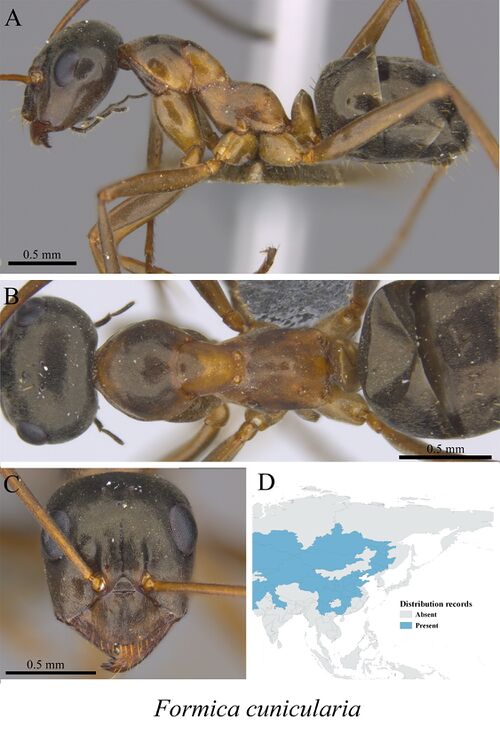
Formica cunicularia
| Formica cunicularia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Formicini |
| Genus: | Formica |
| Species: | F. cunicularia |
| Binomial name | |
| Formica cunicularia Latreille, 1798 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
| Evolutionary Relationships | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Based on Gomez, Lorite, P. et al. 2018. Note that this study was restricted to species near Formica gerardi. |
Species very common throughout Europe, even in disturbed habitats; also reported from Morocco (Rigato & Toni, 2011) and Russia (Zryanin & Zryanina, 2007). In Russia it is found in steppe habitats and dry pine forests. Nests are usually without mounds but mounds occur in some situations such as in meadows. Pashaei Rad et al. (2018) found this species in Iran on parkland ground in a moderate rainfall area. In Greece, Borowiec & Salata (2021) found this species to be common in northern mainland provinces, moderately common in southern mainland, on islands noted only from Aegean Islands and Crete. In northern provinces it was noted mostly from pastures, agricultural areas and rural sites in tourist resorts. In Achaia, it was observed in a rest area around a large pine tree and in high-growing oak forest.
Photo Gallery
Identification
Seifert and Schultz (2009) - A member of the Formica rufibarbis group. The separation of F. cunicularia and Formica clara represents the most difficult discrimination problem within the Formica rufibarbis group because there is a deficiency of strongly discriminating structural characters.
The weak point is that intraspecific colour polymorphism and loss of pigmentation by light or storage media could possibly affect the reliability of the pigmentation characters PIGM and CONT, but just these two characters have the largest loadings (canonical correlations) in the DA. These loadings are 0.788 in PIGM1.4 and 0.391 in CONT1.4 but only 0.336 in EYE1.4 and 0.170 in nPN1.4, the two best structural discriminators. Another problem are the isolated West Mediterranean populations of F. cunicularia from Corsica, Sardinia and the Sierra Nevada which were all allocated in the DA to the F. cunicularia cluster but possibly represent a third species. Integrative approaches including DNA analysis could bring more clarity into this issue.
Collingwood (1979) - Ashy grey black with at least genae and mesopleural articulations reddish; often most of alitrunk and head may be reddish. Gula and occiput bare. Erect hairs normally absent on pronotum but occasionally one or two short erect hairs may be present on promesonotum, never on upper margin of scale. Length: 4.0-6.5 mm.
Keys including this Species
Distribution
Seifert and Schultz (2009) - Temperate, Ponto-south-Siberian and Submediterranean species of the West Palaearctic, occurring from southernmost England and Iberia to West Siberia (85° E). In northwestern Europe, it goes north to southern Sweden (58° N) but has not reached southern Finland so far. Having a planar to colline distribution in the northern parts of its range, it climbs up to 1800 m in the Alps, up to 2400 m in the Caucasus and up to 2000 m in the South Siberian Tarbagatay Mountains.
North Africa to South Scandinavia, Portugal to Urals (Collingwood 1979).
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 59.4242205° to 32.48611°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Oriental Region: India, Pakistan.
Palaearctic Region: Albania, Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Channel Islands, China, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France (type locality), Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iberian Peninsula, Iran, Italy, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mongolia, Montenegro, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, North Macedonia, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
|
Habitat
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - Thermophilous species, noted from both deciduous and coniferous forests, gorges with deciduous forests, mountain pastures, roadsides in coniferous forests, rest area in village with stone walls, old quarry close to coniferous forests, beaches with sparse deciduous trees and in salines. Often observed in grasslands, gardens and parks in towns and tourist resorts. Most records are from low altitude but on sunny slopes of mountains can reach a height of 1550 m.
Biology
Nests in soil or under stones.
Seifert and Schultz (2009) - Moderately thermophilic. Preferred habitats are meagre and semidry grasslands on differing geological outcrop, more rarely extremely xerothermic grasslands and also open ruderal, rural or disturbed habitats, including road or railway verges. In contrast to F. rufibarbis more frequently occurring on loamy soils with more developed herb layer and less often invading the urban zone. Colony foundation usually by single gynes but also pleometrotic. Nests moderately populous, usually containing 1000 - 1800 workers, sometimes weakly polygynous, but polydomous colonies unknown (as in all members of the group). Usually inhabits simple soil nests, construction of high mounds of mineral soil in meagre grassland with higher herb layer regularly observed. Usually timid and fugitive, but populous nests with large workers may be very aggressive during nest defence. Not territorial. Foraging at surface temperatures of up to 50°C, mainly on open surfaces and in the herb layer, but not avoiding bushes and trees. Zoophagous, trophobiotic and nectarivorous. Low position in dominance hierarchies of ant communities, usually inferior to even Lasius niger (Linnaeus, 1758), whom it carefully evades thanks to superior walking speed and well-developed visual sense, thus enabling coexistence at long-term food sources. May snatch large prey items from L. niger by swift surprise attack. Favoured host species for several socially parasitic ant species. Alates occur 7 July ± 12 d [16 June, 1 August], n = 17 (Seifert 2007).
Collingwood (1979) - This is a common species throughout Western Europe, nesting under stones or in small earth mounds, colonising railway embankments, sun exposed borders of woodland, dry open pasture and sea cliffs. Each nest is separate and normally has only one queen. Its habits are mainly predaceous and scavenging. Alatae occur in July and August
Foraging/Diet
Formica cunicularia collect honeydew.
Novgorodova (2015b) investigated ant-aphid interactions of a dozen honeydew collecting ant species in Western Siberia pine and aspen-birch-pine forests (54°7´N, 83°06´E, 200 m, Novosibirsk) and mixed-grass-cereal steppes with aspen-birch groves (53°44´N, 78°02´E, 110 m, near Karasuk) in the Novosibirsk Region and coniferous forests in the northeastern Altai (north end of Lake Teletskoe, 51°48´N, 87°17´E, 434 m). All of the ants studied had workers that showed high fidelity to attending particular aphid colonies, i.e, individual foragers that collect honeydew tend to return to the same location, and group of aphids, every time they leave the nest. F. cunicularia honeydew collecting activities also showed some other specialization but this was dependent on colony size. Smaller colonies (hundreds of workers) did not specialize. Larger colonies (>1,000 workers), during the summer months when the aphids and ants were most active, had individual foragers that specialized on either collecting honeydew, guarding, i.e., protecting aphids from competitors, transporting honeydew, or scouting for new aphid colonies. Some individuals did not specialize and behaved like foragers from smaller colonies, while others would specialize by returning to a specific aphid colony but would as readily guard aphids as they would collect honeydew. F. cunicularia tended Chaitophorus populeti (Panzer) and Aphis craccivora Koch.
Guiliani et al. (2019) observed this species foraging on extrafloral nectaries of the invasive Reynoutria x bohemica (Polygonaceae) in Tuscany. The habitats examined were river banks and disturbed habitats.
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Other Insects
- This species is a host for the ant Formica sanguinea (a dulotic parasite) (Ruano et al., 2018; Seifert, 2018; de la Mora et al., 2021).
- This species is a host for the ant Polyergus rufescens (a dulotic parasite) (Romani et al., 2006; D'Ettorre et al., 2000; Mori et al., 2000; Visiccio et al., 2000; Visiccio et al., 2001; Romani et al., 2006; Seifert, 2018; Trager, 2013; de la Mora et al., 2021).
- This species is a host for the ant Formica exsecta (a temporary parasite) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018).
- This species is a host for the ant Formica pratensis (a temporary parasite) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018).
- This species is a host for the ant Formica rufa (a temporary parasite) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Lasius flavus (a xenobiont) in United Kingdom (Kanizsai et al., 2013; Morley, 1945) (Foreshore. Under stone).
- This species is associated with the aphids Acyrthosiphon pisum, Acyrthosiphon rubi, Aphis acetosae, Aphis brotericola, Aphis craccivora, Aphis fabae, Aphis nasturtii, Aphis pomi, Aphis solanella, Aphis spiraecola, Brachycaudus tragopogonis, Chaitophorus albus, Chaitophorus populeti, Chaitophorus populialbae, Cinara boerneri, Cinara palaestinesis, Cinara pini, Macrosiphoniella pulvera, Macrosiphum rosae and Sipha maydis (Saddiqui et al., 2019 and included references).
- This species is a mutualist for the butterfly Zizeeria knysna (Obregon et al. 2015).
- This species is a host for the braconid wasp Elasmosoma luxemburgense (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the braconid wasp Neoneurus vesculus (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the eucharitid wasp Eucharis adscendens (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (multiple encounter modes; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
Trematoda
- This species is a host for the trematode Dicrocoelium dendriticum (a parasite) in Germany (Hohorst & Graefe, 1961).
- This species is a host for the trematode Dicrocoelium lanceatum (a parasite) in Armenia (Arakelian et al., 1997).
Flight Period
| X | X | ||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Source: antkeeping.info.
- Check details at Worldwide Ant Nuptial Flights Data, AntNupTracker and AntKeeping.
 Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Life History Traits
- Mean colony size: 1,100 (Beckers et al., 1989)
- Foraging behaviour: solitary forager (Beckers et al., 1989)
Castes
Worker
Queen
Images from AntWeb
    
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0173176. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- cunicularia. Formica cunicularia Latreille, 1798: 40 (w.q.m.) FRANCE. Combination in F. (Serviformica): Forel, 1915d: 64. Junior synonym of rufibarbis: Walckenaer, 1802: 161; Dalla Torre, 1893: 209; Ruzsky, 1905b: 385; Forel, 1915d: 64; Emery, 1916b: 255; Emery, 1925b: 250. Revived from synonymy and status as species: Yarrow, 1954a: 231. Senior synonym of rubescens: Yarrow, 1954a: 231; Dlussky, 1967a: 73; Bernard, 1967: 296; Seifert & Schultz, 2009: 261; of fuscorufibarbis: Dlussky, 1967a: 73; Dlussky & Pisarski, 1971: 166; of glebaria: Bernard, 1967: 296; Boven, 1977: 164; Agosti & Collingwood, 1987a: 59; of glauca (and its junior synonyms caucasica, katuniensis, montivaga, montaniformis, volgensis): Atanassov & Dlussky, 1992: 267; of fuscoides: Arakelian, 1994: 94; Seifert & Schultz, 2009: 261.
- fuscorufibarbis. Formica fusca var. fuscorufibarbis Forel, 1874: 54 (w.q.) SWITZERLAND. Combination in F. (Serviformica): Forel, 1915d: 63. Raised to species: Forel, 1906c: 189. Subspecies of glebaria: Bondroit, 1918: 50; of rufibarbis: Dalla Torre, 1893: 210; Stitz, 1939: 357; Novak & Sadil, 1941: 107. Junior synonym of rufibarbis: Bernard, 1967: 297; of cunicularia: Dlussky, 1967a: 73; Dlussky & Pisarski, 1971: 166. See also comment in Seifert, 2002b: 266.
- rubescens. Formica fusca var. rubescens Forel, 1904f: 423 (w.) SWITZERLAND. [Unresolved junior primary homonym of rubescens Leach, above.] Emery, 1909b: 196 (q.); Wheeler, W.M. 1913f: 498 (m.). Subspecies of glebaria: Bondroit, 1918: 50; Boven, 1947: 188. Junior synonym of cunicularia: Yarrow, 1954a: 231; Dlussky, 1967a: 73; Bernard, 1967: 296; Seifert & Schultz, 2009: 261.
- fuscoides. Formica (Serviformica) cunicularia subsp. fuscoides Dlussky, 1967a: 74 (w.q.m.) ARMENIA. Junior synonym of cunicularia: Arakelian, 1994: 94; Seifert & Schultz, 2009: 261.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Seifert and Schultz (2009) - Medium-sized Serviformica species (CS 1.365 mm); head slightly elongated (CL / CW1.4 1.131); Scape moderately long SL / CS1.4 1.073; distance of lateral ocelli moderate (OceD / CS1.4 0.164); eyes rather large (EYE / CS1.4 0.301), petiole rather wide (PEW / CS1.4 0.468). Clypeus with sharp median keel and fine longitudinal micro-carinulae. Frontal triangle finely transversely rippled and with 30 - 60 short pubescence hairs. Eyes with microsetae of 7 - 13 μm maximum length. Total mean of unilateral setae numbers on different body parts predicted for a specimen with CS = 1.4 mm: pronotum 1.1, mesonotum 0.8, petiole scale dorsal of spiracle 0.25, flexor profile of hind tibia 0.3. Posterior margin and underside of head and dorsolateral metapleuron as a rule without setae. Ventral coxae with long setae, dorsum of gaster with scattered, moderately long setae. Dorsal mesonotum in lateral aspect broadly rounded. Metanotal depression in larger individuals relatively deep. Propodeal dome rounded in lateral view, basal profile sometimes concave and in smaller specimens often straight. Dorsal crest of petiole in frontal view bluntly angled in smaller specimens to broadly convex in larger specimens, in some of the large individuals with straight or weekly excavate median portion. Petiole scale in lateral aspect rather thin, with convex anterior and more straight posterior profile. Gaster with transverse microripples of small average distance (RipD 4.6 μm) and covered by dense silvery pubescence (sqPDG 3.1). Pubescence on head, mesosoma and petiole dense. Typical colour pattern: Head with exception of round reddish-yellowish spots on anterior genae, dorsal promesonotum, coxae and all appendages dark brown, gaster blackish brown. Other body parts more or less reddish-yellowish. Nests with much lighter specimens having whole mesosoma, coxae and petiole uniformly reddish and such with very dark specimens having the reddish pigmentation reduced to a very small spot on frontal margin of ventrolateral mesonotum; exceptionally completely dark specimens occur.
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - Large with strongly marked size-variation, HL: 1.174-1.680 (mean 1.421); HW: 0.937-1.349 (mean 1.127); SL: 1.222-1.730 (mean 1.449); EL: 0.397-0.495 (mean 0.444); ML: 1.86-2.56; MW: 0.77-1.16. Color. Head bicolor, clypeus and genae, yellowish to red, rest of surface brown to black, the pale genae sharply limited from the dark posterior part of head also when the area above the genae is lighter brown colored than frontal and occipital parts of head; this sharp border between the light anterior and dark posterior parts of the head is also visible in the color of the underside of the head; mesosoma variably colored, from uniformly yellowish red or red to mostly brown infuscate, often only upper parts of pronotum and mesonotum with obscure spots of diffused borders, these dark spots can also cover the sides of the mesosoma or almost the entire mesosoma is brown and only the intersegmental sutures are lighter; in rare melanistic forms whole mesosoma and petiolar scale are uniformly brown then head always bicolored with gena distinctly paler than dark frons and occipital part of head brown, gaster from yellowish brown to dark brown with transparent white posterior margin of tergites, often anterior slope of first tergite paper colored than dorsal surface of the tergite, antennae yellowish, apical 3-6 antennomeres often gradually infuscate; legs variable colored from uniformly yellowish red to mostly brown, coxa often darker than femora and tibiae, or coxa and femora darker than tibiae and tarsi. Head. 1.2- 1.3 times longer than wide, in front of eyes softly converging anterad, behind eyes softly rounded, occipital margin straight to slightly convex. Clypeus with median keel, on the whole surface distinctly microsculptured, slightly trapezoidal, its anterior margin convex, sides convergent posterad, posterior margin truncate or shallowly concave in the middle, whole clypeal surface with moderately long and moderately dense appressed pubescence, a row of 10-12 moderately long setae close at the anterior margin and usually 8 long erected setae arranged in three rows 4-2-2, sometimes with additional very short, 2-3 erected setae, the longest anterior seta with length 0.190. Head distinctly microreticulate, appears dull and opaque, with short and sparse appressed pubescence not covering head surface, interocular are with two pairs and ocellar area with a pair of moderately long, erected yellow setae, sometimes ocellar area with 1-3 additional short erected setae, occasionally frons with only a pair or without setae, ventral side of head lacking erected setae. Scape moderately long, 1.2-1.4 times longer than width of head, thin, distinctly reaching beyond the occipital margin, distinctly, regularly widened from base to apex, its surface microreticulate, with short and dense appressed pubescence, erected setae absent. Funicular segments elongate, thin, first segment 1.5-1.6 times as long as second segment, the second segment approximately twice as long as wide, only slightly shorter than third segment, the rest of funicular segments clearly longer than broad. Eyes big, elongate oval, approximately 0.31 length of head. Mesosoma. Elongate in dorsal view distinctly constricted in the middle, 2.2-2.4 times as long as wide, dorsally and laterally distinctly microreticulated, surface indistinctly dull and opaque. In lateral view promesonotum convex, mesonotal groove moderately deep, propodeum strongly, regularly convex. Whole mesosomal surface covered with moderately long and moderately dense appressed pubescence not covering the mesosomal surface, pronotum sometimes without, usually with 4-10 (at most 15) short erected setae, the longest with length 0.087, mesonotum without or with 1-6 short erected setae, propodeum lacking erected setae. Waist and gaster. Petiolar scale broad, moderately thick in lateral view, apex rounded without setae. Gaster shorter than mesosoma, all tergites distinctly microreticulate, appears dull and opaque, covered with moderately long and dense appressed pubescence not completely covering surface of tergites. All tergites close to posterior margin with a row of setae, surface of tergites with short, sparse erected setae. Legs. Ventral surface of fore femora with row of 1-5 erected setae, sometimes without setae, of mid femora lacking erected setae or at most with single seta close to trochanter.
Type Material
Seifert and Schultz (2009) - Neotype worker labelled “FRA: 44.4947°N, 0.9597°E, Fumel, 120 m, in a garden, leg. Galkowski 2008.07.25” and “Neotype Formica cunicularia Latreille 1798, des. Seifert & Schultz 2009”; SMN Görlitz. In case of destruction or loss of the neotype specimen, a replacement neotype can be designated from a series of five mounted workers from the same nest series in SMN Görlitz and further five workers in Musee National d'Histoire Naturelle Paris.
Justification of the neotype fixation: A current search in the Latreille collection of MNHN Paris failed to detect a specimen interpretable as a primary type (J. Casevitz-Weulersse, pers. comm. 2008) and the literature gives no indication that a revisor ever has seen one. In order to establish an unambiguous standard for differentiation from similar species, we fixed a neotype in a sample from the terra typica which is in agreement with the traditional morphological conception of F. cunicularia.
Taxonomic Notes
Seifert and Schultz (2009) - West Mediterranean isolated populations: We do not at this time propose these deviating and isolated populations from Corsica, Sardinia and the Sierra Nevada as heterospecific from F. cunicularia. Differences to the continental population are a significantly narrower petiole (PEW / CS1.4 0.433) and slightly longer 1st tergite setae (GHL / CS1.4 7.24%). It seems to be the only species of the group from Corsica where Formica clara and Formica rufibarbis have not been reported so far.
Karyotype
- See additional details at the Ant Chromosome Database.
 Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- n = 27, 2n = 54 (France) (Hauschteck-Jungen & Jungen, 1976).
References
- Agosti, D.; Collingwood, C. A. 1987a. A provisional list of the Balkan ants (Hym. Formicidae) and a key to the worker caste. I. Synonymic list. Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 60: 51-62 (page 59, senior synonym of glebaria)
- Albrecht, A. 1993. Formica cunicularia Latreille (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) new to Finland. Entomol. Fenn. 4: 13 (page 13, record in Finland)
- Alexandrovna, K.A. 2020. Red wood ants (Formica s. str.) as a method of biological protection in phytocenoses of the Mordovia Republic. In: Vavilov Readings - 2020: a collection of articles of the International Scientific and Practical Conference dedicated to the 100th anniversary of the discovery of the law of homological series and the 133rd anniversary of the birth of Academician NI Vavilov, November 24-25, 2020.
- Antonov, I.A., Bukin, Yu.S. 2016. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the ant genus Formica L. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Palearctic region. Russian Journal of Genetics 52(8), 810–820 (doi:10.1134/s1022795416080020).
- Arakelian G. R., Movsessian, S.O., Chubarian, F.A. 1997. Ecological and faunistic review of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) - Supplementary hosts of the trematode Dicrocoelium lanceatum in Armenia (in Russian). Parasitologia 31(3): 239-244.
- Arakelian, G. R. 1994. Fauna of the Republic of Armenia. Hymenopterous insects. Ants (Formicidae). Erevan: Gitutium, 153 pp. (page 94, senior synonym of fuscoides)
- Arcos, J., Chaves, D., Alarcón, P., Rosado, A. 2022. First record of Temnothorax convexus (Forel, 1894) in Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with an updated checklist of the ants from the country. Sociobiology, 69(2), e7623 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v69i2.7623).
- Arcos, J., Chaves, D., Alarcón, P., Rosado, Á. 2022. First record of Temnothorax convexus (Forel, 1894) in Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with an updated checklist of the ants from the country. Sociobiology, 692), e7623 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v69i2.7623).
- Atanassov, N.; Dlussky, G. M. 1992. Fauna of Bulgaria. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Fauna Bûlg. 22: 1-310 (page 267, senior synonym of glauca (and its junior synonyms caucasica, katuniensis, montivaga, montaniformis and volgensis).)
- Báthori, F., Herczeg, G., Vilizzi, L., Jégh, T., Kakas, C., Petrovics, M., Csősz, S. 2024. A survey and risk screening of non-native ant species colonising greenhouses in Hungary. Biological Invasions (doi:10.1007/s10530-023-03227-9).
- Beckers R., Goss, S., Deneubourg, J.L., Pasteels, J.M. 1989. Colony size, communication and ant foraging Strategy. Psyche 96: 239-256 (doi:10.1155/1989/94279).
- Bernard, F. 1967a [1968]. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp. (page 296, senior synonym of rubescens, senior synonym of glebaria)
- Billen, J., Mori, A., Le Moli, F., Grasso, D.A. 2001. Structural and functional changes of the Dufour gland in gynes of the amazon ant Polyergus rufescens (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoomorphology 121, 55–61 (doi:10.1007/s004350100045).
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2021. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Western Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 30: 1-23 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.5571258).
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. A monographic review of ants of Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Vol. 1. Introduction and review of all subfamilies except the subfamily Myrmicinae. Part 1: text. Natural History Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum 1: 1-297.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Thassos Island, Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 31 (online 2): 1-15 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.6123287).
- Borowiec, L., van Delft, J.P.L., van Delft, J.J.C.W., Salata, S. 2023. Five ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) new to the Greek fauna with notes on ants from Greek Thrace. Annales of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 32 (online 008), 1-13 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.10101028).
- Borowiec, M.L., Borowiec, L. 2013. New data on the occurrence of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Lower Silesia and other regions of Poland. Wiadomosci Entomologiczne 32: 49-57.
- Borowiec, M.L., Cover, S.P., Rabeling, C. 2021. The evolution of social parasitism in Formica ants revealed by a global phylogeny. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118, e2026029118 (doi:10.1073/pnas.2026029118).
- Boven, J. K. A. van. 1977. De mierenfauna van België (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Acta Zool. Pathol. Antverp. 67: 1-191 (page 164, senior synonym of glebaria)
- Bracko, G. 2017. First discoveries of colonies of the rare ant species Camponotus tergestinus Müller, 1921 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in situ. Natura Sloveniae 19(2): 5-14.
- Bračko, G. 2019. New data on the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Azerbaijan. Caucasian Entomological Bulletin 15, 165–175 (doi:10.23885/181433262019151-165175).
- Bracko, G., Wagner, H.C., Schulz, A., Gioahin, E., Maticic, J., Trantnik, A. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10: 10-24.
- Castracani, C., Spotti, F.A., Schifani, E., Giannetti, D., Ghizzoni, M., Grasso, D.A., Mori, A. 2020. Public engagement provides first insights on Po Plain ant communities and reveals the ubiquity of the cryptic species Tetramorium immigrans (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insects 11, 678. (doi:10.3390/insects11100678).
- Catarineu, C., Barberá, G.G., Reyes-López, J.L. 2018. Zoogeography of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of southeastern Iberian Peninsula. Sociobiology 65, 383-396 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v65i3.2822).
- Chen, Y., Zhou, S. 2017. Phylogenetic relationships based on DNA barcoding among 16 species of the ant genus Formica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from China. Journal of Insect Science 17(6): 117; 1–7 (doi:10.1093/jisesa/iex092).
- Collingwood, C. A. 1979. The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Fauna Entomol. Scand. 8:1-174.
- Collingwood, C.A., Prince, A. 1998. A guide to ants of Continental Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia. Supl nº5, pp 49.
- Csősz, S., Báthori, F., Gallé, L., Lőrinczi, G., Maák, I., Tartally, A., Kovács, É., Somogyi, A.Á., Markó, B. 2021. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: Survey of ant species with an annotated synonymic inventory. Insects 16;12(1):78 (doi:10.3390/insects12010078).
- Csosz, S., Marko, B., Galle, L. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A. 2006. Formica lusatica SEIFERT, 1997 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), an ant species new to Finland, with notes on its biology and the description of males. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 8: 257-262.
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A., Czechowska, W. 2002. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Poland. MIZ PAS Warsaw.
- Czechowski, W.; Radchenko, A. 2000. Formica glauca Ruzsky, 1895 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Poland. Fragmenta Faunistica 43: 127-129 (page 127, record in Poland)
- Dalla Torre, K. W. von. 1893. Catalogus Hymenopterorum hucusque descriptorum systematicus et synonymicus. Vol. 7. Formicidae (Heterogyna). Leipzig: W. Engelmann, 289 pp. (page 209, junior synonym of rufibarbis)
- de la Mora, A., Sankovitz, M., Purcell, J. 2020. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) as host and intruder: recent advances and future directions in the study of exploitative strategies. Myrmecological News 30: 53-71 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_030:053).
- Dekoninck, W., Ignace, D., Vankerkhoven, F., Wegnez, P. 2012. Verspreidingsatlas van de mieren van België. Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 148: 95-186.
- Devenish, A.J.M., Newton, R.J., Bridle, J.R., Gomez, C., Midgley, J.J., Sumner, S. 2021. Contrasting responses of native ant communities to invasion by an ant invader, Linepithema humile. Biological Invasions 23, 2553–2571 (doi:10.1007/s10530-021-02522-7).
- Dlussky, G. M. 1967a. Ants of the genus Formica (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, g. Formica). Moskva: Nauka Publishing House, 236 pp. (page 73, senior synonym of rubescens, senior synonym of fuscorufibarbis)
- Dlussky, G. M.; Pisarski, B. 1971. Rewizja polskich gatunków mrówek (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) z rodzaju Formica L. Fragmenta Faunistica 16: 145-224 (page 166, senior synonym of fuscorufibarbis)
- Dubovikoff, D.A., Yusupov, Z.M. 2017. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Emery, C. 1916a [1915]. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 47: 79-275 (page 255, junior synonym of rufibarbis)
- Emery, C. 1925d. Hymenoptera. Fam. Formicidae. Subfam. Formicinae. Genera Insectorum 183: 1-302 (page 250, junior synonym of rufibarbis)
- Forel, A. 1915d. Fauna insectorum helvetiae. Hymenoptera. Formicidae. Die Ameisen der Schweiz. Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 12(B Beilage: 1-77 (page 64, combination in F. (Serviformica), junior synonym of rufibarbis)
- Gallé, L. 2017. Climate change impoverishes and homogenizes ants’ community structure: a long term study. Community Ecology 18: 128–136 (doi:10.1556/168.2017.18.2.2).
- García, F., Cuesta-Segura, A.D., Espadaler, X. 2024. Myrmica babiensis sp. nov. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), a new social parasite from the NW Iberian Peninsula. Annales Zoologici 74(1), 113-127 (doi:10.3161/00034541anz2024.74.1.006).
- Giannetti, D., Schifani, E., Castracani, C., Ghizzoni, M., Delaiti, M., Pfenner, F., Spotti, F.A., Mori, A., Ioriatti, C., Grasso, D.A. 2021. Assessing ant diversity in agroecosystems: the case of Italian vineyards of the Adige Valley. Redia 104, 97–109 (doi:10.19263/redia-104.21.11).
- Giuliani, C., L. Lastrucci, L. Cresti, G. Santini, B. Fogg, and M. M. Lippi. 2019. The morphology and activity of the extrafloral nectaries in Reynoutria x bohemica (Polygonaceae). Plant Biology. 21:975-985. doi:10.1111/plb.13004
- Glaser, F. 2016. Artenspektrum, Habitatbindung und naturschutzfachliche Bedeutung von Ameisen (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) am Stutzberg (Vorarlberg, Österreich). inatura – Forschung 34: 26 S.
- Goropashnaya, A.V., Fedorov, V.B., Seifert, B., Pamilo, P. 2012. Phylogenetic relationships of Palaearctic Formica species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) based on mitochondrial Cytochrome b sequences. PLoS ONE 7, e41697 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041697).
- Grasso, D.A., Visicchio, R., Castracani, C., Mori, A., Le Moli, F. 2003. The mandibular glands as a source of sexual pheromones in virgin queens of Polyergus rufescens (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Italian Journal of Zoology 70, 229–232 (doi:10.1080/11250000309356522).
- Haelewaters, D., Boer, P., Noordijk, J. 2015. Studies of Laboulbeniales (Fungi, Ascomycota) on Myrmica ants: Rickia wasmanniii in the Netherlands. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 44, 39–47 (doi:10.3897/jhr.44.4951).
- Hohorst, W., Graefe, G. 1961. Ameisen — obligatorische Zwischenwirte des Lanzettegels (Dicrocoelium dendriticum). Naturwissenschaften 48, 229-230 (doi:10.1007/BF00597502).
- Johnson, C.A. 2000. Mechanisms of dependent colony founding in the slave-making ant, Polyergus breviceps Emery (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ph.D. thesis, City University of New York.
- Kanizsai, O., Lőrinczi, G., Gallé, L. 2013. Nesting associations without interdependence: A preliminary review on plesiobiosis in ants. Psyche 2013, 238602 (doi:10.1155/2013/238602).
- Karaman, C., Kiran, K. 2022. Additional records of parasitic Camponotus Mayr (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species from Turkey with queen description of Camponotus ruseni Karaman, 2012. Zoology in the Middle East 68(2), 156–164 (doi:10.1080/09397140.2022.2051918).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C. 2020. Additions to the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoosystema 42(18), 285-329 (doi:10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a18).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C., Heinze, J. 2021. First record of the inquiline ant Leptothorax kutteri Buschinger, 1965 from Turkey. Sociobiology 68, e7224 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v68i3.7224).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C., Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Aksoy, V. 2017. Two new species of the "ultimate" parasitic ant genus Teleutomyrmex KUTTER, 1950 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Western Palaearctic. Myrmecological News 25, 145-155.
- Kirchmair, G., Friess, T. et al. 2017. Zoologischer Bericht vom Tag der Biodiversität 2017 im Naturpark Südsteiermark. Mitteilungen des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereines für Steiermark 147: 99–134.
- Kök, Ş., Aktaç, N., Kasap, I. 2021. Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) ‐ aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) interactions in different habitats from Turkey with new mutualistic associations. Agricultural and Forest Entomology 12477 (doi:10.1111/afe.12477).
- Lachaud, J.-P., Déjean, A. 1994. Predatory behavior of a seed-eating ant: Brachyponera senaarensis. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 72(2), 145–155 (doi:10.1111/j.1570-7458.1994.tb01812.x).
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Kiran, K. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Strandzha (Istranca) Mountain and adjacent Black Sea coast. North-Western Journal of Zoology 8(1), 72-84.
- Latreille, P. A. 1798. Essai sur l'histoire des fourmis de la France. Brive: F. Bourdeaux, 50 pp. (page 40, worker, queen, male described)
- Lenoir, A., P. D’Ettorre, P., Errard, C., Hefetz, A. 2001. Chemical ecology and social parasitism in ants. Annual Review of Entomology 46: 573–599.
- Liu, C., Fischer, G., Hita Garcia, F., Yamane, S., Liu, Q., Peng, Y.Q., Economo, E.P., Guénard, B., Pierce, N.E. 2020. Ants of the Hengduan Mountains: a new altitudinal survey and updated checklist for Yunnan Province highlight an understudied insect biodiversity hotspot. ZooKeys 978, 1–171 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.978.55767).
- Maák, I., Czekes, Z., Erős, K., Pálfi, Z., Markó, B. 2020. Living on the edge: Changes in the foraging strategy of a territorial ant species occurring with a rival supercolony – a case study. Journal of Insect Behavior 33, 59–68 (doi:10.1007/S10905-020-09745-X).
- Mori, A., Grasso, D.A., Visicchio, R., Le Moli, F. 2000. Colony founding in Polyergus rufescens: the role of the Dufour’s gland. Insectes Sociaux 47: 7-10.
- Mori, A., Visicchio, R., Sledge, M.F., Grasso, D.A., Le Moli, F., Turillazzi, S., Spencer, S., Jones, G.R. 2000. Behavioural assays testing the appeasement allomone of Polyergus rufescens queens during host-colony usurpation. Ethology Ecology, Evolution 12, 315–322 (doi:10.1080/08927014.2000.9522804).
- Morley, D.W. 1945. Observations on some plesiobiotic colonies of ants (Hymenoptera), with notes on some other mixtobiotic colonies. Proceedings of the Royal Entomological Society of London 20, 1–4.
- Nemet, E., Czekes, Z., Tausan, I., Marko, B. 2012. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the Cefa Nature Park (North-Western Romania). Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica Biologia 20, 61-72.
- Novgorodova, T. A. 2015b. Organization of honeydew collection by foragers of different species of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): Effect of colony size and species specificity. European Journal of Entomology. 112:688-697. doi:10.14411/eje.2015.077
- Obregon, R., M. R. Shaw, J. Fernandez-Haeger, and D. Jordano. 2015. Parasitoid and ant interactions of some Iberian butterflies (Insecta: Lepidoptera). Shilap-Revista De Lepidopterologia. 43:439-454.
- Parmentier, T., De Laender, F., Wenseleers, T., Bonte, D. 2018. Prudent behavior rather than chemical deception enables a parasite to exploit its ant host. Behavioral Ecology 29(6), 1225-1233 (doi:10.1093/beheco/ary134).
- Pashaei Rad, S., Taylor, B., Torabi, R., Aram, E., Abolfathi, G., Afshari, R., Borjali, F., Ghatei, M., Hediary, F., Jazini, F., Heidary Kiah, V., Mahmoudi, Z., Safariyan, F., Seiri, M. 2018. Further records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Iran. Zoology in the Middle East 64, 145-159 (doi:10.1080/09397140.2018.1442301).
- Purkart, A., Kollár, J., Goffová, K. 2019. Fauna of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of selected sand habitats in Podunajsko Region, Slovakia. Naturae Tutela 23(1): 101-111.
- Rasheed, M.T., Bodlah, I., Fareen, A.G., Wachkoo, A.A., Huang, X., Akbar, S.A. 2019. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Pakistan. Sociobiology 66(3), 426-439 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v66i3.4330).
- Reznikova, Z. 2020. Spatial cognition in the context of foraging styles and information transfer in ants. Animal Cognition. (doi:10.1007/s10071-020-01423-x).
- Rigato, F.; Toni, I. 2011. Short notes 21. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Pp. 873-882 in: Nardi, G.; Whitmore, D.; Bardiani, M.; Birtele, D.; Mason, F.; Spada, L.; Cerretti, P. (eds.) 2011. Biodiversity of Marganai and Montimannu (Sardinia). Research in the framework of the ICP Forests network. Conservazione Habitat Invertebrati, 5. Sommacampagna, Verona: Cierre Edizioni, 896 pp.
- Romani, R., Grasso, D.A., Mori, A., Isidoro, N., Le Moli, F. 2006. Antennal glands of the slave-making ant Polyergus rufescens and its slave-species Formica cunicularia (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 84(3):490-494 (doi:10.1139/Z05-187).
- Ruano, F., Lenoir, A., Silvestre, M., Khalil, A., Tinaut, A. 2018. Chemical profiles in Iberoformica subrufa and Formica frontalis, a new example of temporary host–parasite interaction. Insectes Sociaux 66, 223–233 (doi:10.1007/S00040-018-00677-6).
- Ruzsky, M. 1905b. The ants of Russia. (Formicariae Imperii Rossici). Systematics, geography and data on the biology of Russian ants. Part I. Tr. Obshch. Estestvoispyt. Imp. Kazan. Univ. 38(4-6 6: 1-800 (page 385, junior synonym of rufibarbis)
- Salata, S., Borowiec, L. 2014. New localities of some rare ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Wiadomości Entomologiczne 33, 77-79.
- Salata, S., Borowiec, L. 2014. New localities of some rare ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Wiadomości Entomologiczne 33, 77-79.
- Salata, S., Borowiec, L., Trichas, A. 2020. Review of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Crete, with keys to species determination and zoogeographical remarks. Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum No 12: 5–296 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.3738001).
- Satria, R. 2017. Taxonomy of the ant genus Odontomachus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Ponerinae) in the Indo-Chinese and Indo-Malayan subregions. Ph.D. thesis, Tokyo Metropolitan University.
- Schär, S., Menchetti, M., Schifani, E., Hinojosa, J.C., Platania, L., Dapporto, L., Vila, R. 2020. Integrative biodiversity inventory of ants from a Sicilian archipelago reveals high diversity on young volcanic islands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Organisms Diversity, Evolution 20, 405–416 (doi:10.1007/s13127-020-00442-3).
- Schifani, E. (2022). The new checklist of the Italian fauna: Formicidae. Biogeographia – The Journal of Integrative Biogeography 37, ucl006 (doi:10.21426/b637155803).
- Schifani, E., Alicata, A., Menchetti, M. 2022. Following the Apennines: updating the distribution of Formica clara and Formica rufibarbis in Italy (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Biogeographia – The Journal of Integrative Biogeography 37: a014 (doi:10.21426/B637155107).
- Schifani, E., Csősz, S., Viviano, R., Alicata, A. 2021. Ant diversity on the largest Mediterranean islands: on the presence or absence of 28 species in Sicily (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natural History Sciences 8, 55–70 (doi:10.4081/nhs.2021.532).
- Schifani, E., Giannetti, D., Csősz, S., Castellucci, F., Luchetti, A., Castracani, C., Spotti, F.A., Mori, A., Grasso, D.A. 2021. Is mimicry a diversification-driver in ants? Biogeography, ecology, ethology, genetics and morphology define a second West-Palaearctic Colobopsis species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 194(4):1424–1450. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlab035
- Schifani, E., Nalini, E., Gentile, V., Alamanni, F., Ancona, C., Caria, M., Cillo, D., Bazzato, E. 2021. Ants of Sardinia: An updated checklist based on new faunistic, morphological and biogeographical notes. Redia 104, 21–35 (doi:10.19263/redia-104.21.03).
- Schultner, E., Pulliainen, U. 2020. Brood recognition and discrimination in ants. Insectes Sociaux 67, 11–34 (doi:10.1007/s00040-019-00747-3).
- Seifert, B. and R. Schultz. 2009. A taxonomic revision of the Formica rufibarbis Fabricius, 1793 group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News. 12:255-272.
- Siddiqui, J. A., Li, J., Zou, X., Bodlah, I., Huang, X. 2019. Meta-analysis of the global diversity and spatial patterns of aphid-ant mutualistic relationships. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 17: 5471-5524 (doi:10.15666/aeer/1703_54715524).
- Snegovaya, N., Shigayev, C. 2021. A checklist of the ants (Insecta, Formicidae) of Azerbaijan Republic. Iranian Journal of Animal Biosystematics 17(2): 179-207 (doi:10.22067/ijab.2022.67343.1000).
- Sondej, I., Domisch, T. 2024. Impact of large-scale fire and habitat type on ant nest density and species abundance in Biebrza National Park, Poland. Forests 151, 123 (doi:10.3390/f15010123).
- Stankovic, B. 2021. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Pomorie, Bulgaria. Ahi Evran International Conference on Scientific Research, pp. 198-204.
- Steiner, F.M., Schlick-Steiner, B.C., Holzinger, W., Komposch, C., Pazoutova, S., Sanetra, M., Christian, E. 2004. A novel relationship between ants and a leafhopper (Hymenoptera: Formicidae; Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). European Journal of Entomology 101, 689-692.
- Stukalyuk, S., Radchenko, A., Akhmedov, A., Reshetov, A., Netsvetov, M. 2021. Acquisition of invasive traits in ant, Crematogaster subdentata Mayr (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in urban environments. Serangga 26: 1-29.
- Stukalyuk, S.V., Kozyr, M.S., Netsvetov, M.V., Zhuravlev, V.V. 2020. Effect of the invasive phanerophytes and associated aphids on the ant (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) assemblages. Halteres 11: 56-89 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.4192900).
- Stukalyuk, S.V., Radchenko, A., Reshetov, A., Akhmedov, A., Goncharenko, I. 2021. Comparative analysis of the population structure of Crematogaster subdentata and Lasius neglectus in the primary and secondary ranges (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Fragmenta Entomologica 53, 43-51 (doi:10.13133/2284-4880/436).
- Tausan, I., Dauber, J., Trica, M.R., Marko, B. 2017. Succession in ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in deciduous forest clear-cuts - an Eastern European case study. European Journal of Entomology 114, 92–100 (doi:10.14411/eje.2017.013).
- van der Kooi, C.J., Stavenga, D.G., Arikawa, K., Belušič, G., Kelber, A. 2020. Evolution of insect color vision: From spectral sensitivity to visual ecology. Annual Review of Entomology 66, annurev-ento-061720–071644. (doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-061720-071644).
- Visicchio, R., Mori, A., Grasso, D.A., Castracani, C., Le Moli, F. 2010. Glandular sources of recruitment, trail, and propaganda semiochemicals in the slave-making ant Polyergus rufescens. Ethology Ecology, Evolution 13, 361–372 (doi:10.1080/08927014.2001.9522767).
- Walckenaer, C. A. 1802. Faune parisienne, insectes. Ou histoire abrégée des insectes des environs de Paris, classés d'après le système de Fabricius. Vol. 2. Paris: Dentu, 438 pp. (page 161, junior synonym of rufibarbis)
- Wiezik, M. 2005b. First record of Formica glauca (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Slovakia. Biológia (Bratisl.) 60: 544 (page 544, see also)
- Wiezik, M., Svitok, M., Wieziková, A., Dovčiak, M. 2013. Shrub encroachment alters composition and diversity of ant communities in abandoned grasslands of western Carpathians. Biodiversity and Conservation 22, 2305–2320 (doi:10.1007/s10531-013-0446-z).
- Wu, J. & Wang, C. 1992. Formicidae (pp. 1301-1320). In Peng, J. et al. Iconography of Forest Insects in Hunan, China. Forest Bureau of Hunan Province: 1473 pp. Hunan Scientific and Technical Publishing House.
- Wu, J. 1990. Taxonomic studies on the genus Formica L. of China (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). For. Res. 3: 1-8 (page 4, senior synonym of glabridorsis)
- Yarrow, I. H. H. 1954a. The British ants allied to Formica fusca L. (Hym., Formicidae). Trans. Soc. Br. Entomol. 11: 229-244 (page 231, revived from synonymy, and status as species1, senior synonym of rubescens)
- Zhu, W., Wu, L., Duan, L., Xu, S. 2022. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in northern Shaanxi Province, China, with one new species of genus Proformica Ruzsky, 1902, Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 25, 101875 (doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2022.101875).
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Abril S., and C. Gomez. 2013. Rapid assessment of ant assemblages in public pine forests of the central Iberian Peninsula. Forest Ecology and Management 293: 7984.
- Agosti D. 1983. Zur Insektenfauna der Umgebung der Vogelwarte Sempach, Kanton Luzern. XIII. Hymenoptera 2: Formicidae (Ameisen). Entomologische Berichte Luzern 10: 91-92.
- Agosti, D. and C.A. Collingwood. 1987. A provisional list of the Balkan ants (Hym. Formicidae) and a key to the worker caste. I. Synonymic list. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, 60: 51-62
- Aktaç, N.. "Studies on the myrmecofauna of Turkey I. Ants of Siirt, Bodrum and Trabzon." Istanbul Universitesi Fen Fakultesi Mecmuasi. Seri B 41 (1977): 115-135.
- Aldawood AS, Sharaf MR (2011) Monomorium dryhimi sp. n., a new ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the M. monomorium group from Saudi Arabia, with a key to the Arabian Monomorium monomorium-group. ZooKeys 106: 4754. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.106.139
- Alvarado M. 2000. Habitat correlates of ant assemblages in different forests of the South Pannonian Plain. Tiscia 32: 35-42.
- Alvarado M., and L. Galle. 2000. Ant assemblages associated with lowland forests in the southern part of the great Hungarian plain. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientarum Hungaricae 46(2): 79-102.
- Andoni V. 1977. Kontribut mbi Himenopteret e familjes Formicidae te vendit tone. Buletini I Shkencave te Natyres 31(2): 93-101.
- AntArea. Accessed on February 5th 2014 at http://antarea.fr/fourmi/
- Antarea (Personal Communication - Rumsais Blatrix- 27 April 2018)
- Antarea (at www.antarea.fr on June 11th 2017)
- Antonov I. A. 2013. Ant Assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Cities of the Temperate Zone of Eurasia. Russian Journal of Ecology 44(6): 523526.
- Antonova V., and L. Penev. 2008. Classification of assemblages of ants in the green areas in Sofia City. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 60(2): 103-110.
- Arakelian G. R., S. O. Movsessian, and F. A. Chubarian. 1997. Ecological and faunistic review of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) - Supplementary hosts of the trematode Dicrocoelium lanceatum in Armenia. Parasitologia 31(3): 239-244.
- Arnan, X., A. Rodrigo and J. Retana. 2006. Post-fire recovery of Mediterranean ground ant communities follows vegetation and dryness gradients. Journal of Biogeography 33(7):1246-1258
- ArtDatabanken Bugs (via GBIG)
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2011. List of species collected during the Taxomara Lisboa 2011. Iberomyrmex 3: 30-31.
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2012. List of species collected during the Taxomara Tres Cantos 2012. Iberomyrmex 4: 17-18.
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2014. List of species collected during the Taxomara 2014 Oviedo. Iberomyrmex 6: 23-24.
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2016. List of species collected during the Taxomara Murcia 2016. Iberomyrmex 8: 48-49.
- Assing V. 1989. Die Ameisenfauna (Hym.: Formicidae) nordwestdeutscher Calluna-Heiden. Drosera 89: 49-62.
- Azcarate F. M., and B. Peco. 2012. Abandonment of grazing in a mediterranean grassland area: consequences for ant assemblages. Insect Conservation and Diversity 5: 279288.
- Babik H. 2011. Ants of Botanical and Zoological Gardens of Warsaw (Poland). Entomologica romanica 16: 53.
- Baroni Urbani C. 1968. Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. V. Aspetti ecologici della Riviera del M. Cònero. Boll. Zool. 35: 39-76.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1976. A Numerical Analysis of the Distribution of British Formicidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata). Verhandlungen der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Basel 85: 51-91.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1977. The zoogeography of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Northern Europe. Acta Zoologica Fennica 152: 1-34.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Catalogo delle specie di Formicidae d'Italia (Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia X)." Memorie della Società Entomologica Italiana Volume 50 (1971): 5-287.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Formiche dell'Italia appenninica (Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia, III)." Memorie del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Verona 12 (1964): 149-172.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. I." Redia 47 (1962): 129-138.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. II. Formiche di Sicilia." Atti dell'Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali in Catania (6) 16 (1964): 25-66.
- Barrett K. E. 1967. Ants in South Brittany. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 79:112-116.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968. Ants in western France. Entomologist 101: 153-155.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968b. The distribution of ants in central southern England. Transactions of the Society for British Entomology 17: 235-250.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1970. Ants in France, 1968-69. Entomologist 103: 270-274.
- Baugnee J. Y. 2003. Camponotus piceus (Leach, 1825), fourmi nouvelle pour la faune belge decouverte dans le parc naturel Viroin-Hermeton (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin S. R. B. E./K. B. V. E. 139: 219-225.
- Baugnee J. Y., and J. F. Godeau. 2000. Signalement de Monomorium monomorium Bolton et de quelques autres fourmis à Belle-Ile-en-Mer, en Bretagne (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société entomologique de France 105(2): 205-208.
- Behr D., S. Lippke, and K. Colln. 1996. Zur kenntnis der ameisen von Koln (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Decheniana-Beihefte (Bonn) 35: 215-232.
- Behr D., and K. Colln. 1993. Zur ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) von Gonnersdorf (Kr. Daun). Dendrocopos 20: 148-160.
- Bernadou A., X. Espadaler, A. Le Goff, and V. Fourcassie. 2015. Ant community organization along elevational gradients in a temperate ecosystem. Insect. Soc. 62:5971
- Bernard F. 1960. Fourmis récoltées en Corse par J. Bonfils (1957). Compte Rendu Sommaire des Séances de la Société de Biogéographie 36: 108-114.
- Bernard F. 1967. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp.
- Bezdecka P., and K. Bezdeckova. 2012. Updated list of the ants of the Czech Republic. Pp 7-12. Bezd??ka P. & Bezd??ková K. (eds) 2012: Blanok?ídlí v ?eských zemích a na Slovensku 8, Chaloupky, 1.-3. ?ervna 2012, sborník abstrakt? z konference. MVJ Jihlava, 37 pp.
- Bharti H., Y. P. Sharma, M. Bharti, and M. Pfeiffer. 2013. Ant species richness, endemicity and functional groups, along an elevational gradient in the Himalayas. Asian Myrmecology 5: 79-101.
- Blacker N. C. 1989. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the Gower Peninsula, West Glamorgan, South Wales. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 101: 261-266.
- Blacker N. C. and C. A. Collingwood. 2002. Some significant new records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Salisbury area, south Wiltshire, England, with a key to the British species of Lasius. British Journal of Entomology and Natural History 15: 25-46
- Blacker N.C. 2007. Ants (Hym., Formicidae) in East Anglia-Additional Records from . Entomologist's Monthly Magazine 143: 69-90
- Blatrix R., C. Lebas, C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, P. Pimenta, and D. Morichon. 2016. Vegetation cover and elevation drive diversity and composition of ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in a Mediterranean ecosystem. – Myrmecological News 22: 119-127.
- Boer P. 2019. Species list of the Netherlands. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/specieslist.html
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. Van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten (Amsterdam) 63: 54-58.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten 63(3): 54-57.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. List of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Belgium and The Netherlands, their status and Dutch vernacular names. Entomologische Berichten 63 (3): 54-58.
- Bonaric J. C. 1971. Contribution a l'etude systematique et ecologique des formicides du Bas-Languedoc. PhD thesis Universite des sciences et techniques du Languedoc, 175 pages.
- Bonaric J. C. 1971. Étude systématique et ecologique des fourmis de lHérault (suite). Ann. Soc. Hortic. Hist. Nat. Hérault 111: 119-126.
- Bonte D., W. Dekoninck, S. Provoost, E. Cosijns, and M. Hoffmann. 2003. Microgeographical distribution of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in coastal dune grassland and their relation to the soil structure and vegetation. Animal Biology 53(4): 367-377.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec L., C. Galkowski, and S. Salata. 2015. What is Tetramorium semilaeve André, 1883? (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). ZooKeys 512:39-62.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2012. Ants of Greece - Checklist, comments and new faunistic data (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus 23(4): 461-563.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2017. Ants of the Peloponnese, Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Polish Journal of Entomology 86: 193-236.
- Boven J. K. A. 1947. Liste de détermination des principales espèces de fourmis belges (Hymenoptera Formicidae). Bulletin et Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 83: 163-190.
- Boven J. van 1949. Notes sur la faune des Hautes-Fagnes en Belgique. Bulletin et Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 85: 135-143.
- Bracko G. 2007. Checklist of the ants of Slovenia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natura Sloveniae 9: 15-24
- Bracko G., H. C. Wagner, A. Schulz, E. Gioahim, J. Maticic, and A. Tratnik. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10(1): 10-24.
- Bracko G., K. Kiran, C. Karaman, S. Salata, and L. Borowiec. 2016. Survey of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Greek Thrace. Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e7945. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e7945
- Bracko, G. 2006. Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) of Croatia. Acta Entomologica Slovenica 14(2): 131-156.
- Bracko, G.. "Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Croatia." Acta Entomologica Slovenica Vol 14 st (2006): 131-156.
- Braschler, B. and B. Baur. 2005. Experimental Small-Scale Grassland Fragmentation Alters Competitive Interactions among Ant Species. Oecologia 143(2):291-300
- Buren W. F. 1983. Artificial faunal replacement for imported fire ant control. Florida Entomologist 66: 93-100.
- Cagniant, H.. "Étude de quelques fourmis marocaines. Statistique provisoire des Formicidae du Maroc." Bulletin de la Société d' Histoire naturelle de l' Afrique du Nord 53 (1964): 83-118.
- Carniel A. 1998. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna delle Prealpi Orobiche (Lombardia) (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atti. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Morbegno 9: 29-39.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J. 1990. Etude Systematique de la Myrmecofaune Corse (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), deuxieme partie. Bull. Mus. Natn. Hist. Nat. Paris. 4eme serie 12, section A(2): 415-442.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J. 1992. La myrmecofaune de la reserve naturelle de Scandola, inventaire spécifique (1984/85-1991). Trav. Sci. Parc nat. Res. Nat. Corse, Fr, 36: 85-108.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and M. Prost. 1991. Fourmis de la Côte-d'Or présentes dans les collections du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Dijon. Bulletin Scientifique de Bourgogne 44: 53-72.
- Casevitz-Weulersse, J.. "Contribution a la connaisance des fourmis de la Corse (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." These de Doctorat Museum Nat (1989): 379pp.
- Castracani C., D. A. Grasso, A. Fanfani, and A. Mori. 2010. The ant fauna of Castelporziano Presidential Reserve (Rome, Italy) as a model for the analysis of ant community structure in relation to environmental variation in Mediterranean ecosystems. J Insect Conserv 14: 585594.
- Cerda X., R. Palacios, and J. Retana. 2009. Ant community structure in Citrus orchards in the Mediterranean basin: impoverishment as a consequence of habitat homogeneity. Environ. Entomol. 38(2): 317-324.
- Chen Y., C. W. Luo, H. W. Li, Y. J. Liu, H. F. Zheng, and F. C. Yang. 2013. Investigation of ant species and distribution on Wuliang Mountain. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences 42(5): 118-122.
- Cheng D., Z. Chen, and S. Zhou. 2015. An analysis on the ant fauna of Jinzhongshan Nature Reserve in Gunagxi, China. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 33(3): 129.137.
- Cherix D., and S. Higashi. 1979. Distribution verticale des fourmis dans le Jura vaudois et recensement prelimaire des bourdons (Hymenoptera, Formicidae et Apidae). Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sc. Nat. 356(74): 315-324.
- Colindre L. 2015. Les fourmis en Picardie: bilan 2014 (Hymenoptera/ Formicidae). Entomologiste Picard 26, 15 pages.
- Colindre L. 2017. Richess et utilite du cortege de fourmis en foret d'Ermenonville, Oise, Region Hauts-de-France. Association des Entomologistes de Picardie. 19 pages.
- Collingwood C. A. 1956. Ant hunting in France. Entomologist 89: 106-108.
- Collingwood C. A. 1971. A synopsis of the Formicidae of north Europe. Entomologist 104: 150-176
- Collingwood C., and A. Prince. 1998. A guide to ants of continental Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia. Suplemento 5: 1-49.
- Collingwood C., and H. Heatwole. 2000. Ants from Northwestern China (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Psyche 103 (1-2): 1-24.
- Collingwood C.A. 1961. New Vice-County Records for British Ants. Entomologist. 73: 90-93
- Collingwood, C. A. 1958b. A key to the species of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) found in Britain. Trans. Soc. Br. Entomol. 13: 69-96
- Collingwood, C. A. 1964. The Identification of British Ants (Hym. Formicidae). Transactions of the Society for British Entomology. 16:93-121.
- Collingwood, C. A., and I. H. H. Yarrow. "A survey of Iberian Formicidae." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 44 (1969): 53-101.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "A provisional list of Iberian Formicidae with a key to the worker caste." EOS (Revista española de entomología) Nº LVII (1978): 65-95.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark." Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 8 (1979): 1-174.
- Csosz S., B. Marko, K. Kiss, A. Tartally, and L. Galle. 2002. The ant fauna of the Ferto-Hansag National Park (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Mahunka, S. (Ed.): The fauna of the Fert?-Hanság National Park. Hungarian Natural History Museum, Budapest, pp. 617-629.
- Csősz S. and Markó, B. 2005. European ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the ant collection of the Natural History Museum of Sibiu (Hermannstadt/Nagyszeben), Romania II. Subfamily Formicinae. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 97: 225-240.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2001. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Stana Valley (Romania): Evaluation of the effectiveness of a myrmecological survey. Entomologica Romanica 6 : 121-126.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski W., A. Radchenko, W. Czechowska and K. Vepsäläinen. 2012. The ants of Poland with reference to the myrmecofauna of Europe. Fauna Poloniae 4. Warsaw: Natura Optima Dux Foundation, 1-496 pp
- Dekoninck W., F. Hendrickx, M. Dethier, and J. P. Maelfait. 2010. Forest Succession Endangers the Special Ant Fauna of Abandoned Quarries along the River Meuse (Wallonia, Belgium). Restoration Ecology 18(5): 681690.
- Dekoninck W., H. De Koninck, J. Y. Baugnee, and J. P. Maelfait. 2007. Ant biodiversity conservation in Belgian calcareous grasslands: active management is vital. Belg. J. Zool. 137 (2): 137-146.
- Della Santa E. 1994. Guide pour l'identification des principales espèces de fourmis de Suisse. Miscellanea Faunistica Helvetiae 3: 1-124.
- Della Santa E. 1995. Fourmis de Provence. Faune Provence 16: 5-37.
- Delye G. 1983. Contribution a l'etude des peuplements des invertebres de milieux extremes: les fourmis des dunes littorales del aCamargue (B. d. Rh) et de l'Espiguette (Gard). Bull. Soc. Linneenne Provence 35: 121-124.
- Dewes E. 2005. Ameisenerfassung im Waldschutzgebiet Steinbachtal/Netzbachtal. Abh. Delattinia 31: 89-118.
- Dlussky G. M., and B. Pisarski. 1970. Formicidae aus der Mongolei. Ergebnisse der Mongolisch-Deutschen Biologischen Expeditionen seit 1962, Nr. 46. Mitteilungen aus dem Zoologischen Museum in Berlin 46: 85-90.
- Donisthorpe H. 1914. Myrmecophilous notes for 1913. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 26: 37-45.
- Du Merle P. 1978. Les peuplements de fourmis et les peuplements d'acridiens du Mont Ventoux II. - Les peuplements de fourmis. Terre Vie 32(1): 161-218.
- Dubovikoff D. A., and Z. M. Yusupov. 2018. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Dusmet, J. M.. "Algunos insectos (la mayor parte himenópteros) cazados en Cataluña en 1925." Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica de España (1927): 21.
- Dvorak, L., P. BOGUSCH, I. MALENOVSKÝ, P. BEZDÌÈKA, K. BEZDÌÈKOVÁ, K. HOLÝ, P. LIKA, J. MACEK, L. ROLLER, M. RÍHA et al. "Hymenoptera of Hády Hill, near the city of Brno (Czech Republic), collected during the Third Czech-Slovak Hymenoptera meeting." Acta Musei Moraviae, Scientiae biologicae (Brno) 93 (2008): 53-92.
- Else G., B. Bolton, and G. Broad. 2016. Checklist of British and Irish Hymenoptera - aculeates (Apoidea, Chrysidoidea and Vespoidea). Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e8050. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e8050
- Emery C. 1916. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bullettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 47: 79-275.
- Espadaler X., F. Garcia, X. Roig, and R. Vila. 2013. Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from the Castell de Montesquiu park (Osona, north-east of the Iberian Peninsula). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa (S.E.A.) 53: 223-227.
- Espadaler X., X. Roig, K. Gómez, and F. García. 2011. Formigues de les Planes de Son i mata de València (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Treballs de la Institució Catalana d'Història Natural 16: 609-627.
- Espadaler, X., I. Zabalegui, and F. Calvo Sanchez. "Primer registro de Myrmica karavajevi (Arnoldi, 1930) en la Península Ibérica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." Heteropterus Revista de Entomología 4 (2004): 81-83.
- Espadaler, X., and X. Roig. "Ants from the Montnegre-Corredor Natural Park with description of the male lasius cinereus Seifert." Miscellanea Zoologica 23 (2) (2001): 45-53. Abstract
- Espadaler, X.. "Formicidos de las sierras de Cazorla, del Pozo y Segura (Jaén, España)." Ecología 11 (1997): 489-499.
- Forel A. 1892. Die Ameisenfauna Bulgariens. (Nebst biologischen Beobachtungen.). 305-318.
- Forel A. 1906. Fourmis d'Asie mineure et de la Dobrudscha récoltées par M. le Dr. Oscar Vogt et Mme Cécile Vogt, Dr. méd. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 50: 187-190.
- Forel, A.. "Südpalaearctische Ameisen." Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gessellschaft 9 (1895): 227-234.
- Formidabel Database
- Fowles, A.P. 1996. A provisional checklist of the invertebrates recorded from Wales. 2. Aculeate wasps, bees and ants (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Countryside Council for Wales
- GRETIA. 2017. Bilan annuel de l'enquete sur la repartition des fourmis armoricaines. 23 pages.
- Galkowski C. 2011. Une liste des fourmis (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) récoltées dans la région de Grasse, avec la mention dune nouvelle espèce de la faune de France. Bulletin de la Société linnéenne de Provence, 62 : 41-44.
- Galkowski C. 2013. Nouvelles données sur la répartition de Strongylognathus huberi Forel, 1874 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en France. Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux (n.s.) 41: 167-174.
- Galkowski C., C. Lebas, P. Wegnez, A. Lenoir, and R. Blatrix. 2017. Redescription of Proformica nasuta (Nylander, 1856) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) using an integrative approach. European Journal of Taxonomy 290: 1–40.
- Galkowski C., and C. Foin. 2013. Nouvelles données sur la répartition de Strongylognathus huberi Forel, 1874 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en France. Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux (n.s.) 41: 167-174.
- Galkowski C., and P Wegnez. 2010. Myrmica constricta Karavaiev 1934, nouvelle espece pour la France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Ent. Mulhouse 66(3): 41-45.
- Galle L. 1972. Study of ant-populations in various grassland ecosystems. Acta Biologica Szeged 18(1-4): 159-164.
- Galle L. 1981. The Formicoid fauna of the Hortobagy. Pp. 307-311 in: Mahunka, S. (ed.) 1981. The fauna of the Hortobágy National Park. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó, 415 pp.
- Galle L. 1993. Data to the ant fauna of the Bukk (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natural history of the national parks of Hungary 7: 445-448.
- Galle L. 1997. Contribution to the ant fauna of Slovenia with special reference to the submediterranean and eudinaric regions. Annals for Istrian and Mediterranean studies 11: 209-214.
- Gallé L., B. Markó, K. Kiss, E. Kovács, H. Dürgő, K. Kőváry, and S. Csősz. 2005. Ant fauna of Tisza river basin (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Gallé, L. (szerk.): Vegetation and Fauna of Tisza River Basin I. Tiscia Monograph Series 7; Szeged, pp. 149-197.
- Garcia Garcia F., and A. D. Cuesta-Esgura. 2017. First catalogue of the ants of Burgos province, Spain (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 60: 245–258.
- García F., X. Espadaler, P. Echave, and R. Vila. 2011. Hormigas (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) de los acantilados de l'Avenc de Tavertet (Osona) Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 47: 363-367.
- Gaspar C. 1968. Les fourmis de la Drome et des Basses-Alpes, en France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Naturaliste can. 95: 747-766.
- Gaspar C., and C. Thirion. 1978. Modification des populations d'Hymenopteres sociaux dans les milieux anthropogenes. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 61-77.
- Gaspare Charles. 1965. Étude myrmécologique d'une région naturelle de Belgique: la Famenne Survey des Fourmis de la Région (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Institut agronomique de l'Etat a' Gembloux. 32(4): 427-434.
- Ghahari H., and C. A. Collingwood. 2013. A study on the ants (Hymenoptera: Vespoidea: Formicidae) from Western Iran. Acta Phytopathologica et Entomologica Hungarica 48 (1): 155164.
- Giacalone I., and M. Moretti. 2001. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) dei castagneti al Sud delle Alpi (ticino, Svizzera). Bollettino della Societa ticinese di Scienze naturali 89(1-2): 51-60.
- Glaser F. 2009. Die Ameisen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Amtlicher Lehrmittelverlag, Vaduz, 2009 (Naturkundliche Forschung im Fürstentum Liechtenstein; Bd. 26).
- Glaser F., A. Freitag, and H. Martz. 2012. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the Münstertal (Val Müstair) a hot spot of regional species richness between Italy and Switzerland. Gredleriana 12: 273 - 284.
- Glaser F., T. Kopf, and K. H. Steiberger. 2003. Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) im Frastanzer Ried und den Illauen (Vorarlberg, Österreich) Artenspektrum, Gefährdung und Schutzempfehlungen. Vorarlberger Naturschau 13: 287-310.
- Gomez C., D. Casellas, J. Oliveras, and J. M. Bas. 2003. Structure of ground-foraging ant assemblages in relation to land-use change in the northwestern Mediterranean region. Biodiversity and Conservation 12: 21352146.
- Gomez K., P. Lorite, F. Garcia, A. Tinaut, X. Espadaler, T. Palomeque, O. Sanllorente, and J. Trager. 2018. Differentiating Iberoformica and Formica (Serviformica) with description of the sexual castes of Formica (Serviformica) gerardi Bondroit, 1917 stat. rev. Sociobiology 65(3): 463-470.
- Gouraud C. 2015. Bilan de l’année 2014 : Atlas des fourmis de Loire-Atlantique (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atlas des Formicidae de Loire-Atlantique, compte rendu de la première année d’étude (2014)
- Gratiashvili N., Barjadze S. 2008. Checklist of the ants (Formicidae Latreille, 1809) of Georgia. Proceedings of the Institute of Zoology (Tbilisi) 23: 130-146.
- Groc S., J. H. C. Delabie, R. Cereghino, J. Orivel, F. Jaladeau, J. Grangier, C. S. F. Mariano, and A. Dejean. 2007. Ant species diversity in the Grands Causses (Aveyron, France): In search of sampling methods adapted to temperate climates. C. R. Biologies 330: 913922.
- Grzes I. M. 2009. Ant species richness and evenness increase along a metal pollution gradient in the Boles?aw zinc smelter area. Pedobiologia 53: 65-73.
- Gulzar A. 2014. Classification and Distribution of ants in Kashgar, Xinjiang. Master's Thesis Shaanxi Normal University, 75 pages.
- Guénard B., and R. R. Dunn. 2012. A checklist of the ants of China. Zootaxa 3558: 1-77.
- Gómez C., and S. Abril. 2011. Selective logging in public pine forests of the central Iberian Peninsula: Effects of the recovery process on ant assemblages Forest Ecology and Management 262: 1061-1066.
- Haguet G., M. Chevrier, and E. Brunel. 2002. Les invertebres de la dune de Bon Abri, premier inventaire. Groupe d'Etude des Invertebres Armoricains, 37 pages.
- Ihnatiuk O. A., and S. V. Stukalyuk. 2015. Degradation changes in the structure of multispecies associations of ants in urbanized areas. Russian Journal of Ecology 46(1): 109–115.
- Jeffery H. G. 1931. The Formicidae (or ants) of the Isle of Wight. Proceedings of the Isle of Wight Natural History and Archaeological Society 2: 125-128.
- Kanizsai O., R. Gallé, and L. Gallé. 2009. Perception of spatial patchiness by ant assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Tiscia 37: 3-7.
- Karaman C., and K. Kiran. 2017. First record of Carebara oertzeni Forel (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the European part of Turkey with worker description. Turkish Journal of Zoology
- Karaman M. G. 2009. An introduction to the ant fauna of Macedonia (Balkan Peninsula), a check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natura Montenegrina 8(3): 151-162.
- Karaman M. G. 2011. A catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Montenegro. Podgorica: Catalogues 3, Volume 2, Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts, 140 pp.
- Karaman M. G., and G. S. Karaman. 2007. Contribution to the Knowledge of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Special nature reserve Zasavica , Serbia. Zbornik “Naucno-strucni skup Zasavica 2007, Sremska Mitrovica, 67-75.
- Kiran K. C. Karaman, A. Lapeva-Gjonova, and V. Aksoy. 2017. Two new species of the "ultimate" parasitic ant genus Teleutomyrmex KUTTER, 1950 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Western Palaearctic. Myrmecological News 25: 145-155.
- Kiran K., and C. Karaman. 2012. First annotated checklist of the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zootaxa 3548: 1-38.
- Kiran K., and N. Aktac. 2006. The vertical distribution of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Samanh Mountains, Turkey. Linzer Biol. Beitr. 38(2): 1105-1122.
- Kiss K., and K. Fetyko. 2008. Notes about the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Tur valley. In. Sike T., Márk-Nagy J. (eds), The flora and fauna of the Tur river natural reserve, Biharean Biologist, II, Oradea, pp.71-76.
- Klesniakova M., M. Holecova, and A. Pavlikova. 2016. Interesting ant species in the urban greenery of Bratislava. Folia Faunistica Slovaca 21(3): 235-238.
- Kofler A. 1995. Nachtrag zur Ameisenfauna Osttirols (Tirol, Österreich) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 1: 14-25.
- Kozisek T. 1987. Ants (Formicoidea) of the Abrod State Nature Reserve. Ochrana Prírody 8: 205-208.
- Kratochvíl J., V. Novák, and J. Snoflák. 1944. Mohelno. Soubor práci venoványch studiu vyznamne památky prírodní. 5. Hymenoptera - Aculeata. Formicidae - Apidae - Vespidae. Arch. Svazu Ochr. Prír. Domov. Moravé 6: 1-155.
- Kvamme T., and A. Wetas. 2010. Revidert liste over norske maur Inkludert dialektiske navn og forslag til nye norske navn og forslag til norske navn. Norsk institutt for skog og landskap, Ås. 127 pp
- Kvamme T., and C. A. Collingwood. 2009. The first records in Norway of Myrmica specioides Bondroit, 1918 and Formica cunicularia Latreille, 1798 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Norw. J. Entomol. 56: 6568.
- Lapeva-Gjonova A., and K. Kiran. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Strandzha (Istranca) Mountain and adjacent Black Sea coast. North-western journal of Zoology 8(1): 72-84.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, L., V. Antonova, A. G. Radchenko, and M. Atanasova. "Catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Bulgaria." ZooKeys 62 (2010): 1-124.
- Le Moli F., and A. Zaccone. 1995. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna del Cansiglio (Prealpi Carniche). Soc. Ven. Sc. Nat. 20: 33-52.
- Lebas C., C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, X. Espadaler, and R. Blatrix. 2015. The exceptional diversity of ants on mount Coronat (Pyrénées-Orientales), and Temnothorax gredosi(Hymenoptera, Formicidae) new to France. R.A.R.E., T. XXIV (1): 24 33
- Legakis A. 1983. The Zoological Museum of the University of Athens 2. The collection of ants from Greece. Biologia Gallo-Hellenica 11(1): 85-87.
- Legakis Collection Database
- Lehouck V., D. Bonte, W. Dekoninck, and J. P. Maelfait. 2004. The distribution of ant nests (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in coastal grey dunes of Flanders (Belgium) and their relationship to myrmecochorous plants. Belg. J. Zool. 134 (2/1) : 89-96.
- Li Z.h. 2006. List of Chinese Insects. Volume 4. Sun Yat-sen University Press
- Lillig M., and E. Dewes. 2015. The former Siegfried Line as habitats for ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Abh. Delattinia 37: 117 - 136
- Livory A. 2003. Les fourmis de la Manche. L'Argiope 39: 25-49.
- Lorinczi G. 2011. Lasius (Chthonolasius) nitidigaster Seifert, 1996 -a new ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) for the Hungarian fauna. Natura Somogyiensis 19: 223-228.
- Majzlan O., and P. Devan. 2009. Selected insect groups (Hymenoptera, Neuroptera, Mecoptera, Raphidioptera) of the Rokoš Massif (Strážovské vrchy Mts.). Rosalia (Nitra), 20, p. 63–70.
- Malozemova L. A. 1972. Ants of steppe forests, their distribution by habitats, and perspectives of their utilization for protection of forests (north Kazakhstan). [In Russian.]. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 51: 57-68.
- Mani M. S., and S. Singh. 1962. Entomological survey of Himalaya. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 59(1): 84-85.
- Marko B. 1999. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the River Somes valley. In: Sárkány-Kiss, A., Hamar, J. (szerk.): The Somes/Szamos River Valley. A study of the geography, hydrobiology and ecology of the river system and its environment. Tiscia Monograph Series 3, Szolnok-Szeged-Tîrgu Mure?, pp. 297-302.
- Marko B. 2008. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Sand Dunes of Foieni Protected Area and Its Surroundings (Satu Mare County, Romania), and a New Species for the Romanian Fauna. Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica 16(3): 87-99.
- Markó B. 1997. Contribution to the Knowledge of the Ant-Fauna (Hymenoptera: Fromicoidea) of the Cri?ul-Repede River-Valley. In: Sárkány-Kiss, A., Hamar, J. (szerk.): The Cri?/Körös Rivers' Valleys. A study of the geography, hydrobiology and ecology of the river system and its environment. Tiscia Monograph Series 2, Szolnok-Szeged-Tîrgu Mure?, pp. 345-352.
- Markó B., B. Sipos, S. Csősz, K. Kiss, I. Boros, and L. Gallé. 2006. A comprehensive list of the ants of Romania (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 9: 65-76.
- Martínez Ibáñez, M. D., C. Ornosa, and P. Gamarra. "Urban fauna. Hymenoptera in Madrid households, with special reference to ants." Entomofauna 18 (26) (1997): 417-428.
- Menozzi C. 1918. Primo contributo alla conoscenza della fauna mirmecologica del Modenese. Atti della Società dei Naturalisti e Matematici di Modena. (5)4: 81-88.
- Menozzi C. 1939. Formiche dell'Himalaya e del Karakorum raccolte dalla Spedizione italiana comandata da S. A. R. il Duca di Spoleto (1929). Atti della Società Italiana di Scienze Naturali e del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano. 78: 285-345.
- Meyer M., C. Braunert, R. Gerend, and I. Schrankel. 2003. Résultats de l'excursion annuelle du groupe de travail entomologique de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois. Bull. Soc. Nat. luxemb. 103: 103-120.
- Mori, A., D.A. Grasso, R. Visicchio and F. Le Moli. 2000. Colony founding in Polyergus rufescens: the role of the Dufours gland. Insectes Sociaux 47:7-10
- Mortazavi Z. S., H. Sadeghi, N. Aktac, L. Depa, L. Fekrat. 2015. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and their aphid partners (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Mashhad region, Razavi Khorasan Province, with new records of aphids and ant species for fauna of Iran. Halteres 6:4-12.
- Muñoz-López M., T. Palomeque, J. A. Carrillo, J. Pons, A. Tinaut, and P. Lorite. 2012. A new taxonomic status for Iberoformica (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) based on the use of molecular markers. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research 50: 30-37.
- Müller, G.. "Le formiche della Venezia Guilia e della Dalmazia." Bollettino della Società Adriatica di Scienze Naturali in Trieste 28 (1923): 11-180.
- Nagy C., A. Tartally, F. Villisics, O. Merkl, E. Szita, A. Podlussany, D. Redei, S. Csosz, G. Pozgai, A. Orosz, G. Szovenyi, and V. Marko. 2009. Effects of the invasive garden ant, Lasius neglectus VAN LOON, BOOMSMA & ANDRÁS-FALVY, 1990 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), on arthropod assemblages: pattern analyses in the type supercolony. Myrmecological News 12: 171-181.
- Nemet E., Z. Czekes, I. Tausan, and B. Marko. 2012. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the Cefa Nature Park (North-Western Romania). Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica 20(1): 61-72.
- Neumeyer R., and B. Seifert. 2005. Commented check list of free living ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species of Switzerland. Bulletin de la Societe Entomologique Suisse 78: 1-17.
- Nielsen M. G. 2011. A check list of Danish ants and proposed common names. Ent. Meddr. 79: 13-18.
- Novgorodova T. A., A. S. Ryabinin. 2015. Trophobiotic associations between ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) and aphids (Hemiptera, Aphidomorpha) in South Zauralye. News of Saratov University. Chemistry Series, Biology, Ecology 2(15): 98-107.
- Nylander, W.. "Synopsis des Formicides de France et d'Algérie." Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie (4)5 (1856): 51-109.
- Núñez-Pérez, E.. "Bases para el desarrollo del control integrado de los pulgones (Hom. Aphididae) de los cultivos de la provincia de León." Universidad de León, Secretariado de Publicaciones Tesis doct (1992): 7 páginas y 4 microfichas. León.
- Obregon R., J. Lopez, J. L. Reyes-Lopez. 2014. A catalogue of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Sierra Mágina (Jaén, southern Spain). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa (S.E.A.), 54: 370374.
- Ordóñez-Urbano C., J. Reyes-López, and S. Carpintero-Ortega. 2007. Estudio faunísidos de los formícidos (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) asociados a los bosques de ribera en la Provincia de Córdoba (España). Primeras Aportaciones. Boletin Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 40: 367-375.
- Ortiz, F. J., and A. Tinaut. "Introducción al conocimiento de las hormigas de la provincia de Almería." Publicaciones del Instituto de Estudios Almerienses. Boletín (Ciencias) 8 (1988): 223-231.
- Ortiz, F. J.. "Formícidos del litoral granadino." Memoria de Licenciatura Universida (1985): 206 pp.
- Ottonetti L., L. Tucci, and G. Santini. 2006. Recolonization Patterns of Ants in a Rehabilitated Lignite Mine in Central Italy: Potential for the Use of Mediterranean Ants as Indicators of Restoration Processes. Restoration Ecology 14(1): 6066.
- Ovazza M. 1950. Contribution à la connaissance des fourmis des Pyrénées-Orientales. Récoltes de J. Hamon Vie et Milieu 1: 93-94.
- Paknia O., A. Radchenko, H. Alipanah, and M. Pfeiffer. 2008. A preliminary checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Iran. Myrmecological News 11: 151-159.
- Palacios, R., M. T. Martínez Ferrer, and X. Cerdá. "Composición, abundancia y fenología de las hormigas en campos de cítricos de Tarragona." Boletín de Sanidad Vegetal 25 (2) (1999): 229-240.
- Paraschivescu D. 1972. Fauna mirmecologica din zonele saline ale Romaniei. Studii si Cercetari de Biologie. Seria Zoologie 24: 489-495.
- Paraschivescu D. 1978. Elemente balcanice in mirmecofauna R. S. Romania. Nymphaea 6: 463- 474.
- Pashaei Rad S., B. Taylor, R. Torabi, E. Aram, G. Abolfathi, R. Afshari, F. Borjali, M. Ghatei, F. Hediary, F. Jazini, V. Heidary Kiah, Z. Mahmoudi, F. Safariyan, and M. Seiri. 2018. Further records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Iran. Zoology in the Middle East 64(2): 145-159.
- Pekar, S. 2004. Predatory Behavior of Two European Ant-Eating Spiders (Araneae, Zodariidae). Journal of Arachnology 32(1): 31-41
- Pekar, S. 2009. Capture Efficiency of an Ant-Eating Spider, Zodariellum asiaticum (Araneae: Zodariidae), from Kazakhstan. Journal of Arachnology 37(3):388-391
- Petal J. 1974. Analysis of a sheep pasture ecosystem in the Pieniny mountains (the Carpathians) XV. The effect of pasture management on ant population. Ekologia Polska 22(3/4): 679-692.
- Petal J. M. 1967. Contribution a la connaissance des fourmis (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) de la region de Lublin. VII. Associations des fourmis des milieux de tourbieres, de forets et de dunes aux environs de Libiszow (dist. De Parczew). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Lublin-Polonia 22(9): 117-130.
- Petal J., and A. Kusinska. 1994. Fractional composition of organic matter in the soil of anthills and of the environement of meadows. Pedobiologia 38: 493-501.
- Petrov I. Z. 1986. Contribution to myrmecofauna in some oak-tree communities on the mountain Jastrebac. Prirodnjackog Muzeja i Beogradu Seriya B Bioloske Nauke Supplement: No. 41: 109-114.
- Petrov I. Z. 2002. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of the Banat Province (Serbia). Archives of Biological Sciences, Belgrade, 54(12): 57-64.
- Petrov I. Z. 2010. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Krusevac and its surroundings. Acta entomologica serbica, 2010, 15(1): 145-148.
- Petrov I. Z. 2012. Preliminary data on ants (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) on Mountain Avala (Belgrade, Serbia). Bulletin of the Natural History Museum 5: 95-99.
- Petrov I. Z., B. Petrov, D. Milicic, T. Karan-Znidarsic. 2007. Contribution to the Myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of East and South Serbia. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 59(3): 295-299.
- Petrov I. Z., and C. A. Collingwood. 1992. Survey of the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of Yugoslavia. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade) 44: 79-91.
- Pisarski B. 1964. Fauna Mrowek Afganistanu. Bibliogr. k. 160-166, Nieoprawiony maszynopis pracy, Praca doktorska. Instytut Zoologiczny PAN, 1964, Bibliogr. p. 160-166
- Pisarski B. 1967. Fourmis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) d'Afghanistan récoltées par M. Dr. K. Lindberg. Annales Zoologici (Warsaw) 24: 375-425.
- Poldi B. 1980. Imenotteri formicidi della Brughiera di Rovasenda (Piemonte). In: Poldi, B. 1980. Quaderni sulla "Struttura delle zoocenosi terrestri". 1. La brughiera pedemontana. III. Serie AQ/1/110. Collana del programma finalizzato "Promozione della qualità dell'ambiente". Roma: Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, pp. 7-19.
- Poldi B., M. Mei, and F. Rigato. 1995. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Vol 102. Checklist delle specie della fauna Italiana: 1-10.
- Pusvaskyte O. 1979. Myrmecofauna of the Lituanian SSR. Acta Entomologica Lituanica 4: 99-105.
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.
- Rasheed M. T., I. Bodlah, A. G. Fareen, A. A. Wachkoo, X. Huang, and S. A. Akbar. 2019. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Pakistan. Sociobiology 66(3): 426-439.
- Retana J., and X. Cerdá X. 2000. Patterns of diversity and composition of Mediterranean ground ant communites tracking spatial and temporal variability in the thermal environment. Oecologia 123: 436-444.
- Retana, J., X. Cerdá, V. Cavia, J. Arnal, and D. Company. "La comunidad de hormigas (Hym. Formicidae) del Boalar de Jaca (Jaca, Huesca)." Lucas Mallada 1 (1989): 133-150.
- Reyes-López J., S. Carpintero-Ortega, and E. Retamoza-Muñoz. 2010. Adiciones a la relación de especies de hormigas (Hym., Formicidae) del Parque Natural del Cabo de Gata- Níjar (Almería, España) Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 34: 67-76.
- Reznikova Z. I. 2003. Distribution patterns of ants in different natural zones and landscapes in Kazakhstan and West Siberia along a meridian trend. Euroasian Entomological Journal 2(4): 235-342.
- Rigato F., and J. K. Wetterer. 2018. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of San Marino. Natural History Sciences. Atti Soc. it. Sci. nat. Museo civ. Stor. nat. Milano, 5(2): https://doi.org/10.4081/nhs.2018.367
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1989. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna della Val Gesso (alpi Marittime) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boll. Mus. Reg. Sci. Nat. Torino 7(2): 427-442.
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1991. The myrmecofauna of the Gesso Valley (Maritime Alps) (Hymenoptera Formicidae). Ethology Ecology and Evolution Special Issue 1: 87-89.
- Rigato S., and I. Toni. 2011. Short notes 21. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Pp. 873-882 in: Nardi, G.; Whitmore, D.; Bardiani, M.; Birtele, D.; Mason, F.; Spada, L.; Cerretti, P. (eds.) 2011. Biodiversity of Marganai and Montimannu (Sardinia). Research in the framework of the ICP Forests network. Conservazione Habitat Invertebrati, 5. Sommacampagna, Verona: Cierre Edizioni, 896 pp.
- Röszler P. 1950. Die Ameisenwelt des Nagy Pietrosz, 2305 m (Ungarn) und Umgebung. Zool. Anz. 145: 210-225.
- Salata S., L. Borowiec, and A.Trichas. 2018. Taxonomic Revision of the Cretan Fauna of the Genus Temnothorax Mayr, 1861 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), with Notes on the Endemism of Ant Fauna of Crete. Annales Zoologici (Warsaw) 68(4): 769-808.
- Salata S., and L. Borowiec. 2018. Taxonomic and faunistic notes on Greek ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 27: 1-51.
- Salata S., and L. Borowiec. 2019. Preliminary division of not socially parasitic Greek Temnothorax Mayr, 1861 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) with a description of three new species. ZooKeys 877: 81-131.
- Sanchez-Gil Jimeno R., and J. L. Reyes-Lopez. 2016. Study of ants species of the Sierra de San Carlos del Valle (Ciudad Real) and updating the provincial check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent. 40 (1-2): 93-109.
- Sanllorente O., P. Lorite, F. Ruano, T. Palomeque, and A. Tinaut. 2017. Phylogenetic relationships between the slave-making ants Rossomyrmex and their Proformica hosts in relation to other genera of the ant tribe Formicini (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J Zool Syst Evol Res. 1–13.
- Santos S. A. P., J. E. Cabanas, and J. A. Pereira. 2007. Abundance and diversity of soil arthropods in olive grove ecosystem (Portugal): Effect of pitfall trap type. European Journal of Soil Biology 43: 77-83.
- Santschi F. 1925. Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1: 339-360.
- Santschi F. 1926. Travaux scientifiques de l'Armée d'Orient (1916-1918). Fourmis. Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle 32: 286-293.
- Santschi, F.. "Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1 (1925): 339-360.
- Schlick-Steiner B. C., and F. M. Steiner. 1999. Faunistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen an den freilebenden Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Wiens. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 3: 9-53.
- Schmitz, H.. "Ein Verzeichnis portugiesischer Ameisen (Formicidae, Hymenoptera)." Brotéria Ser. Cienc. Nat. 24 (1955): 27-37.
- Schultz, R., A. G. Radchenko, and B. Seifert. "A critical checklist of the ants of Kyrgyzstan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." Myrmecologische Nachrichten 8 (2006): 201-207.
- Scupola A. 2016. First records of the ant genus Formica Linnaeus 1758 (Hymenoptera Formicidae) from the coastal pine woods of Salento Peninsula (Apulia, southern Italy). Thalassia Salentina 38: 137-141.
- Seifert B. 1994. Die freilebenden Ameisenarten Deutschlands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) und Angaben zu deren Taxonomie und Verbreitung. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 67(3): 1-44.
- Seifert B. 2007. Die Ameisen Mittel- und Nordeuropas. Tauer: lutra Verlags- und Vertriebsgesellschaft, 368 pp.
- Seifert B., and R. Schultz. 2009. A taxonomic revision of the Formica rufibarbis Fabricius, 1793 group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 12:255-272.
- Sellier Y., C. Galkowski, C. Lebas, and P. Wegnez. 2016. Découverte de Temnothorax pardoi (Tinaut, 1987) dans la réserve naturelle nationale du Pinail (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Revue de l’Association Roussillonnaise d’Entomologie 25(2): 106-113.
- Slipinski P., M. Zmihorski, and W. Czechowski. 2012. Species diversity and nestedness of ant assemblages in an urban environment. Eur. J. Entomol. 109: 197206.
- Sommer F. 1984. Etude de la myrmécofaune de la réserve de la Massane. Laboratoire Arago, Banyuls sur Mer (66), 29 pages.
- Sonnenburg H. 2005. Die Ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Niedersachsens und Bremens. Braunschweiger Naturkundliche Schriften 7: 377-441.
- Steiner F. M., S. Schödl, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2002. Liste der Ameisen Österreichs (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Stand Oktober 2002. Beiträge zur Entomofaunistik 3: 17-25.
- Stukalyuk S. V. 2015. Structure of the ant assemblages (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the broad-leaved forests of Kiev. Entomological Review 95(3): 370–387.
- Suay-Cano, V. A., A. Tinaut, and J. Selfa. "Las hormigas (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) asociadas a pulgones (Hemiptera, Aphididae) en la provincia de Valencia." Graellsia 58(1) (2002): 21-37.
- Suchocka H., W. Czechowski, and A. Radchenko. 2008. Second report on the occurrence of Camponotus truncatus (Spinola) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Poland, with a key to the Polish species of the genus Camponotus Mayr. Fragmenta Faunistica (Warsaw) 51: 9-13.
- Suvak M. 2007. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the stubble-fields of east Slovakia. Acta Zoologica Universitatis Comenianae. 47: 21-33
- Suñer i Escriche, David. "Contribució al coneixement mirmecologic de Gavarres, Montgrí, Guilleríes i la Serralada Transversal." Tesis Doctoral Universida (1991): 577 pp.
- Szujecki A., J. Szyszko, S. Mazur, and S. Perlinski. 1978. A succession of the ants (Formicidae) on afforested arable land and forest soils. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 183-189.
- Tausan I. 2010. Notes on the ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the Rodna Mountains National Park and it's surroundings (Transylvania-Maramures, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 9: 159-166.
- Tausan I., J. Dauber, M. R. Tricia, and B. Marko. 2017. Succession in ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in deciduous forest clear-cuts – an Eastern European case study. European Journal of Entomology 114: 92-100.
- Tausan I., M. M. Jerpel, I. R. Puscasu, C. Sadeanu, R. E. Brutatu, L. A. Radutiu, and V. Giurescu. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Sibiu County (Transylvania, Romania). Brukenthal. Acta Musei 7(3): 499-520.
- Tausan I., and B. Marko. 2009. Comparative analysis of ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the surroundings of Sibiu (Romania). Brukenthal. Acta Musei 4(3): 635-644.
- Ticha, K. 2005. Inventarizacní pruzkum mravencu (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) NPP Svarec. 2005. Acta Rerum Naturalium 1:127-130.
- Tinaut A. 2016. Ants of the Tejeda, Almijara and Alhama Mountains Natural Park (Andalusia, Spain) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent., 40 (1-2): 125-159.
- Tinaut A., and F. J. Ortiz. 1988. Introduccion al conocimiento de las hormigas de la provincia de Almeria (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Publicaciones del Instituto de Estudios Almerienses. Boletín (Ciencias) 8: 223-231.
- Tinaut, A., J. Jiménez Rojas, and R. Pascual. "Estudio de la mirmecofauna de los bosques de Quercus Linneo 1753 de la provincia de Granada." Ecología 8 (1995): 429-438.
- Tinaut, A., and F. Ruano. "Contribución al conocimiento de los formícidos de la Sierra de la Estrella (Portugal)." Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 18 (3-4) (1994): 97-99.
- Tinaut, A.. "Contribución al conocimiento de los formícidos del Parque Nacional de Doñana." Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 15 (1991): 57-63.
- Tizado Morales, E. J.. Estudio comparado de la fauna y la biología de pulgones (Hom.), afidíinos (Hym.) y otros insectos acompañantes en dos áreas de la provincia de León In Secretariado de Publicaciones, Tesis doctoral en microficha, nº 67. León: Universidad de León, 1991.
- Trigos Peral G., and J. Reyes Lopez. 2016. Ants as bioindicators for monitoring of urban green in the south of the Iberian Peninsula. Proposal of functional groups. Iberomyrmex 8: 37-38.
- Trigos-Peral G., and J. L. Reyes-Lopez. 2013. Primera relacion de los formicidos (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) de la Reserva Natural Lagunas de Campillos (Malaga). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent. 37 (3-4): 217-224.
- Tsaryk I. 2012. The spatial restriction of some representatives of family Formicidae in the habitats of Lowland part of Western Ukraine. Visnyk of the Lviv University. Series BIology 60: 203207.
- Vagalinski B., and A. Lapeva-Gjonova. 2012. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Plana Mountain (Bulgaria). Historia naturalis bulgarica 20: 87-101.
- Vogrin, V.. "Prilog fauni Hymenoptera - Aculeata Jugoslavije." Zast. Bilja 31(suppl.) (1955): 1-74.
- Wegnez P. 2014. Premières captures de Lasius distinguendus Emery, 1916 et de Temnothorax albipennis (Curtis, 1854) au Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 150 (2014) : 168-171.
- Wegnez P. 2017. Découverte de Myrmica lobicornis Nylander, 1846 et Lasius jensi Seifert, 1982, deux nouvelles espèces pour le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 153: 46-49.
- Wegnez P. 2018. Premières decouvertes de Myrmica bibikoffi Kutter, 1963 et de Ponera testacea Emery, 1895, au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 154: 263–272.
- Wegnez P., and A. Ronk. 2017. Découverte de Camponotus herculeanus (Linnaeus, 1758) et signalement de quelques autres espèces rares de fourmis au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois 119 : 153–159.
- Wegnez P., and F. Mourey. 2016. Formica uralensis Ruzsky, 1895 une espèce encore présente en France mais pour combien de temps ? (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 152: 72-80.
- Wegnez P., and M. Fichaux. 2015. Liste actualisee des especes de fourmis repertoriees au Grand-Duche de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 150-165
- Wiezik M., A. Wiezikova, and M. Svitok. 2010. Effects of secondary succession in abandoned grassland on the activity of ground-foraging ant assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Acta Soc. Zool. Bohem. 74: 153-160
- Wiezik M., A. Wiezikova, and M. Svitok. 2011. Vegetation structure, ecological stability, and low-disturbance regime of abandoned dry grasslands support specific ant assemblages in Central Slovakia. Tuexenia 31: 301315.
- Wieziková A. 2008. Epigaeic activity of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) at hemerobic gradient: arable land green forage permanent grassland. Acta Facultatis Ecologiae 18: 69-76.
- Wu J. 1990. Taxonomic studies on the genus Formica of China (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Forest Research 3: 1-8.
- Yarrow I. H. H. 1954. The British ants allied to Formica fusca L. (Hym., Formicidae). Trans. Soc. Br. Entomol. 11: 229-244.
- Zimmermann, S.. "Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Ameisenfaunader Quarnerischen Inseln." Verhandlungen der Zoologisch-Botanisch Gesellschaft in Wien 80 (1930): 45-66.
- Zina V., M. Branco, and J. C. Franco. 2017. Ant community associated to citrus canopy in Southern Portugal over a century after the invasion by the Argentine ant. Phytoparasitica 45:183–200.
- Zryanin V. A., and T. A. Zryanina. 2007. New data on the ant fauna Hymenoptera, Formicidae in the middle Volga River Basin. Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii 127(2): 226-240.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica en la Cordillera Ibérica." Orsis 6 (1991): 129-126.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica por Andalucia." Boletín de la Estación Central de Ecología 6 (12) (1977): 85-90.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica por Extremadura (España) y Sao Brás-Almodovar, Alcácer do Sal, Serra da Estrela (Portugal)." Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia Suplemento 3(1) (1992): 95-104.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica por las sierras de Aitana-Alfaro y los cabos de la Nao-San Antonio (Alicante) y su comparación con la fauna balear y de Córcega-Cerdeña." Orsis 3 (1988): 165-172.
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Photo Gallery
- North temperate
- North subtropical
- Ant Associate
- Host of Formica sanguinea
- Host of Polyergus rufescens
- Host of Formica exsecta
- Host of Formica pratensis
- Host of Formica rufa
- Host of Lasius flavus
- Aphid Associate
- Host of Acyrthosiphon pisum
- Host of Acyrthosiphon rubi
- Host of Aphis acetosae
- Host of Aphis brotericola
- Host of Aphis craccivora
- Host of Aphis fabae
- Host of Aphis nasturtii
- Host of Aphis pomi
- Host of Aphis solanella
- Host of Aphis spiraecola
- Host of Brachycaudus tragopogonis
- Host of Chaitophorus albus
- Host of Chaitophorus populeti
- Host of Chaitophorus populialbae
- Host of Cinara boerneri
- Host of Cinara palaestinesis
- Host of Cinara pini
- Host of Macrosiphoniella pulvera
- Host of Macrosiphum rosae
- Host of Sipha maydis
- Butterfly Associate
- Host of Zizeeria knysna
- Braconid wasp Associate
- Host of Elasmosoma luxemburgense
- Host of Neoneurus vesculus
- Eucharitid wasp Associate
- Host of Eucharis adscendens
- Trematode Associate
- Host of Dicrocoelium dendriticum
- Host of Dicrocoelium lanceatum
- FlightMonth
- Karyotype
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Formicini
- Formica
- Formica cunicularia
- Formicinae species
- Formicini species
- Formica species
- Ssr