csősz S. and Markó, B. 2005. European ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the ant collection of the Natural History Museum of Sibiu (Hermannstadt/Nagyszeben), Romania II. Subfamily Formicinae. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 97: 225-240.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2001. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Stana Valley (Romania): Evaluation of the effectiveness of a myrmecological survey. Entomologica Romanica 6 : 121-126.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski W., A. Radchenko, W. Czechowska and K. Vepsäläinen. 2012. The ants of Poland with reference to the myrmecofauna of Europe. Fauna Poloniae 4. Warsaw: Natura Optima Dux Foundation, 1-496 pp
- Dauber J., and D. Simmering. 2006. Ant assemblages in successional stages of Scotch Broom stands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae; Spermatophyta). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 9: 55-64.
- Dauber, J., J. Bengtsson and L. Lenoir. 2006. Evaluating Effects of Habitat Loss and Land-Use Continuity on Ant Species Richness in Seminatural Grassland Remnants. Conservation Biology 20(4):1150-1160
- Dekoninck W., F. Hendrickx, M. Dethier, and J. P. Maelfait. 2010. Forest Succession Endangers the Special Ant Fauna of Abandoned Quarries along the River Meuse (Wallonia, Belgium). Restoration Ecology 18(5): 681690.
- Dekoninck W., H. De Koninck, J. Y. Baugnee, and J. P. Maelfait. 2007. Ant biodiversity conservation in Belgian calcareous grasslands: active management is vital. Belg. J. Zool. 137 (2): 137-146.
- Dekoninck W., K. Desender, and P. Grootaert. 2008. Establishment of ant communities in forests growing on former agricultural fields: Colonisation and 25 years of management are not enough (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 105: 681689.
- Della Santa E. 1994. Guide pour l'identification des principales espèces de fourmis de Suisse. Miscellanea Faunistica Helvetiae 3: 1-124.
- Della Santa E. 1995. Fourmis de Provence. Faune Provence 16: 5-37.
- Dewes E. 2005. Ameisenerfassung im Waldschutzgebiet Steinbachtal/Netzbachtal. Abh. Delattinia 31: 89-118.
- Diniz, M. A.. "Estado actual do conhecimento dos himenópteros de Portugal." Memorias e Estudos do Museu Zoologico da Universidade de Coimbra 259 (1959): 1-42.
- Dlussky G. M., O. S. Soyunov, and S. I. Zabelin. 1990. Ants of Turkmenistan. Ashkabad: Ylym Press, 273 pp.
- Donisthorpe H. 1914. Myrmecophilous notes for 1913. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 26: 37-45.
- Donisthorpe, H.. "A first instalment of the ants of Turkey." Annals and Magazine of Natural History (12)3 (1950): 1057-1067.
- Dostal, P. 2007. Population dynamics of annuals in perennial grassland controlled by ants and environmental stochasticity. Journal of Vegetation Science, 18(1):91-102
- Du Merle P. 1978. Les peuplements de fourmis et les peuplements d'acridiens du Mont Ventoux II. - Les peuplements de fourmis. Terre Vie 32(1): 161-218.
- Dubovikoff D. A., and Z. M. Yusupov. 2018. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Dvorak, L., P. BOGUSCH, I. MALENOVSKÝ, P. BEZDÌÈKA, K. BEZDÌÈKOVÁ, K. HOLÝ, P. LIKA, J. MACEK, L. ROLLER, M. RÍHA et al. "Hymenoptera of Hády Hill, near the city of Brno (Czech Republic), collected during the Third Czech-Slovak Hymenoptera meeting." Acta Musei Moraviae, Scientiae biologicae (Brno) 93 (2008): 53-92.
- Else G., B. Bolton, and G. Broad. 2016. Checklist of British and Irish Hymenoptera - aculeates (Apoidea, Chrysidoidea and Vespoidea). Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e8050. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e8050
- Emery C. 1878. Liste des fourmis de la collection de feu Camille van Volxem, avec la description d'une espèce nouvelle. Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 21: viii-x.
- Emery C. 1897. Anhang. Verzeichniss der auf der zweiten Reise nach Kleinasien (1897) gesammelten Ameisen, mit einer Neubeschreibung. P. 239 in: Escherich, K. 1897. Zur Kenntniss der Myrmecophilen Kleinasiens. I. Coleoptera. Wiener Entomologische Zeitung 16: 229-239.
- Emery C. 1916. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bullettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 47: 79-275.
- Emery, C.. "Catalogo delle formiche esistenti nelle collezioni del Museo Civico di Genova. Parte seconda. Formiche dell'Europa e delle regioni limitrofe in Africa e in Asia." Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 12 (1878): 43-59.
- Emery, C.. "Liste des fourmis de la collection de feu Camille van Volxem, avec la description d'une espèce nouvelle." Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 21 (1878): viii-x.
- Emery, C.. "Spicilegio mirmecologico." Bollettino della Societa Entomologica Italiana 33 (1901): 57-63.
- Entomological Society of Latvia. 2003. http://leb.daba.lv/Formicidae.htm (Accessed on December 1st 2013).
- Espadaler X., X. Roig, K. Gómez, and F. García. 2011. Formigues de les Planes de Son i mata de València (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Treballs de la Institució Catalana d'Història Natural 16: 609-627.
- Espadaler, X., I. Zabalegui, and F. Calvo Sanchez. "Primer registro de Myrmica karavajevi (Arnoldi, 1930) en la Península Ibérica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." Heteropterus Revista de Entomología 4 (2004): 81-83.
- Espadaler, X., X. Roig, and K. Gómez. "Cuatro nuevas citas de hormigas (Hymenopera, Formicidae) y actualización del listado para Cataluña (Península Ibérica)." Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 40 (2007): 313-316.
- Espadaler, X.. "Contribución al conocimiento de los formícidos (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) del Pirineo catalán." Tesis Universida (1979): 285 pp.
- Espadaler, X.. "Formicidos de las sierras de Cazorla, del Pozo y Segura (Jaén, España)." Ecología 11 (1997): 489-499.
- Espadaler, X.. "Formigues del Montseny." in: Terradas, J., Miralles, J. (eds.) El patrimoni biològic del Montseny Catàlegs d (1987): 101-103.
- Espadaler, X.. "Formícidos de los alrededores de la laguna de Sariñena (Huesca). Descripción del macho de Camponotus foreli Emery." Colección Estudios Altoaragoneses 6 (1986): 109-126.
- Fagan K. C., R. F. Pywell, J. M. Bullock, and R. H. Marrs. 2010. Are Ants Useful Indicators of Restoration Success in Temperate Grasslands? Restoration Ecology 18(3): 373379.
- Fiedler, K., F. Kuhlmann, B. C. Schlick-Steiner, F. M. Steiner and G. Gebauer. 2007. Stable N-isotope signatures of central European ants assessing positions in a trophic gradient. Insectes Sociaux 54(4):393-402.
- Finzi, B.. "Formiche dell'isola d'Elba e Monte Argentario." Bollettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 56 (1924): 12-15.
- Finzi, B.. "Raccolte entomologiche nell'Isola di Capraia fatte da C. Mancini e F. Capra (1927-1931). II. Formicidae." Memorie della Società Entomologica Italiana 11 (1933): 162-165.
- Forel A. 1911. Fourmis nouvelles ou intéressantes. Bull. Soc. Vaudoise Sci. Nat. 47: 331-400.
- Forel, A.. "Nouvelles fourmis de Grèce récoltées par M. E. von Oertzen." Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 30 (1886): clix-clxviii.
- Formidabel Database
- Fowles, A.P. 1996. A provisional checklist of the invertebrates recorded from Wales. 2. Aculeate wasps, bees and ants (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Countryside Council for Wales
- Franch, J., and X. Espadaler. "Ants as colonizing agents of pine stumps in San Juan de la Peña (Huesca, Spain)." Vie et Milieu 38 (1988): 149-154.
- Francois J. 1958. Contribution a l'etude ecologique des Formicides (Insectes, Hymenopteres) de la region Dijonnaise. Travaux du laboratoire de Zoologie et de la Station Aquicole Grimaldi de la Faculte des Sciences de Dijon 25, 39 pages.
- GRETIA. 2017. Bilan annuel de l'enquete sur la repartition des fourmis armoricaines. 23 pages.
- Gadeau de Kerville H. 1922. Materiaux pour la Faune des Hymenopteres de la Normandie. Bull. Soc. Amis Sc. Nat. Rouen 1916-1921, 1922: 217-225.
- Galkowski C. 2013. Nouvelles données sur la répartition de Strongylognathus huberi Forel, 1874 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en France. Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux (n.s.) 41: 167-174.
- Galkowski C., and C. Foin. 2013. Nouvelles données sur la répartition de Strongylognathus huberi Forel, 1874 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en France. Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux (n.s.) 41: 167-174.
- Galkowski C., and P Wegnez. 2010. Myrmica constricta Karavaiev 1934, nouvelle espece pour la France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Ent. Mulhouse 66(3): 41-45.
- Galle L. 1972. Study of ant-populations in various grassland ecosystems. Acta Biologica Szeged 18(1-4): 159-164.
- Galle L. 1981. The Formicoid fauna of the Hortobagy. Pp. 307-311 in: Mahunka, S. (ed.) 1981. The fauna of the Hortobágy National Park. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó, 415 pp.
- Galle L. 1984. The ant fauna of Kiskunsag National Park (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea). ). In the Fauna of the Kiskunsig National Park ed. by S' Mahunk, pp 427-434.
- Galle L. 1997. Contribution to the ant fauna of Slovenia with special reference to the submediterranean and eudinaric regions. Annals for Istrian and Mediterranean studies 11: 209-214.
- Galle L., and G. Szonyi. 1988. A check list of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea) of a sandy grassland in Kiskunsag National Park (Hungary). Acta Biol. Szeged 34: 167-168.
- Gallé L., B. Markó, K. Kiss, E. Kovács, H. Dürgő, K. Kőváry, and S. Csősz. 2005. Ant fauna of Tisza river basin (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Gallé, L. (szerk.): Vegetation and Fauna of Tisza River Basin I. Tiscia Monograph Series 7; Szeged, pp. 149-197.
- Garcia Garcia F., and A. D. Cuesta-Esgura. 2017. First catalogue of the ants of Burgos province, Spain (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 60: 245–258.
- Gaspar C. 1968. Les fourmis de la Drome et des Basses-Alpes, en France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Naturaliste can. 95: 747-766.
- Gaspar C., and C. Thirion. 1978. Modification des populations d'Hymenopteres sociaux dans les milieux anthropogenes. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 61-77.
- Gaspare Charles. 1965. Étude myrmécologique d'une région naturelle de Belgique: la Famenne Survey des Fourmis de la Région (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Institut agronomique de l'Etat a' Gembloux. 32(4): 427-434.
- Gasperini, R.. "Notizia sulla fauna imenotterologadalmata, II, Formicidae-Mutillidae-Scoliadae-Sapygidae-Pompilidae-Sphegidae-Chrysididae." Anuario Dalmatico 4 (1887): 143-160.
- Glaser F. 2004. Distribution and conservation of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the floodplain of the river Etsch / Adige (Southern Tyrol, Italy). Gredleriana 4: 203-246.
- Glaser F. 2009. Die Ameisen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Amtlicher Lehrmittelverlag, Vaduz, 2009 (Naturkundliche Forschung im Fürstentum Liechtenstein; Bd. 26).
- Glaser F., A. Freitag, and H. Martz. 2012. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the Münstertal (Val Müstair) a hot spot of regional species richness between Italy and Switzerland. Gredleriana 12: 273 - 284.
- Glaser F., T. Kopf, and K. H. Steiberger. 2003. Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) im Frastanzer Ried und den Illauen (Vorarlberg, Österreich) Artenspektrum, Gefährdung und Schutzempfehlungen. Vorarlberger Naturschau 13: 287-310.
- Goetsch, W.. "Beiträge zur Biologie spanischer Ameisen." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 18 (1942): 175-241.
- Gouraud C. 2015. Bilan de l’année 2014 : Atlas des fourmis de Loire-Atlantique (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atlas des Formicidae de Loire-Atlantique, compte rendu de la première année d’étude (2014)
- Grandi G. 1935. Contributi alla conoscenza degli Imenotteri Aculeati. XV. Boll. R. Ist. Entomol. Univ. Studi Bologna 8: 27-121.
- Gratiashvili N., Barjadze S. 2008. Checklist of the ants (Formicidae Latreille, 1809) of Georgia. Proceedings of the Institute of Zoology (Tbilisi) 23: 130-146.
- Groc S., J. H. C. Delabie, R. Cereghino, J. Orivel, F. Jaladeau, J. Grangier, C. S. F. Mariano, and A. Dejean. 2007. Ant species diversity in the Grands Causses (Aveyron, France): In search of sampling methods adapted to temperate climates. C. R. Biologies 330: 913922.
- Grzes I. M. 2009. Ant species richness and evenness increase along a metal pollution gradient in the Boles?aw zinc smelter area. Pedobiologia 53: 65-73.
- Guénard B., and R. R. Dunn. 2012. A checklist of the ants of China. Zootaxa 3558: 1-77.
- Ha S.J, S.J. Park, and B.J. Kim. 2002. Comparative ant faunas between Seonyudo and seven other islands of West Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(2): 75-79.
- Hauschteck-Jungen E., and H. Jungen. 1983. Ant chromosomes. II. Karyotypes of western palearctic species. Insectes Soc. 30: 149-164.
- Hayashida K. 1957. Ecological distribution of ants in Sapporo and vicinity. (Preliminary report.). Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University. Series VI. Zoology 13:173-177.
- Hayashida K. 1959. Ecological Distribution of Ants in Mt. Atusanupuri, An Active Volcano in Akan National Park, Hokkaido. Jour. Pac. Sci. Hokkaiao Univ. Ser. 4(14): 252-260.
- Hayashida K. 1959. Ecological distribution of ants in Mt. Atusanupuri, an active volcano in Akan National Park, Hokkaido. Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University. Series VI. Zoology 14:252-260.
- Hayashida K. 1961. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Sapporo and its vicinity (1 et 2). Insectes Sociaux 7: 125-162.
- Hayashida K. 1964. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Kutchan and its adjacent area. Journal of the Sapporo Otani Junior College 2: 107-129.
- Hayashida K. 1971. Vertical distribution of ants in the southern part of the Hidaka mountains. [In Japanese.]. Memoirs of the National Science Museum (Tokyo) 4:29-38.
- Hayashida K. 1972. Ecological survey on ants in Nakagawa Experiment Forest of Hokkaido University. Res. Bull. Exper. Forests, Coll. Agr., Hokkaido Univ. 29: 25-36.
- Hayashida K., and S. Maeda. 1960. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Akkeshi. Journ. Sc. Hokkaido Univ., IV. Zool., 14 (3) : 305-319.
- Holgersen H. 1942. Ants of northern Norway (Hym., Form.). Tromso Mus. Årsh. 63(2): 1-34.
- Holgersen H. 1943. Ant studies in Rogaland (south-western Norway). Avhandlingar utgitt av det Norske Videnskaps-Akademi i Oslo. I. Matematisk-Naturvidenskapelig Klasse 1943(7): 1-75.
- Holgersen H. 1944. The ants of Norway (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Nytt Magasin for Naturvidenskapene 84: 165-203.
- Hou J.H., D.W. Zhou, and S.C. Jiang. 2002. Species Composition and Spatial Distribution 0f Ants in the Grassland Region in the West of Jilin Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica 22(10): 1781-1787.
- Hågvar S. 2005. Altitudinal zonation of ants (Formicidae) in a steep fjord landscape in Sogndal, Western Norway. Norw. J. Entomol. 52: 3-12.
- Ichinose K. 1990. The Ant Fauna of the Tomakomai Experiment Forest, Hokkaido University (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with Notes on the Nuptial Season. Research Bulletins of College Experiment Forests 47(1) 137-144.
- Jakubzik A., H. Kinkler, and K. Colln. 2010. Aculeate Hymenoptera from a Humid Biotope in Leverkusen-Steinbüchel. Decheniana (Bonn) 163: 145158.
- Jeffery H. G. 1931. The Formicidae (or ants) of the Isle of Wight. Proceedings of the Isle of Wight Natural History and Archaeological Society 2: 125-128.
- Karaman M. G. 2001. Contribution to the knowledge of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Demir Kapija Crag (Vardar River, Macedonia), second contribution. Protection of nature 53(2): 49-61.
- Karaman M. G. 2009. An introduction to the ant fauna of Macedonia (Balkan Peninsula), a check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natura Montenegrina 8(3): 151-162.
- Karaman M. G. 2011. A catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Montenegro. Podgorica: Catalogues 3, Volume 2, Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts, 140 pp.
- Karaman M. G., and G. S. Karaman. 2003. Contribution to the knowledge of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Serbia. The Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts. Glasnik of the Section of Natural Sciences 15: 39-58.
- Karavaiev V. 1912. Ameisen aus dem paläarktischen Faunengebiete. Rus. Entomol. Obozr. 12: 581-596.
- Karavaiev V. 1926. Beiträge zur Ameisenfauna des Kaukasus, nebst einigen Bemerkungen über andere palaearktische Formen. (Schluss). Konowia 5: 187-199.
- Karavaiev V. 1927. Übersicht der Ameisenfauna der Krim nebst einigen Neubeschreibungen. Konowia 5: 281-303.
- Kim B.J. 1996. Synonymic list and distribution of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) in Korea. Entomological Research Bulletin Supplement 169-196.
- Kim B.J.; Kim, K.G.; Lim, K.H. 1993. Systematic study of ants from Chejudo province. Korean Journal of Entomology 23: 117-114
- Kim C.H., B.M. Choi, and J.R. Bang. 1992. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (8)-Ant fauna in 10 islands, Chollanam-do. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 31(4): 345-359.
- Kim K.I., C.H. Kim, and B. Choi. 1989. The ant fauna of the southern shore in Gyeongsangnamdo, Korea. Journal of Gyeongsang Nat. Univ. 28(2): 213-226.
- Kim et al. 1993. Systematic study of ants from Chejudo Province. Koran Journal of Entomology 23(3): 117-141.
- Kiss K., and K. Fetyko. 2008. Notes about the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Tur valley. In. Sike T., Márk-Nagy J. (eds), The flora and fauna of the Tur river natural reserve, Biharean Biologist, II, Oradea, pp.71-76.
- Kofler A. 1995. Nachtrag zur Ameisenfauna Osttirols (Tirol, Österreich) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 1: 14-25.
- Kondoh M., and Y. Kitazawa. 1984. Ant communities of the campus of UOEH and in an adjacent natural forest. Journal of UOEH 6(3): 221-234.
- Korlevic, A.. "Prilozi fauni hrvatskih opnokrilaca." Glasn. Hrv. Narav. Dr. 5 (1890): 189-250.
- Kozisek T. 1987. Ants (Formicoidea) of the Abrod State Nature Reserve. Ochrana Prírody 8: 205-208.
- Kratochvíl J., V. Novák, and J. Snoflák. 1944. Mohelno. Soubor práci venoványch studiu vyznamne památky prírodní. 5. Hymenoptera - Aculeata. Formicidae - Apidae - Vespidae. Arch. Svazu Ochr. Prír. Domov. Moravé 6: 1-155.
- Kubota. S., and M. Terayama. 1988. Ant fauna of Tokyo. (1) A list of ants collected at the parks. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 16: 14-16
- Kupianskaia A.N. 1990. Murav'I (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Dal'nego Vostoka SSSR (1989). Vladivostok. 258 pages.
- Kupianskaya A. N., Lelej, A.S., and Urbain, B. K. 2000. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist. 92:1-21.
- Kupianskaya A. N., and A. S. Lelej. 2000. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) collected in the Habomai and Shikotan (Kuril Islands) in 1998. Far Eastern entomologist 92: 22-24.
- Kupianskaya, A. N., Lelej, A.S., and Urbain, B. K. 2000. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist. 92:1-21.
- Kupianskaya, A.N., A.S. Lelej and B.K. Urbain. 2000. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist 92:1-21
- Kvamme T. 1982. Atlas of the Formicidae of Norway (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Insecta Norvegiae 2: 1-56.
- Laeger T., and R. Schultz. 2005. Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) als Beifänge in Bodenfallen wie genau spiegeln sie reale Abundanzverhältnisse wider? Myrmecologische Nachrichten 7: 17-24.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, L., V. Antonova, A. G. Radchenko, and M. Atanasova. "Catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Bulgaria." ZooKeys 62 (2010): 1-124.
- Lebas C., C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, X. Espadaler, and R. Blatrix. 2015. The exceptional diversity of ants on mount Coronat (Pyrénées-Orientales), and Temnothorax gredosi(Hymenoptera, Formicidae) new to France. R.A.R.E., T. XXIV (1): 24 33
- Lebas C., and C. Galkowski. 2016. Myrmica hirsuta Elmes, 1978, a new species from France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Linn. Bordeaux 151, 44(2/3): 239-244.
- Leeanne E. Alonso, Liu Shaoying, Shen Xiaoli, and Jennifer McCullough (Editors). 2009. A Rapid Biological Assessment of three sites in the Mountains of Southwest China Hotspot, Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan Province, China. RAP Bulletin of Biological Assessment 52. Conservation International, Arlington, VA, USA.
- Legakis Collection Database
- Lehouck V., D. Bonte, W. Dekoninck, and J. P. Maelfait. 2004. The distribution of ant nests (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in coastal grey dunes of Flanders (Belgium) and their relationship to myrmecochorous plants. Belg. J. Zool. 134 (2/1) : 89-96.
- Lelej A. S. 2012. Annotated catalogue of the Insects of Russian Far East. Volume 1. Hymenoptera. Dalnauka: Vladivostok. 635 p.
- Lenoir A. 1971. Les fourmis de Touraine, leur intérêt biogéographique. Cahiers des Naturalistes 27: 21-30.
- Lenoir L. 2009. Ant Species Composition and Richness in Different Types of Semi Natural Grasslands. Russian Journal of Ecology 40(7): 471-476.
- Li Z.h. 2006. List of Chinese Insects. Volume 4. Sun Yat-sen University Press
- Liu X. 2012. Taxonomy, diversity and spatial distribution characters of the ant family Formicidae (Insecta: Hymenoptera) in southeastern Tibet. PhD Thesis 139 pages
- Liu X., Z. Xu, N. Yu, and C. Zhang. 2016. Distribution patterns of ant species ( Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Galongla Mountains and Medog Valley of Southeastern Tibet. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 52(11): 88-95.
- Livory A. 2003. Les fourmis de la Manche. L'Argiope 39: 25-49.
- Lomnicki J. 1928. Spis mrówek Lwowa i okolicy. Ksiegi Pamiatkowej (Lecia Gimn. IV Jana Dlugosza Lwowie) 50: 1-10.
- Maavara V. 1953. Ants of Estonian SSR. ABIKS loodusevaatlejale 10: 1-44.
- Majzlan O., and P. Devan. 2009. Selected insect groups (Hymenoptera, Neuroptera, Mecoptera, Raphidioptera) of the Rokoš Massif (Strážovské vrchy Mts.). Rosalia (Nitra), 20, p. 63–70.
- Malozemova L. A. 1972. Ants of steppe forests, their distribution by habitats, and perspectives of their utilization for protection of forests (north Kazakhstan). [In Russian.]. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 51: 57-68.
- Manabe K. 1994. Ants of the shrine forest in Fukuoka Prefecture (second report; ants of mountain zone). Ari 17: 8.
- Marikovsky P. I. 1979. Ants of the Semireche Desert. [In Russian.]. Alma Ata: Nauka, 263 pp.
- Marko B. 1999. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the River Somes valley. In: Sárkány-Kiss, A., Hamar, J. (szerk.): The Somes/Szamos River Valley. A study of the geography, hydrobiology and ecology of the river system and its environment. Tiscia Monograph Series 3, Szolnok-Szeged-Tîrgu Mure?, pp. 297-302.
- Markó B. 1997. Contribution to the Knowledge of the Ant-Fauna (Hymenoptera: Fromicoidea) of the Cri?ul-Repede River-Valley. In: Sárkány-Kiss, A., Hamar, J. (szerk.): The Cri?/Körös Rivers' Valleys. A study of the geography, hydrobiology and ecology of the river system and its environment. Tiscia Monograph Series 2, Szolnok-Szeged-Tîrgu Mure?, pp. 345-352.
- Markó B., B. Sipos, S. Csősz, K. Kiss, I. Boros, and L. Gallé. 2006. A comprehensive list of the ants of Romania (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 9: 65-76.
- Menozzi C. 1918. Primo contributo alla conoscenza della fauna mirmecologica del Modenese. Atti della Società dei Naturalisti e Matematici di Modena. (5)4: 81-88.
- Menozzi C. 1932. Contributo alla conoscenza della fauna mirmecologica d'Italia. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Entomologia del Reale Istituto Superiore Agrario di Bologna. 5: 8-12.
- Mizota K. 2002. A check list of insects in Kinkazan Island, Miyagi Pref., Northeastern Japan: A bibliographical Survey. Bulletin of Miyagi University of Education Environmental Education 5: 69-78.
- Mizutani A. 1979. A myrmecofaunal survey at Hiyama Experiment Forest, Hokkaido University. Research Bulletin of the College Experiment Forests, Hokkaido University 36:509-516.
- Mizutani A. 1979. A myrmecofaunal survey at Hiyama Experiment Forest, Hokkaido University. Research Bulletins of the College Experiment Forests Hokkaido University 36(2): 509-516.
- Morisita M. 1945. Ants of the southern part of Hokkaido, Japan. [In Japanese.] Mushi 16:21-28.
- Moscaliuc L. 2008. Notes on the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Rarau mountain. Analele Facult??ii de Biologie, Univ A.I. Cuza Ia?i 54: 53-55.
- Müller, G.. "Le formiche della Venezia Guilia e della Dalmazia." Bollettino della Società Adriatica di Scienze Naturali in Trieste 28 (1923): 11-180.
- Nadig A. 1918. Alcune note sulla fauna dell'alta Valsesia. Formicidae. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 56: 331-341.
- Navás, L.. "Excursió entomologica al Cabrerés (Gerona-Barcelona)." Trab. Mus. Cienc. Nat. Barcelona vol IV nº (1924).
- Nemet E., Z. Czekes, I. Tausan, and B. Marko. 2012. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the Cefa Nature Park (North-Western Romania). Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica 20(1): 61-72.
- Neumeyer R., and B. Seifert. 2005. Commented check list of free living ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species of Switzerland. Bulletin de la Societe Entomologique Suisse 78: 1-17.
- Nezhad S. H., S. P. Rad, F. Firouzi, and D. Agosti. 2012. New and additional records for the ant fauna from Iran (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zoology in the Middle East 55: 65-74.
- Nielsen M. G. 2011. A check list of Danish ants and proposed common names. Ent. Meddr. 79: 13-18.
- Nielsen, M.G. 1986. Respiratory rates of ants from different climatic areas. Journal of Insect Physiology 32(2): 125-131
- Noordijk, J., R. Morssinkhof, P. Boer, A. P. Schaffers, Th. Heijerman and K. V. Sýkora. 2008. How ants find each other; temporal and spatial patterns in nuptial flights. Insectes Sociaux 55(3):266-273.
- Nylander, W.. "Synopsis des Formicides de France et d'Algérie." Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie (4)5 (1856): 51-109.
- O'Rourke F. J. 1948. The distribution and general ecology of the Irish Formicidae. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy. Section B: Biological, Geological, and Chemical Science 52: 383-410.
- Ortiz, F. J., and A. Tinaut. "Introducción al conocimiento de las hormigas de la provincia de Almería." Publicaciones del Instituto de Estudios Almerienses. Boletín (Ciencias) 8 (1988): 223-231.
- Ovazza M. 1950. Contribution à la connaissance des fourmis des Pyrénées-Orientales. Récoltes de J. Hamon Vie et Milieu 1: 93-94.
- Ovazza M. 1953. Contributions a l'etude biologique de la Camargue , Formicides. Vie et Milieu 4(4) : 751-753.
- Paik W.H. 1984. A checklist of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Korea. Korean J. Plant Prot. 23(3): 193-195.
- Paraschivescu D. 1972. Fauna mirmecologica din zonele saline ale Romaniei. Studii si Cercetari de Biologie. Seria Zoologie 24: 489-495.
- Paraschivescu D. 1978. Elemente balcanice in mirmecofauna R. S. Romania. Nymphaea 6: 463- 474.
- Park S.J., and B.J. Kim. 2002. Faunal comparison of ants among Cheongsando and other islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(1): 7-12.
- Park, Seong, Joon and Byung, and Kim, Jin. 2002. Faunal Comparison of Ants among Cheongsando and Other Islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Jornal of Entomology. 32(1):7-12.
- Pavlova N. S. 2014. To ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the floodplain of Medvedista River (Saratov Province). Entomological and parasitological studies in the Volga region 11: 145-147.
- Pech P. 2012. A contribution to the distribution and biology of Myrmica vandeli (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the Czech Republic. Silva Gabreta 18(2): 95-99.
- Pekar, S. 2004. Predatory Behavior of Two European Ant-Eating Spiders (Araneae, Zodariidae). Journal of Arachnology 32(1): 31-41
- Petal J. 1974. Analysis of a sheep pasture ecosystem in the Pieniny mountains (the Carpathians) XV. The effect of pasture management on ant population. Ekologia Polska 22(3/4): 679-692.
- Petal J. 1980. The effect of industrial pollution of Silesia on populations of ants. Polish Ecological Studies 6(4): 665-672.
- Petal J. M. 1963. Faune des fourmis de la reserve de tourbiere en projet a Rakowskie Bagno pres de Frampol (voivodie de Lublin). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sk?odowska 58(7): 143-174.
- Petal J. M. 1967. Contribution a la connaissance des fourmis (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) de la region de Lublin. VII. Associations des fourmis des milieux de tourbieres, de forets et de dunes aux environs de Libiszow (dist. De Parczew). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Lublin-Polonia 22(9): 117-130.
- Petal J., and A. Kusinska. 1994. Fractional composition of organic matter in the soil of anthills and of the environement of meadows. Pedobiologia 38: 493-501.
- Petrov I. Z. 1986. Contribution to myrmecofauna in some oak-tree communities on the mountain Jastrebac. Prirodnjackog Muzeja i Beogradu Seriya B Bioloske Nauke Supplement: No. 41: 109-114.
- Petrov I. Z. 2002. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of the Banat Province (Serbia). Archives of Biological Sciences, Belgrade, 54(12): 57-64.
- Petrov I. Z. 2012. Preliminary data on ants (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) on Mountain Avala (Belgrade, Serbia). Bulletin of the Natural History Museum 5: 95-99.
- Petrov I. Z., B. Petrov, D. Milicic, T. Karan-Znidarsic. 2007. Contribution to the Myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of East and South Serbia. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 59(3): 295-299.
- Petrov I. Z., and C. A. Collingwood. 1992. Survey of the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of Yugoslavia. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade) 44: 79-91.
- Poldi B., M. Mei, and F. Rigato. 1995. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Vol 102. Checklist delle specie della fauna Italiana: 1-10.
- Pusvaskyte O. 1979. Myrmecofauna of the Lituanian SSR. Acta Entomologica Lituanica 4: 99-105.
- Radchenko, A. 2005. Monographic revision of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of North Korea. Annales Zoologici (Warsaw) 55: 127-221.
- Radchenko, A. 2005. Monographic revision of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of North Korea. Annales Zoologici 55(2): 127-221.
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.
- Reznikova Z. I. 2003. Distribution patterns of ants in different natural zones and landscapes in Kazakhstan and West Siberia along a meridian trend. Euroasian Entomological Journal 2(4): 235-342.
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1989. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna della Val Gesso (alpi Marittime) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boll. Mus. Reg. Sci. Nat. Torino 7(2): 427-442.
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1991. The myrmecofauna of the Gesso Valley (Maritime Alps) (Hymenoptera Formicidae). Ethology Ecology and Evolution Special Issue 1: 87-89.
- Ruiz Heras P., M. D. Martinez Ibanez, F. J. Cabrero-Sanudo, and M. A. Vazquez Martinez. 2011. Primeros datos de Formícidos (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en parques urbanos de Madrid. Boletín de la Asociación española de Entomología, 35(1-2): 87-106.
- Ruzsky M. 1916. On zoological research in Yeniseisk province, work of summer of 1915. Izv. Imp. Tomsk. Univ. 65 (3rd p part: 1-21.
- Ruzsky M. 1920. Ants of Kamchatka. Izv. Inst. Issled. Sib. 2: 76-80
- Rzeszowski K., H. Babik, W. Czechowski, and B. Marko. 2013. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Chelmowa Gora in the Swietokrzyski National Park. Fragmenta Faunistica 56(1): 1-15.
- Röszler P. 1950. Die Ameisenwelt des Nagy Pietrosz, 2305 m (Ungarn) und Umgebung. Zool. Anz. 145: 210-225.
- Sakai H. 2002. Reproductive flight season of Japanese ants. Ari 26: 33-39.
- Salata S. 2014. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the National Park of the Stołowe Mts. Przyroda Sudetow 17: 161-172.
- Salata S. 2014. Mrówki (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Parku Narodowego Gór Sto?owych. PRZYRODA SUDETÓW t. 17: 161-172.
- Salata S., and L. Borowiec. 2018. Taxonomic and faunistic notes on Greek ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 27: 1-51.
- Salata S., and L. Borowiec. 2019. Preliminary division of not socially parasitic Greek Temnothorax Mayr, 1861 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) with a description of three new species. ZooKeys 877: 81-131.
- Salgueiro, J.. "Variaçao anual em três comunidades de formicídeos da Serra da Estrela. Adiçao de um género novo e de duas espécies novas para portugal." Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 26 (3-4) (2002): 121-131.
- Sanchez-Gil Jimeno R., and J. L. Reyes-Lopez. 2016. Study of ants species of the Sierra de San Carlos del Valle (Ciudad Real) and updating the provincial check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent. 40 (1-2): 93-109.
- Sanders, D. and C. Platner. 2007. Intraguild Interactions between Spiders and Ants and Top-Down Control in a Grassland Food Web. Oecologia 150(4):611-624
- Santschi F. 1925. Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1: 339-360.
- Santschi F. 1926. Travaux scientifiques de l'Armée d'Orient (1916-1918). Fourmis. Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle 32: 286-293.
- Santschi, F.. "Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1 (1925): 339-360.
- Sato T., N. Tsurusaki, K. Hamaguchi, and K. Kinomura. 2010. Ant fauna of Tottori prefecture, Honshu, Japan. Bulletin of the Tottori Prefectural Museum 47: 27-44.
- Schar S., G Talavera, X. Espadaler, J. D. Rana, A. A. Andersen, S. P. Cover, and R. Vila. 2018. Do Holarctic ant species exist? Trans-Beringian dispersal and homoplasy in the Formicidae. Journal of Biogeography 00: 1-12.
- Schlick-Steiner B. C., and F. M. Steiner. 1999. Faunistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen an den freilebenden Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Wiens. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 3: 9-53.
- Schmitz H. 1950. Formicidae quaedam a cl. A. Stärcke determinatae, quas in Lusitania collegit. Brotéria Ser. Cienc. Nat. 19: 12-16.
- Schultz, R., A. G. Radchenko, and B. Seifert. "A critical checklist of the ants of Kyrgyzstan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." Myrmecologische Nachrichten 8 (2006): 201-207.
- Seifert B. 1983. The taxonomical and ecological status of Lasius myops Forel (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) and first description of its males. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 57(6): 1-16.
- Seifert B. 1994. Die freilebenden Ameisenarten Deutschlands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) und Angaben zu deren Taxonomie und Verbreitung. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 67(3): 1-44.
- Seifert, B.. "The taxonomical and ecological status of Lasius myops Forel and first description of its males." Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Goerlitz 57 (6) (1983): 1-16.
- Sellier Y., C. Galkowski, C. Lebas, and P. Wegnez. 2016. Découverte de Temnothorax pardoi (Tinaut, 1987) dans la réserve naturelle nationale du Pinail (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Revue de l’Association Roussillonnaise d’Entomologie 25(2): 106-113.
- Shilenkov V. G., A. A. Pankratov, and E. V. Sofronova. 2012. Preliminirary notes on species composition of Magdansky Reserve. Baikal Zoological Journal 3: 30-34.
- Shlyakhtenok A. S. 2007. Hymenoptera Aculeata of Raised Bogs in Belarus. Entomological Review 87(2): 136147.
- Shuang Zhao. 2006. Ant of Guangdong Province (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): A taxonomic study of the ants of Guangdong (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Master's thesis in Agriculture Insects and Pest Control. Supervisor Fenglong Jia. 115 pages.
- Slipinski P., B. Marko, K. Rzeszowski, H. Babik, and W. Czechowski. 2014. Lasius fuliginosus(Hymenoptera: Formicidae) shapes local ant assemblages. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10(2): 404-412.
- Slipinski P., M. Zmihorski, and W. Czechowski. 2012. Species diversity and nestedness of ant assemblages in an urban environment. Eur. J. Entomol. 109: 197206.
- Sommer F. 1984. Etude de la myrmécofaune de la réserve de la Massane. Laboratoire Arago, Banyuls sur Mer (66), 29 pages.
- Somogyi A. A., G. Lorinczi, J. Kovacs, and I. E. Maak. 2017. Structure of ant assemblages in planted poplar (Populus alba) forests and the effect of the common milkweek (Asclepias syriaca). Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae 63(4): 443–457.
- Sonobe R. 1977. Ant fauna of Miyagi prefecture , Japan. Japanese Journal of Ecology 27: 111-116.
- Soulie J. 1962. Fourmis des Hautes-Pyrenees. Bull. Soc. Hist. Nat. Toulouse 97: 35-37.
- Soyer B. 1951. Les fourmis des collines des environs de Marseille. Bull Soc Linn Provence 18: 3-6.
- Steffek J., and M. Wiezik. 2008. Exploited peatbog and associated mollusk and ant assemblages: still a reasonable protection? Naturae Tutela 12: 15-19.
- Steiner F. M., S. Schödl, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2002. Liste der Ameisen Österreichs (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Stand Oktober 2002. Beiträge zur Entomofaunistik 3: 17-25.
- Stiprais M. 1973. Materi?li par R?gas kukai?u faunu. - Latvijas Entomologs, 15: 30-32.
- Stukalyuk S. V. 2015. Structure of the ant assemblages (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the broad-leaved forests of Kiev. Entomological Review 95(3): 370–387.
- Stumper R. 1953. Etudes myrmecologiques. XI. Fourmis luxembourgeoises. Bulletin Soc. Nat. luxemb. 57: 122-135.
- Suvak M. 2007. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the stubble-fields of east Slovakia. Acta Zoologica Universitatis Comenianae. 47: 21-33
- Suñer i Escriche, David. "Contribució al coneixement mirmecologic de Gavarres, Montgrí, Guilleríes i la Serralada Transversal." Tesis Doctoral Universida (1991): 577 pp.
- Suñer, D., C. Gomez, and X. Espadaler. "Poblaciones meridionales de Lasius flavus (Fabr.) y L. myops Forel: estudio biométrico." Orsis 6 (1991): 101-108.
- Sveum P. 1979. Notes on the distribution of some Norwegian ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Fauna Norv. ser. B. 26: 10-11.
- Szujecki A., J. Szyszko, S. Mazur, and S. Perlinski. 1978. A succession of the ants (Formicidae) on afforested arable land and forest soils. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 183-189.
- Taheri A., J. Reyes-Lopez, and N. Bennas. 2014. Contribution a l'etude de la fauna myrmecologique du parc national de Talassemtane (nord du Maroc): biodiversite, biogeographie et especes indicatrices. Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa (S.E.A.), 54: 225236.
- Takechi F. 1960. A list of ants unrecorded from Mt. Ishizuchi and Omogo Valley, Iyo, Shikoku (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Transactions of the Shikoku Entomological Society 6:91.
- Tamura H., Y. Nakamura, K. Yamauchi, and T. Fujikawa. 1969. An ecological survey of soil fauna in Hidaka-Mombetsu, Southern Hokkaido. Journal of the Faculty of Science Hokkaido University, Zoology 17(1): 17-57.
- Tausan I., M. M. Jerpel, I. R. Puscasu, C. Sadeanu, R. E. Brutatu, L. A. Radutiu, and V. Giurescu. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Sibiu County (Transylvania, Romania). Brukenthal. Acta Musei 7(3): 499-520.
- Terayama M. 1977. Checklist of the known ants of Saitama Prefecture. Insects and nature 12(4): 26-27
- Terayama M. 1978. Ants of Bukozan. Nature and insects 13(4): 32-34.
- Terayama M. 1992. Structure of ant communities in East Asia. A. Regional differences and species richness. Bulletin of the Bio-geographical Society of Japan 47: 1-31.
- Terayama M. 1994. Ants of Okushiri-to Island, Hokkaido. Ari 18: 28-29.
- Terayama M., Choi, B.M., Kim, C.H. 1992. A check list of ants from Korea, with taxonomic notes. Bulletin of the Toho Gakuen 7:19-54.
- Terayama M., K. Ogata, and B.M. Choi. 1994. Distribution records of ants in 47 prefectures of Japan. Ari (report of the Myrmecologists Society of Japan) 18: 5-17.
- Terayama M., S. Kubota, and K. Eguchi. 2014. Encyclopedia of Japanese ants. Asakura Shoten: Tokyo, 278 pp.
- Terayama M., and S. Kubota. 2002. Ants of Tokyo, Japan. ARI 26: 1-32.
- Terayama. M. 1994. Ants of Okushiri-to Island, Hokkaido. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 18: 28-29
- Terayama. M. 2004. Geological and ecological distribution of Japanese ants communities. (translated from Japanese) Reports of the Saitama Prefecture Animal Research Association. 48:24
- Terayama. M. 2004. Geological and ecological distribution of Japanese ants communities. (translated from Japanese) Reports of the Saitama Prefecture Animal Research Association. 48:31
- Terayama. M. 2004. Geological and ecological distribution of Japanese ants communities. (translated from Japanese) Reports of the Saitama Prefecture Animal Research Association. 48:32
- Teruyama. M. 1988. Ant fauna of Saitama Prefecture, Japan. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 16: 4-13
- Ticha, K. 2005. Inventarizacní pruzkum mravencu (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) NPP Svarec. 2005. Acta Rerum Naturalium 1:127-130.
- Tinaut A. 2016. Ants of the Tejeda, Almijara and Alhama Mountains Natural Park (Andalusia, Spain) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent., 40 (1-2): 125-159.
- Tinaut A., and F. J. Ortiz. 1988. Introduccion al conocimiento de las hormigas de la provincia de Almeria (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Publicaciones del Instituto de Estudios Almerienses. Boletín (Ciencias) 8: 223-231.
- Tinaut, A., J. Jiménez Rojas, and R. Pascual. "Estudio de la mirmecofauna de los bosques de Quercus Linneo 1753 de la provincia de Granada." Ecología 8 (1995): 429-438.
- Tinaut, A.. "Descripción de Leptothorax pardoi nov. sp." EOS (Revista española de entomología) LXIII (1987): 315-320.
- Tsaryk I. 2012. The spatial restriction of some representatives of family Formicidae in the habitats of Lowland part of Western Ukraine. Visnyk of the Lviv University. Series BIology 60: 203207.
- Urbieta Balado A., A. Palanca Soler, C. Castan Lanaspa, and X. Espadaler. 1984. Ants in the supraforestal pastures of the Tendenera massif. Documents dEcologie Pyrénéenne III-IV: 223-224.
- Vele A., J. Holusa, and J. Frouz. 2009. Sampling for ants in different-aged spruce forests: A comparison of methods. European Journal of Soil Biology 45(4): 1-6.
- Vepsalainen K., H. Ikonene, and M. J. Koivula. 2008. The structure of ant assembalges in an urban area of Helsinki, southern Finland. Ann. Zool. Fennici 45: 109-127.
- Verdcourt, B. 2004. Additions to the Wild Fauna and Flora of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew XXXV. Miscellaneous Records. Kew Bulletin 59(4):639-649
- Vesni? A. 2011: Revidirani sistematski prijegled mrava Bosne i Hercegovine. Unutar : S. Lelo (urednik), Fauna Bosne i Hercegovine Biosistematski pregledi. 7. izmijenjeno i popravljeno interno izdanje Udruenja za inventarizaciju i zatitu ivotinja, Ilija, Kanton Sarajevo, pp: 205-207.
- Vlasakova, B., J. Raabova, T. Kyncl, P. Dostal, M. Kavarova, P. Kovar and T. Herben. 2009. Ants accelerate succession from mountain grassland towards spruce forest. Journal of Vegetation Science 20: 577587
- Vogrin, V.. "Prilog fauni Hymenoptera - Aculeata Jugoslavije." Zast. Bilja 31(suppl.) (1955): 1-74.
- Wang Ji-Fei et al. 2009. Study on the Species and Ecological Distribution of Ants on Ningxia Helan Mountain. Journal of Anhui Agri. Sci. 37(23): 11032-11034.
- Wegnez P. 2014. Premières captures de Lasius distinguendus Emery, 1916 et de Temnothorax albipennis (Curtis, 1854) au Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 150 (2014) : 168-171.
- Wegnez P. 2017. Découverte de Myrmica lobicornis Nylander, 1846 et Lasius jensi Seifert, 1982, deux nouvelles espèces pour le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 153: 46-49.
- Wegnez P. 2018. Premières decouvertes de Myrmica bibikoffi Kutter, 1963 et de Ponera testacea Emery, 1895, au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 154: 263–272.
- Wegnez P., D. Ignace, E. Lommelen, M. Hardy, J. Bogaert, and C. Nilsson. 2015. Redécouverte de Teleutomyrmex schneideriKutter, 1950 dans les Alpes françaises (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 52-57.
- Wegnez P., and A. Ronk. 2017. Découverte de Camponotus herculeanus (Linnaeus, 1758) et signalement de quelques autres espèces rares de fourmis au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois 119 : 153–159.
- Wegnez P., and F. Mourey. 2016. Formica uralensis Ruzsky, 1895 une espèce encore présente en France mais pour combien de temps ? (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 152: 72-80.
- Wegnez P., and M. Fichaux. 2015. Liste actualisee des especes de fourmis repertoriees au Grand-Duche de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 150-165
- Wiezik M. 2007. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of mountain and alpine ecosystems at Southern part of Krá?ovoho?ské Tatry Mts. Naturae Tutela 11: 85-90.
- Wiezik M., A. Wiezikova, and M. Svitok. 2011. Vegetation structure, ecological stability, and low-disturbance regime of abandoned dry grasslands support specific ant assemblages in Central Slovakia. Tuexenia 31: 301315.
- Wiezik M., M. Kozon, and A. Wiezikova. 2013. Ants of selected peat bog habitats at the Horná Orava protected area. Naturae Tutela 17(1): 57-63.
- Wieziková A. 2008. Epigaeic activity of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) at hemerobic gradient: arable land green forage permanent grassland. Acta Facultatis Ecologiae 18: 69-76.
- Wilson E. O. 1955. A monographic revision of the ant genus Lasius. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 113: 1-201
- Wlodarczyk T. 2010. Ant species composition in relation to forest associations in Szczecin Landscape Park. Polish Journal of Entomology 79: 91-99.
- Wu wei, Li Xiao Mei, Guo Hong. 2004. A primary study on the fauna of Formicidae in Urumqi and its vicinities. Arid Zone Research 21(2): 179-182
- Yamauchi K. 1968. Additional Notes on the Ecological Distribution of Ants in Sapporo and the Vicinity . Journal of the Faculty of Science Hokaido University, series VI, Zoology 16(3): 382-395.
- Yamauchi K. 1979. Taxonomical and ecological studies on the ant genus Lasius in Japan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). I. Taxonomy. Sci. Rep. Fac. Educ. Gifu Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 6: 147-181.
- Yang Jun, Xu Zheng-hui, Mei Xiang-xin, Zhang Ji-ling, Zhao Yu-xiang. 2004. Taxonomy of Ants on the Eastern Slope of Xishan Mountains in Kunming. Journal of Southwest Forestry College 24(4): 26-37.
- Yoshimura M. 1998. Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 1, Risiri Island). Rishiri Studies 17:33-38.
- Yoshimura M. 1999. Ants in the island of Hokkaido (Part 2, Part Rebun) Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 2, Rebun-Island). Rishiri Studies 18: 49-54.
- Yoshimura M. 2000. Ants in the island of Hokkaido (Part 3, Part ???) Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 3, Teuri Island). Rishiri Studies 19: 27-35.
- Yoshimura M., T. Hirata, A. Nakajima, and K. Onoyama. 2003. Ants found in scats and pellets taken from the nests of the Japanese Wryneck Jynx torquilla japonica. Ornithol. Sci. 2: 127-131.
- Zariquiey, R.. "Formigues de Cadaqués (prov. De Gerona)." Butll. Inst. Catalana Hist. Nat. (1930): 92.
- Zhang C., Z. Xu, N. Yu, Q. He, and X. Liu. 2012. Distribution Patterns of Ant Species on East Slope of Mount Demola and Zayu Valley in Southeastern Tibet. Journal of Northeast Forestry University 40(3): 87-92
- Zhang R. J., L. W. Liang, and S. Y. Zhou. 2014. An analysis on the ant fauna of Nonggang Nature Reserve in Guangxi, China. Journal of Guangxi Normal university: Natural Science Edition 32(3): 86-93.
- Zhou S.-Y. 2001. Ants of Guangxi. Guangxi Normal University Press, Guilin, China, Guilin, China. 255 pp.
- Zhuytszyuan D. 2016. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Nizhne-Svirsky reserve and their environmental features. Master's thesis Saint Petersburg State University.
- Zimmermann, S.. "Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Ameisenfauna Süddalmatiens." Verhandlungen der Zoologisch-Botanisch Gesellschaft in Wien 84 (1935): 1-65.
- Zryanin V. A., and T. A. Zryanina. 2007. New data on the ant fauna Hymenoptera, Formicidae in the middle Volga River Basin. Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii 127(2): 226-240.
- active management is vital. Belg. J. Zool. 137 (2): 137-146.
- de Biseau, J.-C., Y. Quinet, L. Deffernez and J.M. Pasteels. 1997. Explosive food recruitment as a competitive strategy in the ant Myrmica sabuleti (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insectes Sociaux 44:59-73
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Formícidos de las Sierras de Prades-Montsant, Sierras de Cavalls-Alfara-Montes Blancos (Tarragona)." Boletín de la Estación Central de Ecología 10 (1981): 55-58.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica en la Cordillera Ibérica." Orsis 6 (1991): 129-126.
- de Haro, Andrés. "Contribución al conocimiento de los formícidos del cabo de Creus (Gerona)." Pirineos 117 (1982): 49-57.
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Polygynous
- Common Name
- Photo Gallery
- North temperate
- North subtropical
- Ant Associate
- Host of Formica aquilonia
- Host of Formica cunicularia
- Host of Formica fusca
- Host of Formica fuscocinerea
- Host of Lasius niger
- Host of Lasius platythorax
- Host of Myrmica ruginodis
- Host of Myrmica scabrinodis
- Host of Tetramorium caespitum
- FlightMonth
- Host of Lasius carniolicus
- Host of Lasius mixtus
- Host of Lasius orientalis
- Aphid Associate
- Host of Forda marginata
- Ichneumonid wasp Associate
- Host of Hybrizon buccatus
- Phorid fly Associate
- Host of Pseudacteon formicarum
- ''Microdon'' fly Associate
- Host of Microdon sp.
- Fungus Associate
- Host of Aegeritella tuberculata
- Mite Associate
- Host of Imparipes obsoletus
- Host of Petalomium carelitschensis
- Host of Scutacarus longisetus
- Nematode Associate
- Host of Oscheius dolichura
- Host of Pheromermis villosa
- Host of "Mermis"
- Host of Pheromermis myrmecophila
- Host of Mermithidae (unspecified "Mermix")
- Karyotype
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Lasiini
- Lasius
- Lasius flavus
- Formicinae species
- Lasiini species
- Lasius species
- Ssr










