Lasius alienus
| Lasius alienus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Lasiini |
| Genus: | Lasius |
| Section: | niger clade |
| Species group: | alienus |
| Species: | L. alienus |
| Binomial name | |
| Lasius alienus (Foerster, 1850) | |
Common in Europe and Asia, rare in Japan. It shows a preference for habitats that are in open areas such as agricultural fields. It is a common species in Greece where it is known from all provinces. In Achaia and Aetolia-Acarnania, it has been observed in rural sites in tourist resorts, mixed and fir forests and mountain pastures. Nests were located under stones. (Borowiec & Salata, 2021)
| At a Glance | • Limited invasive |
| Common Name | |
|---|---|
| Hime-tobiiro-ke-ari | |
| Language: | Japanese |
| Cornfield Ant | |
| Language: | English |
Identification
Seifert (2020) - Absolute size small (CS 823 µm). Scape length index small, head and maxillary palp length indices medium (SL/ CS900 0.946, CL/CW900 1.069, MP6/CS900 0.181). Number of mandibular dents medium (MaDe900 8.18). Clypeal pubescence moderately dense, intermediate between the situation in the Lasius paralienus and Lasius obscuratus species complexes (sqPDCL900 4.11). Pronotal setae relatively long (PnHL/CS900 0.152). Setae number on hind margin of head low (nOcc900 4.9). Gular setae absent or very few (nGu900 0.8). Dorsum of scape and extensor profile of hind tibia without or with very few semierect setae (nSc900 0.1, nHT900 0.9). The best separation from all other species with reduced scape and tibial pilosity is the strong setae reduction on metapleuron below propodeal spiracle (nSt900 0.3). Frequent coloration: Head, mesosoma, coxae and gaster medium brown; antenna, tibiae and tarsae light yellowish brown; mandibles light reddish brown.
Keys including this Species
- Key to the Lasius of the Indian Himalayas
- Key to Lasius Palaearctic workers
- Key to Lasius males
- Key to Lasius queens
- Key to Europe and Asia Minor Lasius alienus group species
- Key to New England Lasius
- Key to Palaearctic Lasius s. str.
- Key to Palaearctic Lasius subgenus Lasius s. st.
- Key to Lasius species of the subgenus Lasius of Greece
Distribution
This species occurs throughout Europe and Asia, from the British Isles and Scandinavia south to Morocco and Tunisia, east into Lebanon, northern Iraq, and southern China, and north into Russia, Central Asia, China, and Japan (Ellison et al., 2012). Recorded from Japan since the early 20th century (e.g. Wheeler, 1906; Teranishi 1915, 1930; Morisita,1945; Japanese Ant Image Database).
Lasius alienus was recorded from all Greek provinces but due to the recent revision of this genus (Seifert, 2020) its historical records should be reinvestigated (Borowiec et al., 2022).
Long believed to be a holartic species, Schar et al 2018 showed that North American collections once properly identified as Lasius alienus should be referred to Lasius americanus.
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 67.216667° to 22.952079°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Oriental Region: India, Pakistan.
Palaearctic Region: Albania, Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Channel Islands, China, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany (type locality), Greece, Hungary, Iberian Peninsula, Iran, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Mongolia, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkmenistan, Türkiye, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
This name had long been applied to a morphologically similar North American form Lasius americanus (Schär et al. 2018).
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
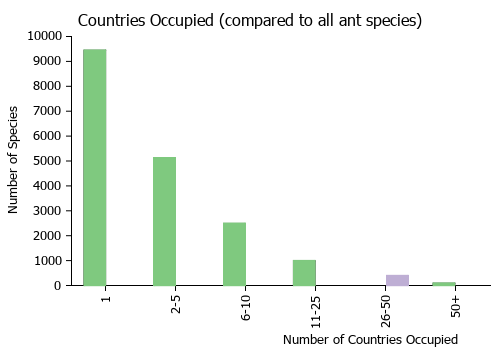
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
|
Habitat
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - In Greece, common species, inhabits a wide variety of habitats from sea level to 1590 m a.s.l. Observed in open areas inside tourist resorts, urban ruderal areas, on roadsides with bushes, on pastures, olive plantations, all types of forests, on higher altitudes in coniferous forests and on pastures with shrubs.
Also see Wilson 1955 (under the Biology heading, just below, on this webpage)
Biology
Wilson (1955) - In North Africa and France (Bernard, 1950; Scherdlin, 1909), Ireland (O’Rourke, 1950), England (Diver, 1940), Germany (Gosswald, 1932), East Prussia (Skwarra, 1929), and Daghestan (Kuznetzov-Ugamskij, 1929), Lasius alienus typically inhabits open dry situations, nesting under stones and occasionally constructing crater entrances in open soil. It shows much less latitude in nesting sites than its sister species Lasius niger, but is more successful in cultivated areas. Bernard notes that in France it is able to replace niger entirely in pastures, even at high elevations, but tends to give way in turn to Tapinoma simrothi and Tapinoma nigerrimum. Diver, in an intensive study of the comparative ecology of alienus and niger in a local area in Dorset, found alienus restricted mostly to dry heath, whereas niger occurred in every major habitat studied. In Daghestan, Kutznezov-Ugamskij found alienus to have more southern affinities than niger. Where the two occur together, alienus is limited mostly to the steppes and mountain meadows (up to 11,000 feet), while niger occurs mostly in the forests.
In Eurasia alienus is replaced in most habitats, including woodland, by its extremely successful and abundant sister species Lasius niger.
Lasius alienus probably does not differ much from niger in food habits and ethology. Several Europeans, including Gosswald and O'Rourke have independently observed that alienus tends to be the more secretive of the two species. This is possibly correlated with the preference of this species in Eurasia for more exposed situations.
Records of nuptial flights in this species are too sparse to allow a rigorous comparison with niger. In Europe winged forms are found in nido during about the same period as for niger. I have records ranging from June (Trieste, MCZ; no further date) to October 28 (Italy, MCZ) without evident preponderance during any part of this period; a single pair were preserved in copula in October (Trieste; MCZ; no further date).
Regional Notes
Europe
Guiliani et al. (2019) observed this species foraging on extrafloral nectaries of the invasive Reynoutria x bohemica (Polygonaceae) in Tuscany. The habitats examined were river banks and disturbed habitats.
Collingwood (1979) - This wide ranging species nests in the soil on sandy lowland heaths, dry open pasture, sea cliffs and rocky outcrops in North Europe. Its habits are mainly subterranean, feeding on the exudates of root aphids but also by scavenging and predating small insects. Workers are generally unobtrusive and non aggressive compared with Lasius niger. Nests are single queened founded by solitary fertilised queens. Mating swarms occur in August.
Flight Period
| X | X | X | |||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Source: antkeeping.info.
- Check details at Worldwide Ant Nuptial Flights Data, AntNupTracker and AntKeeping.
 Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Other Insects
- This species is a host for the temporary parasites Lasius carniolicus (de la Mora et al., 2021; Janda et al., 2004; Seifert, 2018; unconfirmed), Lasius claviger, Lasius distinguendus, Lasius interjectus, Lasius jensi, Lasius latipes, Lasius meridionalis (unconfirmed), Lasius reginae and Lasius umbratus (unconfirmed).
- This species is associated with the aphids Aphis fabae, Aphis galliiscabri, Aphis gossypii, Aphis idaei, Aphis maidi-radicis, Aphis molluginis, Aphis nasturtii, Aphis pomi, Aphis pseudocardui, Aphis solanella, Aphis urticata, Aphis verbasci, Brachycaudus (Appelia) tragopogonis, Brachycaudus cardui, Capitophorus hippophaes, Chaitophorus kapuri, Cinara atlantica, Cinara palaestinesis, Cinara pini, Dysaphis foeniculus, Dysaphis pyri, Myzus cerasi, Neobetulaphis pusilla, Periphyllus bulgaricus, Rhopalosiphum cerasifoliae, Rhopalosiphum maidis, Rhopalosiphum nymphaeae, Sipha maydis and Toxoptera aurantii (Saddiqui et al., 2019 and included references).
- This ant has been associated with the butterflies Glaucopsyche alexis and a species that has recently been split into two species: Polyommatus icarus and Polyommatus celin (Obregon et al. 2015).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon buccatus (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon rileyi (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the phorid fly Pseudacteon formicarum (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the tachinid fly Strongylogaster globula (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a prey for the Microdon fly Microdon ruficrus (a predator) (Quevillon, 2018).
Mites
- This species is a host for the mite Imparipes obsoletus (a parasite) (Khaustov, 2015) (ectoparasite).
- This species is a host for the mite Petalomium carelitschensis (a parasite) (Khaustov, 2015) (ectoparasite).
- This species is a host for the mite Scutacarus longisetus (a parasite) (Khaustov, 2015) (ectoparasite).
Nematode
- This species is a host for the nematode "Mermis" (a parasite) in England (Oxford, Cornwal) (Crawley & Baylis, 1921).
- This species is a host for the nematode Mermithidae (unspecified "Mermix") (a parasite) in Germany (Wuerzburg) (Gösswald, 1938; Laciny, 2021).
- This species is a host for the nematode Mermis myrmecophila (a parasite) in Germany (Gosswald, 1929; Laciny, 2021).
Fungi
- This species is a host for the fungus Laboulbenia formicarum (a parasite) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission within nest).
- This species is a host for the fungus Laboulbenia formicarum (a pathogen) (Espadaler & Santamaria, 2012).
The reported host/parasite relationship between Lasius distinguendus and Lasius alienus as reported by Janda et al. (2004) should be investigated in the field as Seifert (2018) could not corroborated this relationship (de la Mora et al., 2021).
Reports of Lasius fuliginosus invading Lasius alienus nests (Janda et al., 2004) are unlikely based on biology (Seifert, pers. comm., in de la Mora et al., 2021).
Reports of Lasius mixtus invading Lasius alienus nests (Janda et al., 2004) are a possible misidentification of the host due to subsequent taxonomic revision (de la Mora et al., 2021).
Life History Traits
- Queen number: monogynous (Frumhoff & Ward, 1992)
Castes
Queen
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0173158. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Male
Images from AntWeb
     
| |
| Worker. Specimen code casent0172725. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- alienus. Formica aliena Foerster, 1850a: 36 (w.m.) GERMANY.
- Foerster, 1850a: 71 (q.); Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1953c: 147 (l.); Hauschteck, 1962: 219 (k.).
- Combination in Lasius: Mayr, 1861: 49 (in key);
- Combination in Lasius (Lasius): Ruzsky, 1912: 633; Forel, 1915d: 53; Wheeler, W.M. 1916k: 172; Karavaiev, 1936: 205;
- Combination in Donisthorpea: Donisthorpe, 1915d: 212;
- Combination in Formicina (Donisthorpea): Emery, 1916b: 240;
- Combination in Formicina: Bondroit, 1918: 25;
- Combination in Lasius (Donisthorpea): Nadig, 1918: 340;
- Combination in Acanthomyops: Ruzsky, 1925b: 44;
- Combination in Acanthomyops (Donisthorpea): Betrem, 1926: 215; Donisthorpe, 1927a: 8; Donisthorpe, 1950e: 1063;
- Combination in Lasius: Ruzsky, 1916: 5; Wheeler, W.M. 1917i: 463; Menozzi, 1921: 32; Müller, 1923b: 125; Emery, 1925b: 230; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1929a: 27.
- Combination in Lasius (Lasius): Wilson, 1955a: 77.
- Subspecies of niger: Forel, 1874: 46 (in key); Mayr, 1877: 20 (in list); Emery & Forel, 1879: 452; Mayr, 1886d: 429; Forel, 1886e: clxvii; Provancher, 1887: 236 (in key); Cresson, 1887: 255; Forel, 1889: 256; Forel, 1890a: lxvii; Emery, 1891b: 16; Forel, 1892i: 307; Lameere, 1892: 64; Emery, in Dalla Torre, 1893: 187 (footnote); Forel, 1894c: 404; Forel, 1894d: 12; Ruzsky, 1896: 71; Saunders, E. 1896: 25; Ruzsky, 1902a: 233; Ruzsky, 1903b: 306; Forel, 1904b: 386; Ruzsky, 1905b: 304; Wheeler, W.M. 1906c: 322; Forel, 1906b: 85; Forel, 1906c: 189; Wasmann, 1906: 114 (in key); Forel, 1909c: 105; Yano, 1910: 421; Bondroit, 1910: 485; Forel, 1910a: 23; Karavaiev, 1910a: 268; Forel, 1911d: 352; Karavaiev, 1912b: 588; Krausse, 1912b: 165; Forel, 1913d: 438; Ruzsky, 1914a: 61; Stitz, 1914: 84; Emery, 1914d: 159; Ruzsky, 1915a: 434; Forel, 1915d: 53 (in key); Emery, 1916b: 240; Ruzsky, 1916: 5; Wheeler, W.M. 1916k: 172; Escherich, 1917: 332 (in key); Wheeler, W.M. 1917a: 525; Wheeler, W.M. 1917i: 463; Nadig, 1918: 340; Santschi, 1919e: 246; Menozzi, 1921: 32; Menozzi, 1922b: 331; Soudek, 1922: 69; Kulmatycki, 1922: 80; Finzi, 1923: 4; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1923: 243; Emery, 1925b: 230; Ruzsky, 1925a: 288; Ruzsky, 1925b: 44; Santschi, 1925g: 349; Soudek, 1925b: 16; Santschi, 1926f: 289; Menozzi, 1926b: 182; Karavaiev, 1927a: 300; Karavaiev, 1927c: 280 (in key); Karavaiev, 1927d: 347; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1927e: 188; Menozzi, 1927b: 91; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1928b: 20; Lomnicki, 1928: 8; Wheeler, W.M. 1928c: 38; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1929a: 27; Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1929b: 37; Karavaiev, 1930b: 147; Wheeler, W.M. 1930h: 80; Karavaiev, 1931e: 214; Soudek, 1931: 13; Gösswald, 1932: 57; Menozzi, 1932b: 311; Wheeler, W.M. 1932a: 16; Arnol’di, 1933b: 603 (in key); Grandi, 1935: 103; Karavaiev, 1935b: 108; Menozzi, 1936d: 305; Karavaiev, 1936: 205 (redescription); Karavaiev, 1937: 175; Menozzi, 1939a: 312; Morisita, 1945: 22; Ruzsky, 1946: 69; Azuma, 1951: 88; Smith, M.R. 1951a: 850; Chapman & Capco, 1951: 202; Azuma, 1953: 4; Azuma, 1955: 80; Ceballos, 1956: 316.
- Status as species: Schenck, 1852: 51; Mayr, 1855: 360 (redescription); Nylander, 1856b: 68; Gredler, 1858: 13; Smith, F. 1858b: 7; Mayr, 1861: 49 (in key); Roger, 1861b: 165; Roger, 1863b: 11; Mayr, 1863: 425; Smith, F. 1871b: 2; André, 1874: 180 (in key); Mayr, 1877: 6; Emery, 1878b: 47; Saunders, E. 1880: 209; Mayr, 1880: 26; André, 1882b: 192 (in key); White, W.F. 1884: 255; Nasonov, 1889: 22; Emery, 1891b: 16; Dalla Torre, 1893: 181; Emery, 1897f: 238; Ruzsky, 1902d: 16; Ruzsky, 1903c: 207; Bingham, 1903: 342; Viehmeyer, 1906: 56; Emery, 1908d: 24; Bondroit, 1911: 11; Donisthorpe, 1915d: 212; Bondroit, 1918: 25; Crawley, 1920b: 177; Müller, 1923a: 74; Müller, 1923b: 125; Lomnicki, 1925b: 3; Betrem, 1926: 215; Stärcke, 1926: 124 (in key); Donisthorpe, 1927a: 8; Donisthorpe, 1927b: 242; Finzi, 1933: 165; Stitz, 1934: 9; Zimmermann, 1935: 48; Ruzsky, 1936: 90; Finzi, 1939c: 160; Stitz, 1939: 279; Novák & Sadil, 1941: 101 (in key); Röszler, 1942a: 53; Stärcke, 1944a: 153; van Boven, 1947: 186 (in key); Arnol'di, 1948: 212 (in list); Creighton, 1950a: 419; Röszler, 1951: 91; Consani & Zangheri, 1952: 44; Wilson, 1955a: 77 (redescription); Bernard, 1956b: 261; Bernard, 1959: 351; Dlussky, 1962: 182; Baroni Urbani, 1964a: 7; Baroni Urbani, 1964b: 63; Baroni Urbani, 1964c: 166; Cagniant, 1964: 92; Cagniant, 1966b: 281; Bernard, 1967: 356 (redescription); Baroni Urbani, 1968b: 488; Cagniant, 1968a: 146; Kutter, 1968a: 61; Baroni Urbani, 1969a: 334; Collingwood & Yarrow, 1969: 79; Pisarski, 1969a: 231; Pisarski, 1969b: 306; Dlussky & Pisarski, 1970: 87; Cagniant, 1970c: 38; Baroni Urbani, 1971c: 200; Bourne, 1973: 24; Pisarski, 1975: 34; Tarbinsky, 1976: 138 (redescription); Collingwood, 1976: 305; Aktaç, 1977: 126; Azuma, 1977: 117; van Boven, 1977: 144; Kutter, 1977c: 227; Arnol’di & Dlussky, 1978: 555 (in key); Collingwood, 1978: 89 (in key); Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1978: 393; Smith, D.R. 1979: 1435; Collingwood, 1979: 97; Yamauchi, 1979: 156; Pisarski & Krzysztofiak, 1981: 160; Schembri & Collingwood, 1981: 438; Collingwood, 1981: 27; Allred, 1982: 479; Collingwood, 1982: 285; Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1986g: 65; Agosti & Collingwood, 1987b: 282 (in key); Nilsson & Douwes, 1987: 70; DuBois & LaBerge, 1988: 149; Deyrup, et al. 1989: 99; Kupyanskaya, 1990: 218; Dlussky, Soyunov & Zabelin, 1990: 159; Casevitz-Weulersse, 1990c: 428; Morisita, et al. 1991: 27; Wu, J. & Wang, 1992: 1312; Atanassov & Dlussky, 1992: 237; Seifert, 1992b: 13 (redescription); Arakelian, 1994: 116; Radchenko, 1994b: 115 (in key); Douwes, 1995: 94; Bolton, 1995b: 221; Wu, J. & Wang, 1995: 155; Tang, Li, et al. 1995: 108; Collingwood & Prince, 1998: 23 (in key); Czechowski, et al. 2002: 105; Mackay & Mackay, 2002: 379; Deyrup, 2003: 45; Imai, et al. 2003: 63; Coovert, 2005: 120; Csösz, & Markó, 2005: 230; Karaman, G.S. & Karaman, 2005: 56; MacGown & Forster, 2005: 64; Bračko, 2006: 148; Bračko, 2007: 20; Seifert, 2007: 272; Werner & Wiezik, 2007: 153; Zryanin & Zryanina, 2007: 234; Gratiashvili & Barjadze, 2008: 136; Casevitz-Weulersse & Galkowsky, 2009: 483; Lapeva-Gjonova, et al. 2010: 35; Boer, 2010: 42; Csösz, et al. 2011: 58; Legakis, 2011: 26; Borowiec, L. & Salata, 2012: 498; Czechowski, et al. 2012: 263; Ellison, et al. 2012: 189; Borowiec, L. 2014: 83; Seifert & Galkowski, 2016: 52 (in key); Radchenko, 2016: 362; Deyrup, 2017: 206; Schar et al., 2018: 6.
- Senior synonym of pannonica: Wilson, 1955a: 77; Radchenko, 2016: 362.
- Material of the unavailable names alienoamericanus, flavidus, turkmenus referred here by Wilson, 1955a: 77.
Type Material
- Neotype worker plus 10 workers from the neotype nest labelled GER: Eifel, 7.9. 1991, 37 km SE Aachen, Schleiden ; depositories SMN Görlitz, BMNH London (Seifert, 2020).
Wilson (1955) - Dr. H. Bischoff has informed me that no syntypes of Lasius alienus can be located in the Foerster Collection in the Berlin Museum. What may be part of the type series has been found instead in the Mayr Collection and lent me by Dr. M. Beier. This consists of two pins, one holding two workers and the other a single male, labelled "Aach. Forst/Las. alienus det. Mayr." The workers are identifiable as typical alienus.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Wilson (1955) - Within the PW range of 0.53-0.70 mm., the seta count is always less than 20 and usually less than 10. The seta count is strongly allometric, making it advisable to determine individual specimens by comparing them with the regression zones of Figure 6. In Europe the regression zones of Lasius niger and Lasius alienus are parallel but well segregated; the alienus line is set so that the great majority of workers have seta counts of less than 5, while most niger exceed 20. In eastern Asia, on the other hand, alienus evidently becomes scarcer, and the niger zone shifts down and forward to become contiguous with that of alienus. As a result, a small number of individuals cannot be safely determined to either species.
Size ranging and averaging smaller than in niger. In a sample of 147, with no more than 2 per nest series, mean with standard error 0.56 ± 0.004 mm., standard deviation 0.054 mm, Color averaging lighter than niger, although total variation in both species shows complete overlap.
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - Small to moderately large, HL 0.742-1.035 (mean 0.836), HW 0.663-0.977 (mean 0.807), ML 0.80-1.06. Scape moderately elongate, SL 0.684-0.926 (mean 0.788). Color. Body unicolor with head, mesosoma, coxae and gaster medium brown. Antennae, tibiae and tarsi light yellowish brown, mandibles light reddish brown. Sometimes whole body and appendages are yellowish brown. Structure and setation. Head oval, always longer than wide, lateral surfaces above eyes convex, occipital margin of head straight to slightly concave. Occipital part of head with less than 15 (usually 8-12) erected setae, ventral part of head lacking erected setae, mesosomal dorsum with numerous, long erected setae. Below propodeal spiracle usually no erected setae or at most single short seta. Mandibles usually with 8 dents. Antennal scapi with smooth pubescence lacking erected setae, at most with few semierect hair, hind tibiae lacking erected setae or at most with 1-2, occasionally 3-4, short setae in basal part. Ventral surface of fore femora with 4-6 and mid femora 2-4 erected setae, of hind femora without or 1-2 setae close to base of femur, anterior surface of fore coxa with several long erected setae. Pubescence on the whole body with rather dense, appressed pubescence, surface with weak microreticulation, appears rather shining. Pubescence of clypeus dense, not as dense as in Lasius paralienus or Lasius bombycina but denser than in Lasius psammophilus or Lasius creticus. First gastral tergite on the whole surface with numerous erected setae. Propodeum in lateral view with straight anterior and posterior surface, conical and equal in height or slightly higher to mesonotum, metanotal groove deep.
Queen
Wilson (1955) - Seta count never exceeding 10 and usually 0.
Size averaging smaller than niger when the North American populations are included.
Male
Wilson (1955) - Seta count almost always 0.
Size range about the same as in Lasius niger and showing parallel geographic variation. Mandibles typically of niger type, but in two series (Engadin, Switzerland, Kutter leg. and Coll., Hornet, Beltrami Co., Minn., A. Achenbach leg., G. C. Wheeler Coll.) the mandible type is closer to the intermediate type of Lasius brunneus. Subgenital plate showing the same wide variation as in Lasius niger; series from Godinne, Belgium (A. Raignier leg.; MCZ) and the Engadin Valley, Switzerland (Kutter) encompass within themselves the full variation from the unilobed to bilobed condition.
Karyotype
- See additional details at the Ant Chromosome Database.
 Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- n = 15, 2n = 30 (Germany; Switzerland) (Hauschteck-Jungen & Jungen, 1983) (n=14 was also reported, Lorite and Palomeque 2010 suggested that such karyotype is due Robertsonian polymorphism).
- 2n = 28 (Switzerland) (Hauschteck, 1962).
Worker Morphology
 Explore: Show all Worker Morphology data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Worker Morphology data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
References
- Seifert, B. 1992b. A taxonomic revision of the Palaearctic members of the ant subgenus Lasius s.str. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Abh. Ber. Naturkundemus. Görlitz 66(5): 1-67.
- Alatorre-Bracamontes, C.E., Vásquez-Bolaños, M. 2010. Lista comentada de las hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) del norte de México. Dugesiana 17(1): 9-36.
- André, E. 1882c. Les fourmis. [part]. Pp. 153-232 in: André, Edm. 1881-1886. Species des Hyménoptères d'Europe et d'Algérie. Tome Deuxième. Beaune: Edmond André, 919 + 48 pp. (page 192, Status as species)
- Atanassov, N.; Dlussky, G. M. 1992. Fauna of Bulgaria. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Fauna Bûlg. 22: 1-310 (page 237, Status as species)
- Baer, B. 2011. The copulation biology of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 14: 55-68.
- Baroni Urbani, C. 1971c. Catalogo delle specie di Formicidae d'Italia (Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia X). Memorie della Societa Entomologica Italiana 50: 5-287 (page 200, Status as species)
- Bernadou, A., Fourcassié, V., Espadaler, X. 2013. A preliminary checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Andorra. ZooKeys 277, 13–23 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.277.4684).
- Bondroit, J. 1911a. Contribution à la faune de Belgique. Notes diverses. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 55: 8-13 (page 11, Status as species)
- Bondroit, J. 1918. Les fourmis de France et de Belgique. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 87: 1-174 (page 25, Status as species)
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec, L., Lebas, C., Salata, S. 2022. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from three northern Aegean islands – Lemnos, Samothraki and Thasos. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 31: 1-14 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.7346453).
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2017. First certain record of Lasius alienus (F RSTER, 1850) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and three ant species new to the Republic of Macedonia. Acta Entomologica Silesiana 25(online 019): 1–4.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2021. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Western Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 30: 1-23 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.5571258).
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. A monographic review of ants of Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Vol. 1. Introduction and review of all subfamilies except the subfamily Myrmicinae. Part 1: text. Natural History Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum 1: 1-297.
- Borowiec, L., van Delft, J.P.L., van Delft, J.J.C.W., Salata, S. 2023. Five ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) new to the Greek fauna with notes on ants from Greek Thrace. Annales of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 32 (online 008), 1-13 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.10101028).
- Borowiec, L., Wieczorek, K., Salata, S. 2021. Review of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Dodecanese Archipelago, Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 30: 1-33 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.5571270).
- Boudinot, B.E., Borowiec, M.L., Prebus, M.M. 2022. Phylogeny, evolution, and classification of the ant genus Lasius, the tribe Lasiini and the subfamily Formicinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Systematic Entomology 47, 113-151 (doi:10.1111/syen.12522).
- Bulter, I. 2020. Hybridization in ants. Ph.D. thesis, Rockefeller University.
- Carroll, T.M. 2011. The ants of Indiana (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). M.S. thesis, Purdue University.
- Catarineu, C., Barberá, G.G., Reyes-López, J.L. 2018. Zoogeography of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of southeastern Iberian Peninsula. Sociobiology 65, 383-396 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v65i3.2822).
- Chick, L.D., Lessard, J.-P., Dunn, R.R., Sanders, N.J. 2020. The coupled influence of thermal physiology and biotic interactions on the distribution and density of ant species along an elevational gradient. Diversity 12, 456 (doi:10.3390/d12120456).
- Collingwood, C. A. 1979. The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Fauna Entomol. Scand. 8: 1-174 (page 97, Status as species)
- Collingwood, C. A. 1982. Himalayan ants of the genus Lasius (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Syst. Entomol. 7: 283-296 (page 285, Status as species)
- Crawley, W.C., Baylis, H.A. 1921. Mermis parasitic on ants of the genus Lasius. Journal of the Royal Microscopy Society 257: 353–72 (doi:10.1111/j.1365-2818.1921.tb01370.x).
- Csősz, S., Báthori, F., Gallé, L., Lőrinczi, G., Maák, I., Tartally, A., Kovács, É., Somogyi, A.Á., Markó, B. 2021. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: Survey of ant species with an annotated synonymic inventory. Insects 16;12(1):78 (doi:10.3390/insects12010078).
- Csosz, S., Marko, B., Galle, L. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A., Czechowska, W. 2002. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Poland. MIZ PAS Warsaw.
- Davis, T. 2009. The ants of South Carolina (thesis, Clemson University).
- Dekoninck, W., Ignace, D., Vankerkhoven, F., Wegnez, P. 2012. Verspreidingsatlas van de mieren van België. Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 148: 95-186.
- Donisthorpe, H. 1915f. British ants, their life-history and classification. Plymouth: Brendon & Son Ltd., xv + 379 pp. (page 212, Combination in Donisthorpea, Status as species)
- Dubovikoff, D.A., Yusupov, Z.M. 2017. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Dušátková, L.P., Pekár, S., Michálek, O., Líznarová, E., Symondson, W.O.C. 2020. Estimation of trophic niches in myrmecophagous spider predators. Scientific Reports 10: 8683 (doi:10.1038/s41598-020-65623-8).
- Ellison, A.M., Gotelli, N.J., Farnsworht, E.J., Alpert, G.D. 2012. A Field Guide to the Ants of New England. Yale University Press, 256 pp.
- Emery, C. 1897g. Anhang. Verzeichniss der auf der zweiten Reise nach Kleinasien (1897) gesammelten Ameisen, mit einer Neubeschreibung. P. 239 in: Escherich, K. Zur Kenntniss der Myrmecophilen Kleinasiens. I. Coleoptera. Wien. Entomol. Ztg. 16:229-239. (page 238, Status as species)
- Emery, C. 1908e. [Untitled. Descriptions of new taxa: Tetramorium caespitum var. diomedea Emery, nova varietas; Strongylognathus huberi For., subsp. rehbinderi For., var. cecconii Emery, nova varietas.]. P. 24 in: Cecconi, G. Contributo alla fauna delle Isole Tremiti. Boll. Mus. Zool. Anat. Comp. R. Univ. Torino 583:1-53. (page 24, status as species)
- Emery, C. 1916a [1915]. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 47: 79-275 (page 240, Combination in Formicina, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Emery, C. 1925d. Hymenoptera. Fam. Formicidae. Subfam. Formicinae. Genera Insectorum 183: 1-302 (page 230, Combination in Lasius)
- Espadaler, X., Santamaria, S. 2012. Ecto- and Endoparasitic Fungi on Ants from the Holarctic Region. Psyche Article ID 168478, 10 pages (doi:10.1155/2012/168478).
- Fairweather, A.D., Lewis, J.H., Hunt, L., Smith, M.A., McAlpine, D.F. 2020. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Rockwood Park, New Brunswick: An assessment of species richness and habitat. Northwestern Naturalist 27(3):576–584.
- Foerster, A. 1850a. Hymenopterologische Studien. 1. Formicariae. Aachen: Ernst Ter Meer, 74 pp. (page 36, worker, male described; page 71, queen described)
- Forel, A. 1874. Les fourmis de la Suisse. Systématique, notices anatomiques et physiologiques, architecture, distribution géographique, nouvelles expériences et observations de moeurs. Neue Denkschr. Allg. Schweiz. Ges. Gesammten Naturwiss. 26: 1-452 (page 46, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Forel, A. 1892j. Die Ameisenfauna Bulgariens. (Nebst biologischen Beobachtungen.). Verh. K-K. Zool.-Bot. Ges. Wien 42: 305-318 (page 307, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Forel, A. 1904c [1903]. Note sur les fourmis du Musée Zoologique de l'Académie Impériale des Sciences à St. Pétersbourg. Ezheg. Zool. Muz. 8: 368-388 (page 386, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Forel, A. 1913d. Fourmis de la faune méditerranéenne récoltées par MM. U. et J. Sahlberg. Rev. Suisse Zool. 21: 427-438 (page 438, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Forel, A. 1915d. Fauna insectorum helvetiae. Hymenoptera. Formicidae. Die Ameisen der Schweiz. Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 12(B Beilage: 1-77 (page 53, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Gallé, L. 2017. Climate change impoverishes and homogenizes ants’ community structure: a long term study. Community Ecology 18: 128–136 (doi:10.1556/168.2017.18.2.2).
- Giuliani, C., L. Lastrucci, L. Cresti, G. Santini, B. Fogg, and M. M. Lippi. 2019. The morphology and activity of the extrafloral nectaries in Reynoutria x bohemica (Polygonaceae). Plant Biology. 21:975-985. doi:10.1111/plb.13004
- Gochnour, B.M., Suiter, D.R., Booher, D. 2019. Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) fauna of the Marine Port of Savannah, Garden City, Georgia (USA). Journal of Entomological Science 54, 417-429 (doi:10.18474/jes18-132).
- Gösswald, K. 1929. Mermithogynen von Lasius alienus, gefunden in der Umgebung von Würzburg. Zoologischer Anzeiger 84: 202-204.
- Gösswald, K. 1938. Über bisher unbekannte, durch den Parasitismus der Mermithiden (Nemat.) verursachte Formveränderungen bei Ameisen. Parasitology Research 10: 138-152.
- Hauschteck, E. 1962. Die Chromosomen einiger in der Schweiz vorkommender Ameisenarten. Vierteljahrsschr. Naturforsch. Ges. Zür. 107: 213-220 (page 219, karyotype described)
- Higgins, R. J. and B. S. Lindgren. 2015. Seral changes in ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) assemblages in the sub-boreal forests of British Columbia. Insect Conservation and Diversity. 8:337-347. doi:10.1111/icad.12112
- Imai, H.T., Kihara, A., Kondoh, M., Kubota, M., Kuribayashi, S., Ogata, K., Onoyama, K., Taylor, R.W., Terayama, M., Yoshimura, M., Ugawa, Y. 2003. Ants of Japan. 224 pp, Gakken, Japan.
- Ipser, R.M., Brinkman, M.A., Gardner, W.A., Peeler, H.B. 2004. A survey of ground-dwelling ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Georgia. Florida Entomologist 87: 253-260.
- Ivanov, K. 2019. The ants of Ohio (Hymenoptera, Formicidae): an updated checklist. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 70: 65–87 (doi:10.3897@jhr.70.35207).
- Jacobs, S. 2020. Population genetic and behavioral aspects of male mating monopolies in Cardiocondyla venustula (Ph.D. thesis).
- Jansen, G., Savolainen, R. 2010. Molecular phylogeny of the ant tribe Myrmicini (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 160(3), 482–495 (doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00604.x).
- Jansen, G., Savolainen, R., Vepsäläinen, K. 2010. Phylogeny, divergence-time estimation, biogeography and social parasite–host relationships of the Holarctic ant genus Myrmica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 561, 294–304 (doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.01.029).
- Kar, S., Akyildiz, G., Sirin, D., Rodriguez, S.E., Camlitepe, Y. 2021. First evidence of predation of the ant species Lasius alienus on the poultry red mite Dermanyssus gallinae. Acarologia 61, 115–120 (doi:10.24349/ACAROLOGIA/20214420).
- Karaman, C., Kiran, K. 2022. Additional records of parasitic Camponotus Mayr (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species from Turkey with queen description of Camponotus ruseni Karaman, 2012. Zoology in the Middle East 68(2), 156–164 (doi:10.1080/09397140.2022.2051918).
- Karavaiev, V. 1927d. The ant fauna of Ukraine. Zb. Prats Zool. Muz. 2:1-52 [= Tr. Ukr. Akad. Nauk Fiz.-Mat. Vidd. 4:247-296] (page 280, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Khaustov, A.A. 2015. Myrmecophilous pygmephoroid mites (Acari: Pygmephoroidea) associated withLasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Western Siberia, Russia. International Journal of Acarology 42(2): 92–105 (doi:10.1080/01647954.2015.1124921).
- Khudadad, S., Rafi, M.A., Zia, A., Khan, M.S., Parveen, G., Sheikh, M.K., Naz, F., Qasim, M., Shah, S.W. 2021. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of District Mansehra, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Research 34: 664-671 (doi:10.17582/journal.pjar/2021/34.3.664.671).
- Kim, G., Lyu, D. 2012. Distribution of Ants (Insecta, Hymenoptera) in Chiaksan Mountain, Prov. Gangweon, Korea. Journal of Korean Nature 5, 127–129 (doi:10.7229/jkn.2012.5.2.127).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C. 2020. Additions to the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoosystema 42(18), 285-329 (doi:10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a18).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C., Heinze, J. 2021. First record of the inquiline ant Leptothorax kutteri Buschinger, 1965 from Turkey. Sociobiology 68, e7224 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v68i3.7224).
- Kirchmair, G., Friess, T. et al. 2017. Zoologischer Bericht vom Tag der Biodiversität 2017 im Naturpark Südsteiermark. Mitteilungen des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereines für Steiermark 147: 99–134.
- Kök, Ş., Aktaç, N., Kasap, I. 2021. Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) ‐ aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) interactions in different habitats from Turkey with new mutualistic associations. Agricultural and Forest Entomology 12477 (doi:10.1111/afe.12477).
- Kupyanskaya, A. N. 1990a. Ants of the Far Eastern USSR. Vladivostok: Akademiya Nauk SSSR, 258 pp. (page 218, Status as species)
- Kutter, H. 1977c. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Insecta Helv. Fauna 6: 1-298 (page 227, Status as species)
- Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, N. N. 1929a. Die Ameisen des Süd-Ussuri-Gebietes. Zool. Anz. 83: 16-34 (page 27, Combination in Lasius)
- Laciny, A. 2021. Among the shapeshifters: parasite-induced morphologies in ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) and their relevance within the EcoEvoDevo framework. EvoDevo 12, 2 (doi:10.1186/s13227-021-00173-2).
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Antonova, V., Ljubomirov, T. 2021. Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Sarnena Sredna Gora Mountains (Bulgaria). Fauna of Sarnena Sredna Gora Mts, Part 2 ZooNotes, Supplement 10: 18-27.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Borowiec, L. 2022. New and little-known ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Bulgaria. Biodiversity Data Journal, 10: e83658 (doi:10.3897/bdj.10.e83658).
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Kiran, K. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Strandzha (Istranca) Mountain and adjacent Black Sea coast. North-Western Journal of Zoology 8(1), 72-84.
- Lebes, C., Galkowski, C. 2021. Description de la reine et du mâle de Lasius casevitzi Seifert & Galkowski, 2016 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Linn. Bordeaux 156, nouv. série n° 49 (4): 386-390.
- Liu, C., Fischer, G., Hita Garcia, F., Yamane, S., Liu, Q., Peng, Y.Q., Economo, E.P., Guénard, B., Pierce, N.E. 2020. Ants of the Hengduan Mountains: a new altitudinal survey and updated checklist for Yunnan Province highlight an understudied insect biodiversity hotspot. ZooKeys 978, 1–171 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.978.55767).
- MacGown, J.A., Booher, D., Richter, H., Wetterer, J.K., Hill, J.G. 2021. An updated list of ants of Alabama (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with new state records. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 147: 961-981 (doi:10.3157/061.147.0409).
- Mackay, W. P. and E. Mackay. 2002. The ants of New Mexico (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Edwin Mellen Press, Lewiston, NY.
- Mayr, G. 1861. Die europäischen Formiciden. Nach der analytischen Methode bearbeitet. Wien: C. Gerolds Sohn, 80 pp. (page 49, Combination in Lasius)
- Mayr, G. 1886d. Die Formiciden der Vereinigten Staaten von Nordamerika. Verh. K-K. Zool.-Bot. Ges. Wien 36: 419-464 (page 429, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Menozzi, C. 1921. Formiche dei dintorni di Sambiase di Calabria. Boll. Lab. Zool. Gen. Agrar. R. Sc. Super. Agric. 15: 24-32 (page 32, Combination in Lasius)
- Menozzi, C. 1936b. Nuovi contributi alla conoscenza della fauna delle Isole italiane dell'Egeo. VI. Hymenoptera - Formicidae. Boll. Lab. Zool. Gen. Agrar. R. Sc. Super. Agric. 29: 262-311 (page 305, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Menozzi, C. 1939a. Formiche dell'Himalaya e del Karakorum raccolte dalla Spedizione italiana comandata da S. A. R. il Duca di Spoleto (1929). Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 78: 285-345 (page 312, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Moura, M.N., Cardoso, D.C., Cristiano, M.P. 2020. The tight genome size of ants: diversity and evolution under ancestral state reconstruction and base composition. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, zlaa135 (doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa135).
- Müller, G. 1923b. Le formiche della Venezia Guilia e della Dalmazia. Boll. Soc. Adriat. Sci. Nat. Trieste 28: 11-180 (page 125, Combination in Lasius)
- Nasonov, N. V. 1889. Contribution to the natural history of the ants primarily of Russia. 1. Contribution to the ant fauna of Russia. Izv. Imp. Obshch. Lyubit. Estestvozn. Antropol. Etnogr. Imp. Mosk. Univ. 58: 1-78 (page 22, Status as species)
- Német, E., Czekes, Z., Markó, B., Rákosy, L. 2016. Host plant preference in the protected myrmecophilous Transylvanian Blue (Pseudophilotes bavius hungarica) butterfly (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) and its relationship with potential ant partners. Journal of Insect Conservation 20, 765–772 (doi:10.1007/S10841-016-9907-5).
- Novák, V.; Sadil, J. 1941. Klíc k urcování mravencu strední Evropy se zvlástním zretelem k mravencí zvírene Cech a Moravy. Entomol. Listy 4: 65-115 (page 101, Status as species)
- Obregon, R., M. R. Shaw, J. Fernandez-Haeger, and D. Jordano. 2015. Parasitoid and ant interactions of some Iberian butterflies (Insecta: Lepidoptera). Shilap-Revista De Lepidopterologia. 43:439-454.
- Park, S.-H., Hosoishi, S., Ogata, K., Kasuya, E. 2014. Changes of species diversity of ants over time: A case study in two urban parks. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University 59(1), 71–76.
- Park, S.-H., Hosoishi, S., Ogata, K., Kuboki, Y. 2014. Clustering of ant communities and indicator species analysis using self-organizing maps. Comptes Rendus Biologies 337, 545–552 (doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2014.07.003).
- Rasheed, M.T., Bodlah, I., Fareen, A.G., Wachkoo, A.A., Huang, X., Akbar, S.A. 2019. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Pakistan. Sociobiology 66(3), 426-439 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v66i3.4330).
- Roszler, P. 1942a. Myrmecologisches 1938. Tijdschr. Entomol. 85: 50-71 (page 53, Status as species)
- Ruzsky, M. 1902d. Material on the ant fauna of the Caucasus and the Crimea. Protok. Obshch. Estestvoispyt. Imp. Kazan. Univ. 206(su suppl: 1-33 (page 16, Status as species)
- Ruzsky, M. 1925b. New data on the ant fauna of Siberia. Rus. Entomol. Obozr. 19: 41-46 (page 44, Combination in Acanthomyops)
- Salata, S., Borowiec, L., Trichas, A. 2020. Review of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Crete, with keys to species determination and zoogeographical remarks. Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum No 12: 5–296 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.3738001).
- Santschi, F. 1925g. Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espèces paléarctiques (Hymenopt.). EOS. Rev. Esp. Entomol. 1: 339-360 (page 349, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Saunders, E. 1880. Synopsis of the British Heterogyna and fossorial Hymenoptera. Trans. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1880: 201-304 (page 209, Status as species)
- Schär, S., Menchetti, M., Schifani, E., Hinojosa, J.C., Platania, L., Dapporto, L., Vila, R. 2020. Integrative biodiversity inventory of ants from a Sicilian archipelago reveals high diversity on young volcanic islands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Organisms Diversity, Evolution 20, 405–416 (doi:10.1007/s13127-020-00442-3).
- Schar, S., Talavera, G., Espadaler, X., Rana, J.D., Andersen, A.A., Cover, S.P., Vila, R. 2018. Do Holarctic ant species exist? Trans-Beringian dispersal and homoplasy in the Formicidae. Journal of Biogeography 2018:1–12 (doi:10.1111/jbi.13380).
- Schär, S., Talavera, G., Rana, J.D., Espadaler, X., Cover, S.P., Shattuck, S.O., Vila, R. 2022. Integrative taxonomy reveals cryptic diversity in North American Lasius ants, and an overlooked introduced species. Scientific Reports 12: 5970: 1-12 (doi:10.1038/s41598-022-10047-9).
- Schifani, E. (2022). The new checklist of the Italian fauna: Formicidae. Biogeographia – The Journal of Integrative Biogeography 37, ucl006 (doi:10.21426/b637155803).
- Schifani, E., Csősz, S., Viviano, R., Alicata, A. 2021. Ant diversity on the largest Mediterranean islands: on the presence or absence of 28 species in Sicily (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natural History Sciences 8, 55–70 (doi:10.4081/nhs.2021.532).
- Seifert, B. 2020. A taxonomic revision of the Palaearctic members of the subgenus Lasius s.str. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Soil Organisms 92(1): 15-86 (doi:10.25674/so92iss1pp15).
- Siddiqui, J. A., Li, J., Zou, X., Bodlah, I., Huang, X. 2019. Meta-analysis of the global diversity and spatial patterns of aphid-ant mutualistic relationships. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 17: 5471-5524 (doi:10.15666/aeer/1703_54715524).
- Snegovaya, N., Shigayev, C. 2021. A checklist of the ants (Insecta, Formicidae) of Azerbaijan Republic. Iranian Journal of Animal Biosystematics 17(2): 179-207 (doi:10.22067/ijab.2022.67343.1000).
- Sondej, I., Domisch, T. 2024. Impact of large-scale fire and habitat type on ant nest density and species abundance in Biebrza National Park, Poland. Forests 151, 123 (doi:10.3390/f15010123).
- Stärcke, A. 1944b. Retouches sur quelques fourmis d'Europe. III. Autres Lasius. Entomol. Ber. (Amst.) 11: 153-158 (page 153, Status as species)
- Steiner, F.M., Schlick-Steiner, B.C., Holzinger, W., Komposch, C., Pazoutova, S., Sanetra, M., Christian, E. 2004. A novel relationship between ants and a leafhopper (Hymenoptera: Formicidae; Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). European Journal of Entomology 101, 689-692.
- Stitz, H. 1939. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der angrenzenden Meersteile nach ihren Merkmalen und nach ihrer Lebensweise. 37. Theil. Hautflüger oder Hymenoptera. I: Ameisen oder Formicidae. Jena: G. Fischer, 428 pp. (page 279, Status as species)
- Stukalyuk, S.V., Radchenko, A., Reshetov, A., Akhmedov, A., Goncharenko, I. 2021. Comparative analysis of the population structure of Crematogaster subdentata and Lasius neglectus in the primary and secondary ranges (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Fragmenta Entomologica 53, 43-51 (doi:10.13133/2284-4880/436).
- Warren II, R.J., Bayba, S., Krupp, K.T. 2018. Interacting effects of urbanization and coastal gradients on ant thermal responses. Journal of Urban Ecology 4: 1-11 (doi:10.1093/jue/juy026).
- Warren, R.J., Elliott, K.J., Giladi, I., King, J.R., Bradford, M.A. 2019. Field experiments show contradictory short- and long-term myrmecochorous plant impacts on seed-dispersing ants. Ecological Entomology 44, 30–39 (doi:10.1111/EEN.12666).
- Wegnez, P. 2017. Découverte de Myrmica lobicornis Nylander, 1846 et Lasius jensi Seifert, 1982, deux nouvelles espèces pour le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie153, 46–49.
- Wheeler, W. M. 1906h. The ants of Japan. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 22: 301-328 (page 322, Variety/race/subspecies of niger)
- Wiezik, M., Svitok, M., Wieziková, A., Dovčiak, M. 2013. Shrub encroachment alters composition and diversity of ant communities in abandoned grasslands of western Carpathians. Biodiversity and Conservation 22, 2305–2320 (doi:10.1007/s10531-013-0446-z).
- Wilson, E. O. 1955a. A monographic revision of the ant genus Lasius. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology. 113:1-201. (page 77, Status as species, Senior synonym of americanus and pannonica, and material of the unavailable names alienoamericanus, flavidus and turkmenus referred here.)
- Wu, J. & Wang, C. 1992. Formicidae (pp. 1301-1320). In Peng, J. et al. Iconography of Forest Insects in Hunan, China. Forest Bureau of Hunan Province: 1473 pp. Hunan Scientific and Technical Publishing House.
- Zhu, W., Wu, L., Duan, L., Xu, S. 2022. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in northern Shaanxi Province, China, with one new species of genus Proformica Ruzsky, 1902, Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 25, 101875 (doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2022.101875).
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Abril S., C. Gómez. 2012. Lista actualizada de las especies de hormigas de Menorca (Islas Baleares, España) y primera cita de Monomorium andrei Saunders, 1890 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) de la isla Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 50: 403-407.
- Abril S., and C. Gomez. 2013. Rapid assessment of ant assemblages in public pine forests of the central Iberian Peninsula. Forest Ecology and Management 293: 7984.
- Acosta, F. J., M. D. Martínez Ibáñez, and M. A. Morales. "Contribución al conocimiento de la mirmecofauna del encinar peninsular. I." Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 6 (2) (1983): 379-391.
- Aktaç, N.. "Studies on the myrmecofauna of Turkey I. Ants of Siirt, Bodrum and Trabzon." Istanbul Universitesi Fen Fakultesi Mecmuasi. Seri B 41 (1977): 115-135.
- Aldawood AS, Sharaf MR (2011) Monomorium dryhimi sp. n., a new ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the M. monomorium group from Saudi Arabia, with a key to the Arabian Monomorium monomorium-group. ZooKeys 106: 4754. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.106.139
- Alvarado M., and L. Galle. 2000. Ant assemblages associated with lowland forests in the southern part of the great Hungarian plain. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientarum Hungaricae 46(2): 79-102.
- AntArea. Accessed on February 5th 2014 at http://antarea.fr/fourmi/
- Antarea (Personal Communication - Rumsais Blatrix- 27 April 2018)
- Antonova V., and L. Penev. 2008. Classification of assemblages of ants in the green areas in Sofia City. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 60(2): 103-110.
- ArtDatabanken Bugs (via GBIG)
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2011. List of species collected during the Taxomara Lisboa 2011. Iberomyrmex 3: 30-31.
- Assing V. 1989. Die Ameisenfauna (Hym.: Formicidae) nordwestdeutscher Calluna-Heiden. Drosera 89: 49-62.
- Astruc C., J. F. Julien, C. Errard, and A. Lenoir. 2004. Phylogeny of ants based on morphology and DNA sequence data. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 31: 880-893.
- Azuma M. 1951. On the Myrmecological fauna of Osaka Prefecture, Japan with description of new species (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). Hyogo Biology 1(5): 1-5.
- Azuma M. 1955. A list of ants (Formicidae) from Hokkaido Is. Hyogo Biology 3:79-80.
- Baroni Urbani C. 1968. Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. IV. La fauna mirmecologica delle isole Maltesi ed il suo significato ecologico e biogeografico. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Giacomo Doria 77: 408-559.
- Baroni Urbani C. 1969. Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. VIII. L'Isola di Giannutri ed alcuni scogli minori dell'arcipelago Toscano. Atti Soc. Toscana Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. B 75: 325-338.
- Baroni Urbani C. 1974. Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. XII. Le Isole Pontine. Fragm. Entomol. 9: 225-252.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1976. A Numerical Analysis of the Distribution of British Formicidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata). Verhandlungen der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Basel 85: 51-91.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1977. The zoogeography of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Northern Europe. Acta Zoologica Fennica 152: 1-34.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Formiche dell'Italia appenninica (Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia, III)." Memorie del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Verona 12 (1964): 149-172.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Studi sulla mirmecofauna d'Italia. II. Formiche di Sicilia." Atti dell'Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali in Catania (6) 16 (1964): 25-66.
- Baroni Urbani, C.. "Su alcune formiche raccolte in Turchia." Annuario dell'Istituto e Museo di Zoologia dell'Università di Napoli 16 (1964): 1-12.
- Baroni-Urbani 1969. Ant Communities of the High-Altitude Appennine Grasslands. Ecology 50(3): 488-492.
- Barrett K. E. 1967. Ants in South Brittany. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 79:112-116.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968. Ants in western France. Entomologist 101: 153-155.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968b. The distribution of ants in central southern England. Transactions of the Society for British Entomology 17: 235-250.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1970. Ants in France, 1968-69. Entomologist 103: 270-274.
- Baugnee J. Y. 2003. Camponotus piceus (Leach, 1825), fourmi nouvelle pour la faune belge decouverte dans le parc naturel Viroin-Hermeton (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin S. R. B. E./K. B. V. E. 139: 219-225.
- Behr D., and K. Colln. 1993. Zur ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) von Gonnersdorf (Kr. Daun). Dendrocopos 20: 148-160.
- Bernadou A., X. Espadaler, A. Le Goff, and V. Fourcassie. 2015. Ant community organization along elevational gradients in a temperate ecosystem. Insect. Soc. 62:5971
- Bernadou, A., G. Latil, V. Fourcassié, and X. Espadaler. "Les formigues de la Vall del Madriu-Perafita-Claror : diversitat i distribució." Hàbitats, 13 (2006): 10-21.
- Bernard F. 1959. Les fourmis de l'île de Port-Cros. Contribution à l'écologie des anciennes forêts méditerranéennes. Vie Milieu 9: 340-360.
- Bernard F. 1967. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp.
- Bernard F. 1967. Recherches sur les fourmis des Monts-Dore. Annales de la Station biologique de Besse-en-Chandesse : 1-11.
- Bernard F. 1975. Rapports entre fourmis et vegetation pres des Gorges du Verdon. Annales du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Nice 2: 57-79.
- Bernard F. 1976. Écologie des fourmis des grès d'Annot, comparées à celles de la Provence calcaire. Annales du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Nice 3: 33-54.
- Bernard F. 1977. Écologie des fourmis du Parc national de Port-Cros. Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle. Écologie Générale (3)36: 53-82.
- Bernard F. 1978. Révision des Diplorhoptrum de France, fourmis plus différenciées par l'écologie que par leurs formes (Hym. Formicidae). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. (n.s.) 13: 543-577.
- Bernard, F.. "Remarques sur le peuplement des Baléares en fourmis." Bulletin de la Société d' Histoire naturelle de l' Afrique du Nord 47 (1956): 254-266.
- Berville L., C. Santelli, J. Reybaud, M. Renucci, P. Ponel, O. Blight, and E. Provost. 2014. Suivi d’un site atelier dans le golfe de Fos: Une diversite myrmecologique insoupconne. Etudes Vauclusiennes 82: 71-78.
- Berville L., M. Renucci, and E. Provost. 2012. Mise en place de protocoles de contrôle de la fourmi dArgentine (Linepithema humile) sur les îles de Port-Cros et de Porquerolles (Var, France). Sci. Rep. Port-Cros natl. Park, 26: 91-108.
- Bezdecka P. 1996. The ants of Slovakia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomofauna carpathica 8: 108-114.
- Bezdecka P., and K. Bezdeckova. 2012. Updated list of the ants of the Czech Republic. Pp 7-12. Bezd??ka P. & Bezd??ková K. (eds) 2012: Blanok?ídlí v ?eských zemích a na Slovensku 8, Chaloupky, 1.-3. ?ervna 2012, sborník abstrakt? z konference. MVJ Jihlava, 37 pp.
- Bharti H., Y. P. Sharma, M. Bharti, and M. Pfeiffer. 2013. Ant species richness, endemicity and functional groups, along an elevational gradient in the Himalayas. Asian Myrmecology 5: 79-101.
- Blacker N. C. 1989. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the Gower Peninsula, West Glamorgan, South Wales. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 101: 261-266.
- Blacker N. C. and C. A. Collingwood. 2002. Some significant new records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Salisbury area, south Wiltshire, England, with a key to the British species of Lasius. British Journal of Entomology and Natural History 15: 25-46
- Blatrix R., C. Lebas, C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, P. Pimenta, and D. Morichon. 2016. Vegetation cover and elevation drive diversity and composition of ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in a Mediterranean ecosystem. – Myrmecological News 22: 119-127.
- Boer P. 2019. Species list of the Netherlands. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/specieslist.html
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. Van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten (Amsterdam) 63: 54-58.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten 63(3): 54-57.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. List of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Belgium and The Netherlands, their status and Dutch vernacular names. Entomologische Berichten 63 (3): 54-58.
- Bonaric J. C. 1971. Contribution a l'etude systematique et ecologique des formicides du Bas-Languedoc. PhD thesis Universite des sciences et techniques du Languedoc, 175 pages.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2012. Ants of Greece - Checklist, comments and new faunistic data (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus 23(4): 461-563.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2017. Ants of the Peloponnese, Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Polish Journal of Entomology 86: 193-236.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2018. Notes on ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Samos Island, Greece. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 27: 1-13.
- Bourne R. A. 1973. A taxonomic study of the ant genus Lasius Fabricius in the British Isles (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Entomol. Ser. B 42: 17-27 .
- Boven J. K. A. 1947. Liste de détermination des principales espèces de fourmis belges (Hymenoptera Formicidae). Bulletin et Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 83: 163-190.
- Bracko G. 2007. Checklist of the ants of Slovenia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natura Sloveniae 9: 15-24
- Bracko G., K. Kiran, C. Karaman, S. Salata, and L. Borowiec. 2016. Survey of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Greek Thrace. Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e7945. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e7945
- Bracko, G. 2006. Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) of Croatia. Acta Entomologica Slovenica 14(2): 131-156.
- Brangham A. N. 1938. Additions to the wild fauna and flora of the Royal Botanic gardens, Kew: XVIII. Bulletin of Miscellaneous Information (Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew), 9: 390-396.
- Cagniant, H. 1968. Liste preliminaire de fourmis forestieres d'Algerie. Resultats obtenus de 1963 a 1964. Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse 104: 138-147
- Cagniant, H.. "Contribution à la connaissance des fourmis marocaines: Aphaenogaster baronii n. sp. (Hyménoptères, Formicoidea, Myrmicidae)." Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse 124 (1988): 43-50.
- Cagniant, H.. "Deuxième liste de fourmis d'Algérie, récoltées principalement en forêt (Deuxième partie)." Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse 106 (1970): 28-40.
- Cagniant, H.. "Note sur le peuplement en fourmis d'une montagne de la région d'Alger, l'Atlas de Blida." Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse 102 (1966): 278-284.
- Cagniant, H.. "Nouvelle description d'Aphaenogaster (Attomyrma) crocea (André) Hyménoptère Formicidae. Représentation des trois castes. Notes biologiques." Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France 91 (1966): 61-69.
- Cagniant, H.. Les peuplements de fourmis des forêts algériennes: écologie, biocénotique, essai biologique. Universite de Toulouse, 1973.
- Carniel A. 1998. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna delle Prealpi Orobiche (Lombardia) (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atti. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Morbegno 9: 29-39.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J. 1990. Etude Systematique de la Myrmecofaune Corse (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), deuxieme partie. Bull. Mus. Natn. Hist. Nat. Paris. 4eme serie 12, section A(2): 415-442.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J. 1992. La myrmecofaune de la reserve naturelle de Scandola, inventaire spécifique (1984/85-1991). Trav. Sci. Parc nat. Res. Nat. Corse, Fr, 36: 85-108.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and C. Galkowski. 2009. Liste actualisee des Fourmis de France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 114: 475-510.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and M. Prost. 1991. Fourmis de la Côte-d'Or présentes dans les collections du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Dijon. Bulletin Scientifique de Bourgogne 44: 53-72.
- Casevitz-Weulersse, J.. "Contribution a la connaisance des fourmis de la Corse (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." These de Doctorat Museum Nat (1989): 379pp.
- Cecconi G. 1908. Contributo alla fauna delle Isole Tremiti. Bollettino dei Musei di Zoologia ed Anatomia Comparata della Reale Università di Torino 23(583): 1-53.
- Chen Y., C. W. Luo, H. W. Li, Y. J. Liu, H. F. Zheng, and F. C. Yang. 2013. Investigation of ant species and distribution on Wuliang Mountain. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences 42(5): 118-122.
- Cherix D., and S. Higashi. 1979. Distribution verticale des fourmis dans le Jura vaudois et recensement prelimaire des bourdons (Hymenoptera, Formicidae et Apidae). Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sc. Nat. 356(74): 315-324.
- Chevrier M., and C. Mouquet C. 2005. Etude des peuplements des invertébrés des dunes de Bretagne. Rapport GRETIA, avenant au Contrat-Nature 2, Conseil Régional de Bretagne, Conseils Généraux des Côtes d'Armor, du Finistère et du Morbihan : 127 p.
- Choi B.-M. 1987. Taxonomic study on ants (Formicidae) in Korea (1). On the genus Monomorium. Journal of the Institute of Science Education (Cheongju National Teachers' College) 11:17-30.
- Choi B.M. 1985. Study on distribution of ants (Formicidae) from Korea (1). Formic fauna in Mt. Songni. Cheongju Sabom Taehak Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National Teachers' College) 22:401-437.
- Choi B.M. 1986. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea. Journal of Chongju National Teacher College 23: 317-386.
- Choi B.M. 1988. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (5) Ant fauna in Is. Kanghwado. Chongju Sabom Taehak Nonmunjip (Journal of Chongju National Teacher' College) 25: 217-231.
- Choi B.M. 1996. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (15) -Ant fauna islands Ullungdo and Dokdo. Journal of Chongju National University of Education 33: 201-219.
- Choi B.M. 1997. Distribution of Ants (Formicidae) in Korea (18). Ants Fauna in island Paekryongdo and Taechongdo. Journal of Chongju National University of Education 34: 119-138.
- Choi B.M., Bang, J.R. 1992. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (9). Ant fauna in Mt. Togyusan. Korean Journal of Applied Entomology 31:101-112.
- Choi B.M., I. H. Lee. 1995. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (14). Ant fauna in island Sohuksando. Korean Journal of Applied Entomology 34(3): 191-197.
- Choi B.M., K. Ogata, and M. Terayama. 1993. Comparative studies of ant faunas of Korea and Japan. 1. Faunal comparison among islands of Southern Korean and northern Kyushu, Japan. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Japan 48(1): 37-49.
- Choi B.M., Kim, C.H., Bang, J.R. 1993. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (13). A checklist of ants from each province (Do), with taxonomic notes. Cheongju Sabom Taehakkyo Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National University of Education) 30: 331-380.
- Choi B.M., and H.S. Lee. 1999. Studies on the distribution ants in Korea (21) - Ant fauna in Kwanaksan. Korean J. Soil Zoology 4(1): 1-4.
- Choi B.M., and J. R. Bang. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (12): the analysis of ant communities in 23 islands. Journal of Cheongju National University of Education 30:317-330.
- Colindre L. 2015. Les fourmis en Picardie: bilan 2014 (Hymenoptera/ Formicidae). Entomologiste Picard 26, 15 pages.
- Colindre L. 2017. Richess et utilite du cortege de fourmis en foret d'Ermenonville, Oise, Region Hauts-de-France. Association des Entomologistes de Picardie. 19 pages.
- Collingwood C. A. 1955. Ants in S.W. Scotland. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 67: 11-12.
- Collingwood C. A. 1956. Ant hunting in France. Entomologist 89: 106-108.
- Collingwood C. A. 1971. A synopsis of the Formicidae of north Europe. Entomologist 104: 150-176
- Collingwood C. A. 1976. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from North Korea. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 68:
- Collingwood C. A. 1981. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Korea, 2. Folia Entomologica Hungarica 42(34): 25-30.
- Collingwood C. A. 1982. Himalayan ants of the genus Lasius (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Systematic Entomology 7: 283-296.
- Collingwood C., and A. Prince. 1998. A guide to ants of continental Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia. Suplemento 5: 1-49.
- Collingwood C.A. 1955. Ants in S.W. Scotland. Entomol.Rec. 67: 11-12
- Collingwood C.A. 1957. The Species of Ants of the Genus Lasius in Britain. Journal of the Society for British Entomology. 5: 204-214
- Collingwood C.A. 1959. Scandinavian Ants. Entomol. Rec. 71: 78-83
- Collingwood C.A. 1961. New Vice-County Records for British Ants. Entomologist. 73: 90-93
- Collingwood, C. A. 1958b. A key to the species of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) found in Britain. Trans. Soc. Br. Entomol. 13: 69-96
- Collingwood, C. A. 1964. The Identification of British Ants (Hym. Formicidae). Transactions of the Society for British Entomology. 16:93-121.
- Collingwood, C. A. 1974. A revised list of Norwegian ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Norsk Entomologisk Tidsskrift 21: 31-35.
- Collingwood, C. A. 1993. A Comparitive Study of the Ant Fauna of Five Greek Islands. Biologia Gallo-hellenica. 20,1:191-197
- Collingwood, C. A., and I. H. H. Yarrow. "A survey of Iberian Formicidae." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 44 (1969): 53-101.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "A comparative study of the ant fauna of five Greek islands." Biologia Gallo-Hellenica 20 (1993): 191-197.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark." Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 8 (1979): 1-174.
- Collingwood, C.A. 1958. A survey of Irish Formicidae. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy 59B:213-219
- Comín del Río, P., and Andrés de Haro. "Datos iniciales para un estudio ecológico de las hormigas de Menorca." Bolletí de la Societat d´Historia Natural de les Balears 24 (1980): 23-48.
- Comín del Río, P., and X. Espadaler. "Ants of the Pityusic islands." In Biogeography of the Pityusic Islands, edited by H. Kuhbler, J. A. Alcover and C. Guerau, 278-231. The Hague: Junk, 1984.
- Comín del Río, P.. "Los Formícidos de Menorca. Contribución al estudio taxonómico, geográfico y biológico." Tesina de licenciatura Universida (1977): 135 pp.
- Comín del Río, P.. Estudio de los formícidos de Baleares: Contribución al estudio taxonómico, geográfìco y biológico. Palma de Mallorca: Universidad de las Islas Baleares, 1988.
- Consani M., and P. Zangheri. 1952. Fauna di Romagna. Imenotteri - Formicidi. Memorie della Societa Entomologica Italiana 31: 38-48.
- Csosz S., B. Marko, K. Kiss, A. Tartally, and L. Galle. 2002. The ant fauna of the Ferto-Hansag National Park (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Mahunka, S. (Ed.): The fauna of the Fert?-Hanság National Park. Hungarian Natural History Museum, Budapest, pp. 617-629.
- Csősz S. and Markó, B. 2005. European ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the ant collection of the Natural History Museum of Sibiu (Hermannstadt/Nagyszeben), Romania II. Subfamily Formicinae. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 97: 225-240.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2001. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Stana Valley (Romania): Evaluation of the effectiveness of a myrmecological survey. Entomologica Romanica 6 : 121-126.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski W., A. Radchenko, W. Czechowska and K. Vepsäläinen. 2012. The ants of Poland with reference to the myrmecofauna of Europe. Fauna Poloniae 4. Warsaw: Natura Optima Dux Foundation, 1-496 pp
- Dattilo W. et al. 2019. MEXICO ANTS: incidence and abundance along the Nearctic-Neotropical interface. Ecology https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2944
- De Stefani T. 1889. Miscellanea imenotterologica sicula. Nat. Sicil. 8: 140-145.
- Dekoninck W., F. Hendrickx, M. Dethier, and J. P. Maelfait. 2010. Forest Succession Endangers the Special Ant Fauna of Abandoned Quarries along the River Meuse (Wallonia, Belgium). Restoration Ecology 18(5): 681690.
- Dekoninck W., H. De Koninck, J. Y. Baugnee, and J. P. Maelfait. 2007. Ant biodiversity conservation in Belgian calcareous grasslands: active management is vital. Belg. J. Zool. 137 (2): 137-146.
- Della Santa E. 1994. Guide pour l'identification des principales espèces de fourmis de Suisse. Miscellanea Faunistica Helvetiae 3: 1-124.
- Della Santa E. 1995. Fourmis de Provence. Faune Provence 16: 5-37.
- Dlussky G. M., O. S. Soyunov, and S. I. Zabelin. 1990. Ants of Turkmenistan. Ashkabad: Ylym Press, 273 pp.
- Dlussky G. M., and B. Pisarski. 1970. Formicidae aus der Mongolei. Ergebnisse der Mongolisch-Deutschen Biologischen Expeditionen seit 1962, Nr. 46. Mitteilungen aus dem Zoologischen Museum in Berlin 46: 85-90.
- Donisthorpe H. 1914. Myrmecophilous notes for 1913. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 26: 37-45.
- Donisthorpe, H.. "A first instalment of the ants of Turkey." Annals and Magazine of Natural History (12)3 (1950): 1057-1067.
- Donisthorpe, H.. "British ants, their life history and classification (2nd edn.)." London: G Routledge (1927): xvi + 436 pp.
- Du Merle P. 1978. Les peuplements de fourmis et les peuplements d'acridiens du Mont Ventoux II. - Les peuplements de fourmis. Terre Vie 32(1): 161-218.
- Dubovikoff D. A., and Z. M. Yusupov. 2018. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Dusmet, J. M.. "Algunos formícidos y mutílidos de España." Actas de la Sociedad Española de Historia Natural Tomo XXVII (1899): 109.
- Dvorak, L., P. BOGUSCH, I. MALENOVSKÝ, P. BEZDÌÈKA, K. BEZDÌÈKOVÁ, K. HOLÝ, P. LIKA, J. MACEK, L. ROLLER, M. RÍHA et al. "Hymenoptera of Hády Hill, near the city of Brno (Czech Republic), collected during the Third Czech-Slovak Hymenoptera meeting." Acta Musei Moraviae, Scientiae biologicae (Brno) 93 (2008): 53-92.
- Eidmann, H.. "Die Ameisenfauna der Balearen." Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere 6 (1926): 694-742.
- Eidmann, H.. "Zur Kenntnis der Insektekfauna der Balearischen Inseln." Entomologische Mitteilungen 16 (1927): 24-37.
- Else G., B. Bolton, and G. Broad. 2016. Checklist of British and Irish Hymenoptera - aculeates (Apoidea, Chrysidoidea and Vespoidea). Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e8050. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e8050
- Emery C. 1897. Anhang. Verzeichniss der auf der zweiten Reise nach Kleinasien (1897) gesammelten Ameisen, mit einer Neubeschreibung. P. 239 in: Escherich, K. 1897. Zur Kenntniss der Myrmecophilen Kleinasiens. I. Coleoptera. Wiener Entomologische Zeitung 16: 229-239.
- Emery, C.. "Alcune formiche dell'isola di Creta." Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. Resoc. Adun. 26 (1894): 7-10.
- Emery, C.. "Catalogo delle formiche esistenti nelle collezioni del Museo Civico di Genova. Parte seconda. Formiche dell'Europa e delle regioni limitrofe in Africa e in Asia." Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 12 (1878): 43-59.
- Emery, C.. "Exploration scientifique de la Tunisie. Zoologie. - Hyménoptères. Révision critique des fourmis de la Tunisie." Explor. Scient. De la Tunisie Zoll. Hym. (Folleto) Paris. Imp (1891): iii + 21 pp.
- Espadaler X., X. Roig, K. Gómez, and F. García. 2011. Formigues de les Planes de Son i mata de València (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Treballs de la Institució Catalana d'Història Natural 16: 609-627.
- Espadaler, X. and H. Cagniant. 1991. Psyche. 98: 351-354.
- Espadaler, X., J. Pujade-Villar, and A. Bernadou. "Contribució al coneixement de la taxonomia i la fenologia de les formigues (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) d'Andorra." Butlletí de l' Institució Catalana d'Història Natural 74 (2006): 81-90.
- Espadaler, X., X. Roig, and K. Gómez. "Cuatro nuevas citas de hormigas (Hymenopera, Formicidae) y actualización del listado para Cataluña (Península Ibérica)." Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 40 (2007): 313-316.
- Espadaler, X., and H. Cagniant. "Plagiolepis xene Starckë, the first inquiline ant from the Balearic Islands (Spain)." Psyche 98 (4) (1992): 351-354.
- Espadaler, X., and L. Lopez Soria. "Rareness of certain Mediterranean ant species: fact or artifact?" Insectes Sociaux 38 (1991): 365-377.
- Espadaler, X.. "Contribución al conocimiento de los formícidos (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) del Pirineo catalán." Tesis Universida (1979): 285 pp.
- Fagan K. C., R. F. Pywell, J. M. Bullock, and R. H. Marrs. 2010. Are Ants Useful Indicators of Restoration Success in Temperate Grasslands? Restoration Ecology 18(3): 373379.
- Fiedler, K., F. Kuhlmann, B. C. Schlick-Steiner, F. M. Steiner and G. Gebauer. 2007. Stable N-isotope signatures of central European ants assessing positions in a trophic gradient. Insectes Sociaux 54(4):393-402.
- Field Museum Collection, Chicago, Illinois (C. Moreau)
- Finzi, B.. "Quarto contributo alla conoscenza della fauna mirmecologica della Venezia Giulia." Bollettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 60 (1928): 128-130.
- Finzi, B.. "Raccolte entomologiche nell'Isola di Capraia fatte da C. Mancini e F. Capra (1927-1931). II. Formicidae." Memorie della Società Entomologica Italiana 11 (1933): 162-165.
- Finzi, B.. "Risultati scientifici della spedizione Ravasini-Lona in Albania. III. Formiche." Bollettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 55 (1923): 1-4.
- Forel A. 1890. Fourmis de Tunisie et de l'Algérie orientale. Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 34: lxi-lxxvi.
- Forel A. 1892. Die Ameisenfauna Bulgariens. (Nebst biologischen Beobachtungen.). 305-318.
- Forel A. 1904. Note sur les fourmis du Musée Zoologique de l'Académie Impériale des Sciences à St. Pétersbourg. Ezheg. Zool. Muz. 8: 368-388.
- Forel A. 1906. Fourmis d'Asie mineure et de la Dobrudscha récoltées par M. le Dr. Oscar Vogt et Mme Cécile Vogt, Dr. méd. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 50: 187-190.
- Forel A. 1911. Fourmis nouvelles ou intéressantes. Bull. Soc. Vaudoise Sci. Nat. 47: 331-400.
- Forel, A.. "Ameisen aus den Sporaden, den Cykladen und Griechenland, gesammelt 1887 von Herrn von Oertzen." Berliner Entomologische Zeitschrift 32 (1889): 255-265.
- Forel, A.. "Nouvelles fourmis de Grèce récoltées par M. E. von Oertzen." Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 30 (1886): clix-clxviii.
- Formidabel Database
- Fowles, A.P. 1996. A provisional checklist of the invertebrates recorded from Wales. 2. Aculeate wasps, bees and ants (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Countryside Council for Wales
- Franch, J., and X. Espadaler. "Ants as colonizing agents of pine stumps in San Juan de la Peña (Huesca, Spain)." Vie et Milieu 38 (1988): 149-154.
- Francois J. 1958. Contribution a l'etude ecologique des Formicides (Insectes, Hymenopteres) de la region Dijonnaise. Travaux du laboratoire de Zoologie et de la Station Aquicole Grimaldi de la Faculte des Sciences de Dijon 25, 39 pages.
- GRETIA. 2017. Bilan annuel de l'enquete sur la repartition des fourmis armoricaines. 23 pages.
- Gadeau de Kerville H. 1922. Materiaux pour la Faune des Hymenopteres de la Normandie. Bull. Soc. Amis Sc. Nat. Rouen 1916-1921, 1922: 217-225.
- Galle L. 1981. The Formicoid fauna of the Hortobagy. Pp. 307-311 in: Mahunka, S. (ed.) 1981. The fauna of the Hortobágy National Park. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó, 415 pp.
- Galle L. 1993. Data to the ant fauna of the Bukk (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natural history of the national parks of Hungary 7: 445-448.
- Galle L. 1997. Contribution to the ant fauna of Slovenia with special reference to the submediterranean and eudinaric regions. Annals for Istrian and Mediterranean studies 11: 209-214.
- Galle L., and G. Szonyi. 1988. A check list of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea) of a sandy grassland in Kiskunsag National Park (Hungary). Acta Biol. Szeged 34: 167-168.
- Gallé L. 1991. Structure and succession of ant assemblages in a north European sand dune area. Holarctic Ecology 14: 31-37.
- Gallé L., B. Markó, K. Kiss, E. Kovács, H. Dürgő, K. Kőváry, and S. Csősz. 2005. Ant fauna of Tisza river basin (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Gallé, L. (szerk.): Vegetation and Fauna of Tisza River Basin I. Tiscia Monograph Series 7; Szeged, pp. 149-197.
- Garcia Garcia F., and A. D. Cuesta-Esgura. 2017. First catalogue of the ants of Burgos province, Spain (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 60: 245–258.
- García F., X. Espadaler, P. Echave, and R. Vila. 2011. Hormigas (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) de los acantilados de l'Avenc de Tavertet (Osona) Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 47: 363-367.
- Gaspar C. 1968. Les fourmis de la Drome et des Basses-Alpes, en France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Naturaliste can. 95: 747-766.
- Gaspare Charles. 1965. Étude myrmécologique d'une région naturelle de Belgique: la Famenne Survey des Fourmis de la Région (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Institut agronomique de l'Etat a' Gembloux. 32(4): 427-434.
- Gilev A. V., I. V. Kuzmin, V. A. Stolbov, and S. D. Sheikin. 2012. Materials on the fauna and ecology of ants (formicidae) Southern part of the Tyumen region. Tyumen State University Herald 6: 86-91.
- Gippet J. M., N. Mondy, J. Diallo-Dudek, A. Bellec, A. Dumet, L. Mistler, and B. Kauffmann. 2016. I’m not like everybody else: urbanization factors shaping spatial distribution of native and invasive ants are species-specific. Urban Ecosystems DOI 10.1007/s11252-016-0576-7
- Goetsch, W.. "Beiträge zur Biologie spanischer Ameisen." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 18 (1942): 175-241.
- Gouraud C. 2015. Bilan de l’année 2014 : Atlas des fourmis de Loire-Atlantique (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atlas des Formicidae de Loire-Atlantique, compte rendu de la première année d’étude (2014)
- Grandi G. 1935. Contributi alla conoscenza degli Imenotteri Aculeati. XV. Boll. R. Ist. Entomol. Univ. Studi Bologna 8: 27-121.
- Gratiashvili N., Barjadze S. 2008. Checklist of the ants (Formicidae Latreille, 1809) of Georgia. Proceedings of the Institute of Zoology (Tbilisi) 23: 130-146.
- Gribodo, G., Emery C.. "Ordo Hymenoptera." Pp. 81-85 in: Cavanna, G. Parte II.- Catalogo degli animali raccolti al Vulture, al Pollino ed in altri luoghi dell'Italia meridionale e centrale Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 14 (1882): 31-87.
- Groc S., J. H. C. Delabie, R. Cereghino, J. Orivel, F. Jaladeau, J. Grangier, C. S. F. Mariano, and A. Dejean. 2007. Ant species diversity in the Grands Causses (Aveyron, France): In search of sampling methods adapted to temperate climates. C. R. Biologies 330: 913922.
- Grzes I. M. 2009. Ant species richness and evenness increase along a metal pollution gradient in the Boles?aw zinc smelter area. Pedobiologia 53: 65-73.
- Guénard B., and R. R. Dunn. 2012. A checklist of the ants of China. Zootaxa 3558: 1-77.
- Gómez C., and S. Abril. 2011. Selective logging in public pine forests of the central Iberian Peninsula: Effects of the recovery process on ant assemblages Forest Ecology and Management 262: 1061-1066.
- Ha S.J, S.J. Park, and B.J. Kim. 2002. Comparative ant faunas between Seonyudo and seven other islands of West Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(2): 75-79.
- Hauschteck-Jungen E., and H. Jungen. 1983. Ant chromosomes. II. Karyotypes of western palearctic species. Insectes Soc. 30: 149-164.
- Hayashida K. 1959. Ecological Distribution of Ants in Mt. Atusanupuri, An Active Volcano in Akan National Park, Hokkaido. Jour. Pac. Sci. Hokkaiao Univ. Ser. 4(14): 252-260.
- Hayashida K. 1959. Ecological distribution of ants in Mt. Atusanupuri, an active volcano in Akan National Park, Hokkaido. Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University. Series VI. Zoology 14:252-260.
- Hayashida K. 1961. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Sapporo and its vicinity (1 et 2). Insectes Sociaux 7: 125-162.
- Hayashida K. 1964. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Kutchan and its adjacent area. Journal of the Sapporo Otani Junior College 2: 107-129.
- Hayashida K., and S. Maeda. 1960. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Akkeshi. Journ. Sc. Hokkaido Univ., IV. Zool., 14 (3) : 305-319.
- Holecova M., M. Klesniakova, K. Holla, and A. Sestakova. 2017. Winter activity in scots pine canopies in Borska Nizina Lowland (SW Slovakia)
- Holgersen H. 1944. The ants of Norway (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Nytt Magasin for Naturvidenskapene 84: 165-203.
- Hosoishi S. 2006. Ant fauna of Noko Island. pp99-107. In: The floristic and faunistic surveys of the Noko Island.
- Hosoishi, S., S. Yamane and K. Ogata. 2010. Subterranean species of the ant genus Crematogaster in Asia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomological Science 13:345-350.
- Hou J.H., D.W. Zhou, and S.C. Jiang. 2002. Species Composition and Spatial Distribution 0f Ants in the Grassland Region in the West of Jilin Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica 22(10): 1781-1787.
- Izhaki I., B. Idelovich, R. Laster, and Y. Ofer. 2009. The impact of macro- vs micro environmental factors on the structure of ant communities inhabiting East-Mediterranean Aleppo pine forests. Israel Journal of Entomology 39: 129-146.
- Jeffery H. G. 1931. The Formicidae (or ants) of the Isle of Wight. Proceedings of the Isle of Wight Natural History and Archaeological Society 2: 125-128.
- Karaman C., K. Kiran, and V. Aksoy. 2014. New records of the genus Strumigenys Smith, 1860 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Black Sea region of Turkey. Trakya University Journal of Natural Sciences, 15(2): 59-63.
- Karaman M. G. 2009. An introduction to the ant fauna of Macedonia (Balkan Peninsula), a check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natura Montenegrina 8(3): 151-162.
- Karaman M. G. 2011. A catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Montenegro. Podgorica: Catalogues 3, Volume 2, Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts, 140 pp.
- Karaman M. G., and G. S. Karaman. 2007. Contribution to the Knowledge of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Special nature reserve Zasavica , Serbia. Zbornik “Naucno-strucni skup Zasavica 2007, Sremska Mitrovica, 67-75.
- Karavaiev V. 1912. Ameisen aus Tunesien und Algerien, nebst einigen unterwegs in Italien gesammelten Arten. Rus. Entomol. Obozr. 12: 1-22.
- Karavaiev V. 1912. Ameisen aus dem paläarktischen Faunengebiete. Rus. Entomol. Obozr. 12: 581-596.
- Karavaiev V. 1927. Übersicht der Ameisenfauna der Krim nebst einigen Neubeschreibungen. Konowia 5: 281-303.
- Kim B., Ryu D., Park S., and J. Kim. 1994. Systematic study on ants from coasts of Korean Peninsula (Hym: Formicidae). Korean journal of entomology 24: 293-309.
- Kim B.J. 1986. A systematic study of ants in Island Ullungdo of Korea on the basis of external fine features. The journal of Natural Science 5(2): 84-94.
- Kim B.J. 1996. Synonymic list and distribution of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) in Korea. Entomological Research Bulletin Supplement 169-196.
- Kim B.J., K.G. Kim, D.P. Ryu, J.H. Kim. 1995. Ants of Chindo island in Korea (Hymenoptera; Formicidae). The Korean Journal of Systematic Zoology 11(1): 101-113.
- Kim B.J., S.J. Park, and J.H. Kim. 1996. Ants from Naejangsan national park (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Korean J. Soil. Zoology &(2): 120-133.
- Kim C.H., B.M. Choi, and J.R. Bang. 1992. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (8)-Ant fauna in 10 islands, Chollanam-do. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 31(4): 345-359.
- Kim C.H.; Choi, B.M. 1987. On the kinds of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and vertical distribution in Jiri Mountain. Korean Journal of Plant Protection 26:123-132.
- Kim K.I., C.H. Kim, and B. Choi. 1989. The ant fauna of the southern shore in Gyeongsangnamdo, Korea. Journal of Gyeongsang Nat. Univ. 28(2): 213-226.
- Kim et al. 1993. Systematic study of ants from Chejudo Province. Koran Journal of Entomology 23(3): 117-141.
- Kim, Byung-Jin, Ky-Gyong Kim, Dong-Pyo Ryu and Joong-Hyon Kim. 1995. The Korean Journal of Systematic Zoology. 11(1):101-113.
- Kiran K., and C. Karaman. 2012. First annotated checklist of the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zootaxa 3548: 1-38.
- Kiran K., and N. Aktac. 2006. The vertical distribution of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Samanh Mountains, Turkey. Linzer Biol. Beitr. 38(2): 1105-1122.
- Kofler A. 1995. Nachtrag zur Ameisenfauna Osttirols (Tirol, Österreich) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 1: 14-25.
- Korlevic, A.. "Prilozi fauni hrvatskih opnokrilaca." Glasn. Hrv. Narav. Dr. 5 (1890): 189-250.
- Kratochvíl J., V. Novák, and J. Snoflák. 1944. Mohelno. Soubor práci venoványch studiu vyznamne památky prírodní. 5. Hymenoptera - Aculeata. Formicidae - Apidae - Vespidae. Arch. Svazu Ochr. Prír. Domov. Moravé 6: 1-155.
- Krausse, A. H.. "Ueber sardische Ameisen." Archiv für Naturgeschichte, Berlin A 78(7) (1912): 162-166.
- Kugler J. 1988. The zoogeography of Israel. 9. The zoogeography of social insects of Israel and Sinai. Monographiae biologicae 62: 251-275.
- Kuznetsov G. T. 1990. Comparative analysis of Hymenoptera (Formicidae) population on altitudinal zones of central Kopetdag. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk Turkmenskoi SSR. Seriya Biologicheskikh Nauk 1990(3): 64-67.
- Kvamme T. 1982. Atlas of the Formicidae of Norway (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Insecta Norvegiae 2: 1-56.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, L., V. Antonova, A. G. Radchenko, and M. Atanasova. "Catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Bulgaria." ZooKeys 62 (2010): 1-124.
- Le Moli F., and A. Zaccone. 1995. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna del Cansiglio (Prealpi Carniche). Soc. Ven. Sc. Nat. 20: 33-52.
- Le Moli F., and M. R. Rose. 1991. Atti della Societa Italiana di Societa Italiana di Scienze Naturali e del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milan. Atti della Società Italiana di Scienze Naturali e del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano 132:25-40.
- Lebas C., C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, X. Espadaler, and R. Blatrix. 2015. The exceptional diversity of ants on mount Coronat (Pyrénées-Orientales), and Temnothorax gredosi(Hymenoptera, Formicidae) new to France. R.A.R.E., T. XXIV (1): 24 33
- Legakis A. 1983. The Zoological Museum of the University of Athens 2. The collection of ants from Greece. Biologia Gallo-Hellenica 11(1): 85-87.
- Legakis Collection Database
- Lelej A. S. 2012. Annotated catalogue of the Insects of Russian Far East. Volume 1. Hymenoptera. Dalnauka: Vladivostok. 635 p.
- Lenoir A. 1971. Les fourmis de Touraine, leur intérêt biogéographique. Cahiers des Naturalistes 27: 21-30.
- Li Z.h. 2006. List of Chinese Insects. Volume 4. Sun Yat-sen University Press
- Livory A. 2003. Les fourmis de la Manche. L'Argiope 39: 25-49.
- Livory A. Un Nouvel Inventaire: les Fourmis. Argiope 29: 27-34.
- Lomnicki J. 1928. Spis mrówek Lwowa i okolicy. Ksiegi Pamiatkowej (Lecia Gimn. IV Jana Dlugosza Lwowie) 50: 1-10.
- Lomnicki, J.. "Une contribution à la connaissance de la faune des fourmis des îles Baléares." Polskie Pismo Entomologiczne - Bulletin Entomologique de Pologne 4 (1925): 1-3.
- Maavara V. 1953. Ants of Estonian SSR. ABIKS loodusevaatlejale 10: 1-44.
- Majzlan O., and P. Devan. 2009. Selected insect groups (Hymenoptera, Neuroptera, Mecoptera, Raphidioptera) of the Rokoš Massif (Strážovské vrchy Mts.). Rosalia (Nitra), 20, p. 63–70.
- Malozemova L. A. 1972. Ants of steppe forests, their distribution by habitats, and perspectives of their utilization for protection of forests (north Kazakhstan). [In Russian.]. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 51: 57-68.
- Marikovsky P. I. 1979. Ants of the Semireche Desert. [In Russian.]. Alma Ata: Nauka, 263 pp.
- Markó B. 1997. Contribution to the Knowledge of the Ant-Fauna (Hymenoptera: Fromicoidea) of the Cri?ul-Repede River-Valley. In: Sárkány-Kiss, A., Hamar, J. (szerk.): The Cri?/Körös Rivers' Valleys. A study of the geography, hydrobiology and ecology of the river system and its environment. Tiscia Monograph Series 2, Szolnok-Szeged-Tîrgu Mure?, pp. 345-352.
- Markó B., B. Sipos, S. Csősz, K. Kiss, I. Boros, and L. Gallé. 2006. A comprehensive list of the ants of Romania (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 9: 65-76.
- Martínez Ibáñez, M. D., C. Ornosa, and P. Gamarra. "Urban fauna. Hymenoptera in Madrid households, with special reference to ants." Entomofauna 18 (26) (1997): 417-428.
- Martínez Ibáñez, M. D., and J. M. Serrano Talavera. "Contribución al conocimiento de las hormigas (Hym. Formicidae) del sabinar español." Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia Suplemento Actas Do I (1985): 33-41.
- Maruyama M., F. M. Steiner, C. Stauffer, T. Akino, R. H. Crozier, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2008. A DNA and morphology based phylogenetic framework of the ant genus Lasius with hypotheses for the evolution of social parasitism and fungiculture. BMC Evolutionary Biology 8:Article 237 (doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-237).
- Mayr, G.. "Formicina austriaca. Beschreibung der bisher im österreichischen Kaiserstaate aufgefundenen Ameisen, nebst Hinzufügung jener in Deutschland, in der Schweiz und in Italien vorkommenden Arten." Verhandlungen der Zoologisch-Botanischen Vereins in Wien 5 (1855): 273-478.
- Menozzi C. 1928. Note sulla mirmecofauna paleartica. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Zoologia Generale e Agraria della Reale Scuola Superiore d'Agricoltura. Portici. 21: 126-129.
- Menozzi C. 1939. Formiche dell'Himalaya e del Karakorum raccolte dalla Spedizione italiana comandata da S. A. R. il Duca di Spoleto (1929). Atti della Società Italiana di Scienze Naturali e del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano. 78: 285-345.
- Menozzi, C.. "Zur Kenntnis der Ameisenfauna der Balearen." Zoologischer Anzeiger 66 (1926): 180-182.
- Meyer M., C. Braunert, R. Gerend, and I. Schrankel. 2003. Résultats de l'excursion annuelle du groupe de travail entomologique de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois. Bull. Soc. Nat. luxemb. 103: 103-120.
- Morisita M. 1945. Ants of the southern part of Hokkaido, Japan. [In Japanese.] Mushi 16:21-28.
- Mortazavi Z. S., H. Sadeghi, N. Aktac, L. Depa, L. Fekrat. 2015. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and their aphid partners (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Mashhad region, Razavi Khorasan Province, with new records of aphids and ant species for fauna of Iran. Halteres 6:4-12.
- Müller, G.. "Le formiche della Venezia Guilia e della Dalmazia." Bollettino della Società Adriatica di Scienze Naturali in Trieste 28 (1923): 11-180.
- Nadig A. 1918. Alcune note sulla fauna dell'alta Valsesia. Formicidae. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 56: 331-341.
- Navás, L.. "Excursió entomologica al Cabrerés (Gerona-Barcelona)." Trab. Mus. Cienc. Nat. Barcelona vol IV nº (1924).
- Neumeyer R., and B. Seifert. 2005. Commented check list of free living ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species of Switzerland. Bulletin de la Societe Entomologique Suisse 78: 1-17.
- Nielsen M. G. 2011. A check list of Danish ants and proposed common names. Ent. Meddr. 79: 13-18.
- Novgorodova T. A., A. S. Ryabinin. 2015. Trophobiotic associations between ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) and aphids (Hemiptera, Aphidomorpha) in South Zauralye. News of Saratov University. Chemistry Series, Biology, Ecology 2(15): 98-107.
- Nylander, W.. "Synopsis des Formicides de France et d'Algérie." Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie (4)5 (1856): 51-109.
- O'Rourke F. J. 1948. The distribution and general ecology of the Irish Formicidae. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy. Section B: Biological, Geological, and Chemical Science 52: 383-410.
- Ogata. K., Touyama, Y. and Choi, B. M. 1994. Ant fauna of Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 18: 18-25
- Ortiz, F. J.. "Formícidos del litoral granadino." Memoria de Licenciatura Universida (1985): 206 pp.
- Paik W.H. 1984. A checklist of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Korea. Korean J. Plant Prot. 23(3): 193-195.
- Palanca, A., A. Urbieta, C. Castán, and X. Espadaler. "Ants in the supraforestal pastures of the Tendeñera massif." Écologie des milieux montagnards et de haute altitude. Documents d'Ecologie Pyrénéenne III-IV (1984): 223-224.
- Paraschivescu D. 1972. Fauna mirmecologica din zonele saline ale Romaniei. Studii si Cercetari de Biologie. Seria Zoologie 24: 489-495.
- Paraschivescu D. 1978. Elemente balcanice in mirmecofauna R. S. Romania. Nymphaea 6: 463- 474.
- Park S. H., S. Hosoishi, K. Ogata, and Y. Kuboki. 2014. Clustering of ant communities and indicator species analysis using self-organizing maps. Comptes Rendus Biologies http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2014.07.003
- Park S.J., and B.J. Kim. 2002. Faunal comparison of ants among Cheongsando and other islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(1): 7-12.
- Park, Seong, Joon and Byung, and Kim, Jin. 2002. Faunal Comparison of Ants among Cheongsando and Other Islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Jornal of Entomology. 32(1):7-12.
- Pashaei Rad S., B. Taylor, R. Torabi, E. Aram, G. Abolfathi, R. Afshari, F. Borjali, M. Ghatei, F. Hediary, F. Jazini, V. Heidary Kiah, Z. Mahmoudi, F. Safariyan, and M. Seiri. 2018. Further records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Iran. Zoology in the Middle East 64(2): 145-159.
- Pavlova N. S. 2014. To ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the floodplain of Medvedista River (Saratov Province). Entomological and parasitological studies in the Volga region 11: 145-147.
- Petal J. M. 1967. Contribution a la connaissance des fourmis (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) de la region de Lublin. VII. Associations des fourmis des milieux de tourbieres, de forets et de dunes aux environs de Libiszow (dist. De Parczew). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Lublin-Polonia 22(9): 117-130.
- Petrov I. Z. 1986. Contribution to myrmecofauna in some oak-tree communities on the mountain Jastrebac. Prirodnjackog Muzeja i Beogradu Seriya B Bioloske Nauke Supplement: No. 41: 109-114.
- Petrov I. Z. 2010. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Krusevac and its surroundings. Acta entomologica serbica, 2010, 15(1): 145-148.
- Petrov I. Z. 2012. Preliminary data on ants (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) on Mountain Avala (Belgrade, Serbia). Bulletin of the Natural History Museum 5: 95-99.
- Petrov I. Z., B. Petrov, D. Milicic, T. Karan-Znidarsic. 2007. Contribution to the Myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of East and South Serbia. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 59(3): 295-299.
- Petrov I. Z., and C. A. Collingwood. 1992. Survey of the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of Yugoslavia. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade) 44: 79-91.
- Pisarski B. 1969. Fourmis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) de la Mongolie. Fragmenta Faunistica (Warsaw). 15: 221-236.
- Poldi B., M. Mei, and F. Rigato. 1995. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Vol 102. Checklist delle specie della fauna Italiana: 1-10.
- Pusvaskyte O. 1979. Myrmecofauna of the Lituanian SSR. Acta Entomologica Lituanica 4: 99-105.
- Radchenko A., W. Czechowska, W. Czechowski, and E. Siedlar. 1999. Four species of the ant genus Lasius F. new to Poland, with additions to the records for previously reported species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Fragmenta Faunistica 42(11): 115-121.
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.
- Rasheed M. T., I. Bodlah, A. G. Fareen, A. A. Wachkoo, X. Huang, and S. A. Akbar. 2019. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Pakistan. Sociobiology 66(3): 426-439.
- Restrepo, C., X. Espadaler, and Andrés de Haro. "Contribución al conocimiento faunístico de los formícidos del Macizo de Garraf (Barcelona)." Orsis (Organismes i Sistemes) 1 (1986): 113-129.
- Retana J., and X. Cerdá X. 2000. Patterns of diversity and composition of Mediterranean ground ant communites tracking spatial and temporal variability in the thermal environment. Oecologia 123: 436-444.
- Reznikova Z. I. 2003. Distribution patterns of ants in different natural zones and landscapes in Kazakhstan and West Siberia along a meridian trend. Euroasian Entomological Journal 2(4): 235-342.
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1989. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna della Val Gesso (alpi Marittime) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boll. Mus. Reg. Sci. Nat. Torino 7(2): 427-442.
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1991. The myrmecofauna of the Gesso Valley (Maritime Alps) (Hymenoptera Formicidae). Ethology Ecology and Evolution Special Issue 1: 87-89.
- Ruzsky M. 1916. On zoological research in Yeniseisk province, work of summer of 1915. Izv. Imp. Tomsk. Univ. 65 (3rd p part: 1-21.
- Rzeszowski K., H. Babik, W. Czechowski, and B. Marko. 2013. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Chelmowa Gora in the Swietokrzyski National Park. Fragmenta Faunistica 56(1): 1-15.
- Salata S., and L Borowiec. 2017. Species of Tetramorium semilaeve complex from Balkans and western Turkey, with description of two new species of (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Myrmicinae). Annales Zoologici (Warsaw) 62:279–313.
- Salata S., and L. Borowiec. 2018. Taxonomic and faunistic notes on Greek ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Entomology 27: 1-51.
- Salata S., and L. Borowiec. 2019. Preliminary division of not socially parasitic Greek Temnothorax Mayr, 1861 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) with a description of three new species. ZooKeys 877: 81-131.
- Sanchez-Gil Jimeno R., and J. L. Reyes-Lopez. 2016. Study of ants species of the Sierra de San Carlos del Valle (Ciudad Real) and updating the provincial check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent. 40 (1-2): 93-109.
- Sanders, D. and C. Platner. 2007. Intraguild Interactions between Spiders and Ants and Top-Down Control in a Grassland Food Web. Oecologia 150(4):611-624
- Santschi F. 1925. Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1: 339-360.
- Santschi F. 1926. Travaux scientifiques de l'Armée d'Orient (1916-1918). Fourmis. Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle 32: 286-293.
- Santschi, F.. "Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques." EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1 (1925): 339-360.
- Sato T., N. Tsurusaki, K. Hamaguchi, and K. Kinomura. 2010. Ant fauna of Tottori prefecture, Honshu, Japan. Bulletin of the Tottori Prefectural Museum 47: 27-44.
- Schar S., G Talavera, X. Espadaler, J. D. Rana, A. A. Andersen, S. P. Cover, and R. Vila. 2018. Do Holarctic ant species exist? Trans-Beringian dispersal and homoplasy in the Formicidae. Journal of Biogeography 00: 1-12.
- Schembri, Stephen P. and Cedric A. Collingwood. A Revision of the Myrmecofauna of the Maltese Islands. 417-442.
- Schlick-Steiner B. C., and F. M. Steiner. 1999. Faunistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen an den freilebenden Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Wiens. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 3: 9-53.
- Scupola I. 2009. Le formiche delle Isole Egadi (Sicilia) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bollettino del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Verona Botanica Zoologia 33: 97-103
- Seifert B. 1992. A taxonomic revision of the Palaearctic members of the ant subgenus Lasius s.str. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 66(5): 1-67.
- Seifert, B.. "A taxonomic revision of the Palaearctic members of the ant subgenus Lasius s. str." Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Goerlitz 66(5) (1992): 1-66.
- Sellier Y., C. Galkowski, C. Lebas, and P. Wegnez. 2016. Découverte de Temnothorax pardoi (Tinaut, 1987) dans la réserve naturelle nationale du Pinail (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Revue de l’Association Roussillonnaise d’Entomologie 25(2): 106-113.
- Shilenkov V. G., A. A. Pankratov, and E. V. Sofronova. 2012. Preliminirary notes on species composition of Magdansky Reserve. Baikal Zoological Journal 3: 30-34.
- Siberian Zoological Museum. Website available at http://szmn.sbras.ru/old/Hymenop/Formicid.htm. Accessed on January 27th 2014.
- So, Ha, Seong, Jin, Park, Joon and Byung, and Kim, Jin. 2002. Comparitive Ant Faunas between Seonyudo and Seven other Islands of West Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology. 32:75-79.
- Sommer F. 1984. Etude de la myrmécofaune de la réserve de la Massane. Laboratoire Arago, Banyuls sur Mer (66), 29 pages.
- Sommer F., and H. Cagniant. 1988. Peuplements de fourmis des Albères Orientales (Pyrénées-Orientales, France) (Première partie). Vie Milieu 38: 189-200.
- Sonnenburg H. 2005. Die Ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Niedersachsens und Bremens. Braunschweiger Naturkundliche Schriften 7: 377-441.
- Soudek, S.. "Dalmatsti mravenci." Casopis Csl. Spolecnosti Entomologické 20 (1-2) (1925): 12-17.
- Soulie J. 1962. Fourmis des Hautes-Pyrenees. Bull. Soc. Hist. Nat. Toulouse 97: 35-37.
- Staab M., A. Schuldt, T. Assmann, H. Bruelheide, and A.M. Klein. 2014. Ant community structure during forest succession in a subtropical forest in South-East China. Acta Oecologia 61: 32-40.
- Steiner F. M., S. Schödl, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2002. Liste der Ameisen Österreichs (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Stand Oktober 2002. Beiträge zur Entomofaunistik 3: 17-25.
- Stiprais M. 1973. Materi?li par R?gas kukai?u faunu. - Latvijas Entomologs, 15: 30-32.
- Stumper R. 1953. Etudes myrmecologiques. XI. Fourmis luxembourgeoises. Bulletin Soc. Nat. luxemb. 57: 122-135.
- Suvak M. 2007. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the stubble-fields of east Slovakia. Acta Zoologica Universitatis Comenianae. 47: 21-33
- Suñer i Escriche, David. "Contribució al coneixement mirmecologic de Gavarres, Montgrí, Guilleríes i la Serralada Transversal." Tesis Doctoral Universida (1991): 577 pp.
- Szujecki A., J. Szyszko, S. Mazur, and S. Perlinski. 1978. A succession of the ants (Formicidae) on afforested arable land and forest soils. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 183-189.
- Talavera G., X. Espadaler, and R. Vila. Discovered just before extinction? The first endemic ant from the Balearic Islands (Lasius balearicus sp. nov.) is endangered by climate change. Journal of Biogeography doi:10.1111/jbi.12438
- Tang Jue, Li Shen, Huang Enyou, Zhang Benyue. 1985. Notes on ants from Zhoushan islands , Zhejiang (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Chekianensis 11(3): 307-318.
- Tang Jue, Li Shen, Huang Enyou, Zhang Benyue. 1985. Notes on ants from Zhoushan Islands Zhejiang (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric.& Life Sci.) 3.
- Tausan I., M. M. Jerpel, I. R. Puscasu, C. Sadeanu, R. E. Brutatu, L. A. Radutiu, and V. Giurescu. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Sibiu County (Transylvania, Romania). Brukenthal. Acta Musei 7(3): 499-520.
- Terayama M. 1977. Checklist of the known ants of Saitama Prefecture. Insects and nature 12(4): 26-27
- Terayama M. 1992. Structure of ant communities in East Asia. A. Regional differences and species richness. Bulletin of the Bio-geographical Society of Japan 47: 1-31.
- Terayama M., Choi, B.M., Kim, C.H. 1992. A check list of ants from Korea, with taxonomic notes. Bulletin of the Toho Gakuen 7:19-54.
- Terayama M., K. Ogata, and B.M. Choi. 1994. Distribution records of ants in 47 prefectures of Japan. Ari (report of the Myrmecologists Society of Japan) 18: 5-17.
- Terayama M., and R. Sonobe. 2002. Ants from the Nasu Imperial Villa, Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. Flora and fauna of the Tochigi Prefectural Museum research report Nasu Imperial Villa 157-161.
- Ticha, K. 2005. Inventarizacní pruzkum mravencu (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) NPP Svarec. 2005. Acta Rerum Naturalium 1:127-130.
- Tinaut A. 2016. Ants of the Tejeda, Almijara and Alhama Mountains Natural Park (Andalusia, Spain) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent., 40 (1-2): 125-159.
- Tinaut, A., J. Jiménez Rojas, and R. Pascual. "Estudio de la mirmecofauna de los bosques de Quercus Linneo 1753 de la provincia de Granada." Ecología 8 (1995): 429-438.
- Tinaut, A., M. D. Martínez Ibáñez, and J. Vidal. "Primer inventario de los formícidos de Navarra. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae)." Munibe 58 (2010): 79-84.
- Tiwari R.N., B.G. Kundu, S. Roychowdhury, S.N. Ghosh. 1999. Insecta: Hymenoptera: Formicidae. Pp. 211-294 in: Director; Zoological Survey of India (ed.) 1999. Fauna of West Bengal. Part 8. Insecta (Trichoptera, Thysanoptera, Neuroptera, Hymenoptera and Anoplura). Calcutta: Zoological Survey of India, iv + 442 pp.
- Tizado Morales, E. J.. Estudio comparado de la fauna y la biología de pulgones (Hom.), afidíinos (Hym.) y otros insectos acompañantes en dos áreas de la provincia de León In Secretariado de Publicaciones, Tesis doctoral en microficha, nº 67. León: Universidad de León, 1991.
- Tohme G. 1996. Formicidae. Etude de la diversité biologique n° 4 . Ministère de lAgriculture à Beyrouth (Eds.). P85-87.
- Tohme G., and H. Tohme. 2014. Nouvelles liste des especes de fourmis du Liban (Hymenoptera, Formicoidea). Lebanese Science Journal 15(1): 133-141.
- Umair M., A. Zia, M. Naeem, and M. T. Chaudhry. 2012. Species composition of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Potohar Plateau of Punjab Province, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Zoology 44(3): 669-705.
- Urbieta Balado A., A. Palanca Soler, C. Castan Lanaspa, and X. Espadaler. 1984. Ants in the supraforestal pastures of the Tendenera massif. Documents dEcologie Pyrénéenne III-IV: 223-224.
- Vagalinski B., and A. Lapeva-Gjonova. 2012. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Plana Mountain (Bulgaria). Historia naturalis bulgarica 20: 87-101.
- Van Loon A. J., J. J. Boomsma, and A. Andrasfalvy. 1990. A new polygynous Lasius species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from central Europe. I. Description and general biology. Insectes Soc. 37: 348-362.
- Vassilev I. 1987. The ants (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) from the valley of the river Racene. Annuaire de l'Universite de Sofia Kliment Ohridski Faceulte de Biologie 78: 74-79.
- Vele A., J. Holisa, J. Tragnerova. 2015. Ant succession on burned areas in forested landscape: a case study from the Bohemian Switzerland National Forest. Zpravy Lesnickeho Vyzkumu 60(1): 47-52.
- Vesni? A. 2011: Revidirani sistematski prijegled mrava Bosne i Hercegovine. Unutar : S. Lelo (urednik), Fauna Bosne i Hercegovine Biosistematski pregledi. 7. izmijenjeno i popravljeno interno izdanje Udruenja za inventarizaciju i zatitu ivotinja, Ilija, Kanton Sarajevo, pp: 205-207.
- Vicidomini S., and C. Pignataro. 2007. Contributo alla conoscenza della biodiversità del Parco Nazionale del Cilento e Vallo di Diano: gli Imenotteri veleniferi più comuni e check-list delle specie di Apoidea e Formicidae della provincia di Salerno. Il Naturalista Campano 34: 1-15.
- Vogrin, V.. "Prilog fauni Hymenoptera - Aculeata Jugoslavije." Zast. Bilja 31(suppl.) (1955): 1-74.
- Wegnez P. 2014. Premières captures de Lasius distinguendus Emery, 1916 et de Temnothorax albipennis (Curtis, 1854) au Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 150 (2014) : 168-171.
- Wegnez P. 2018. Premières decouvertes de Myrmica bibikoffi Kutter, 1963 et de Ponera testacea Emery, 1895, au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 154: 263–272.
- Wegnez P., and A. Ronk. 2017. Découverte de Camponotus herculeanus (Linnaeus, 1758) et signalement de quelques autres espèces rares de fourmis au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois 119 : 153–159.
- Wegnez P., and M. Fichaux. 2015. Liste actualisee des especes de fourmis repertoriees au Grand-Duche de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 150-165
- Wheeler W. M. 1928. Ants collected by Professor F. Silvestri in China. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Zoologia Generale e Agraria della Reale Scuola Superiore d'Agricoltura. Portici 22: 3-38.
- Wheeler W. M. 1930. A list of the known Chinese ants. Peking Natural History Bulletin 5: 53-81.
- Wiezick M. 2008. Ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of forest-steppe habitats at southern and South-Western slopes of Plesivecka a Planina plateau at Slovensky Kras Karst. Natura Carpatica 49: 85-94.
- Wiezik M. 2006. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formiciadae) of the Sitno National Nature Reserve (tiavnické vrchy Protected Landscape Area). Naturae Tutela 10: 73-77.
- Wiezik M., A. Wiezikova, and M. Svitok. 2011. Vegetation structure, ecological stability, and low-disturbance regime of abandoned dry grasslands support specific ant assemblages in Central Slovakia. Tuexenia 31: 301315.
- Wilson E. O. 1955. A monographic revision of the ant genus Lasius. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 113: 1-201
- Wu wei, Li Xiao Mei, Guo Hong. 2004. A primary study on the fauna of Formicidae in Urumqi and its vicinities. Arid Zone Research 21(2): 179-182
- Xin M. et al. 2011. Community structure of Hymenoptera fauna in Helan Mountain of Ningxia. Journal of Anhui Agri. Sci. 39(25): 15339-15341.
- Yamauchi K. 1968. Additional Notes on the Ecological Distribution of Ants in Sapporo and the Vicinity . Journal of the Faculty of Science Hokaido University, series VI, Zoology 16(3): 382-395.
- Yamauchi K. 1979. Taxonomical and ecological studies on the ant genus Lasius in Japan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). I. Taxonomy. Sci. Rep. Fac. Educ. Gifu Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 6: 147-181.
- Yang Jun, Xu Zheng-hui, Mei Xiang-xin, Zhang Ji-ling, Zhao Yu-xiang. 2004. Taxonomy of Ants on the Eastern Slope of Xishan Mountains in Kunming. Journal of Southwest Forestry College 24(4): 26-37.
- Yoshimura M. 1999. Ants in the island of Hokkaido (Part 2, Part Rebun) Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 2, Rebun-Island). Rishiri Studies 18: 49-54.
- Zhigulskaya Z. A. 2009. The ants of the Chuya Depression and the Yustyd river basin in Southeastern Altai. Contemporary Problems of Ecology 2009 2(3): 210-215.
- Zhigulskaya Z. A., T. M. Krugova, and N. A. Bulakhova. 2018. Wintering conditions and the cold resistance of ants Lasius alienus and L. psammophilus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the south of Siberia. Fauna of the Urals and Siberia 2: 16-24.
- Zhu Xun. 2002. Study on flora of ants in Hunan province. Journal of Hunan Environment-Biological Polytechnic 8(3): 172-174.
- Zimmermann, S.. "Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Ameisenfauna Süddalmatiens." Verhandlungen der Zoologisch-Botanisch Gesellschaft in Wien 84 (1935): 1-65.
- Zimmermann, S.. "Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Ameisenfaunader Quarnerischen Inseln." Verhandlungen der Zoologisch-Botanisch Gesellschaft in Wien 80 (1930): 45-66.
- Zryanin V. A., and T. A. Zryanina. 2007. New data on the ant fauna Hymenoptera, Formicidae in the middle Volga River Basin. Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii 127(2): 226-240.
- de Biseau, J.-C., Y. Quinet, L. Deffernez and J.M. Pasteels. 1997. Explosive food recruitment as a competitive strategy in the ant Myrmica sabuleti (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insectes Sociaux 44:59-73
- de Haro, Andrés, C. A. Collingwood, and P. Comín del Río. "Prospección mirmecológica por Ibiza y Formentera (Baleares)." Orsis 2 (1986): 115-120.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Formícidos de las Sierras de Prades-Montsant, Sierras de Cavalls-Alfara-Montes Blancos (Tarragona)." Boletín de la Estación Central de Ecología 10 (1981): 55-58.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica en la Cordillera Ibérica." Orsis 6 (1991): 129-126.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica por las sierras de Aitana-Alfaro y los cabos de la Nao-San Antonio (Alicante) y su comparación con la fauna balear y de Córcega-Cerdeña." Orsis 3 (1988): 165-172.
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Limited invasive
- Common Name
- North temperate
- North subtropical
- Tropical
- FlightMonth
- Ant Associate
- Host of Lasius carniolicus
- Host of Lasius claviger
- Host of Lasius distinguendus
- Host of Lasius interjectus
- Host of Lasius jensi
- Host of Lasius latipes
- Host of Lasius meridionalis
- Host of Lasius reginae
- Host of Lasius umbratus
- Aphid Associate
- Host of Aphis fabae
- Host of Aphis galliiscabri
- Host of Aphis gossypii
- Host of Aphis idaei
- Host of Aphis maidi-radicis
- Host of Aphis molluginis
- Host of Aphis nasturtii
- Host of Aphis pomi
- Host of Aphis pseudocardui
- Host of Aphis solanella
- Host of Aphis urticata
- Host of Aphis verbasci
- Host of Brachycaudus (Appelia) tragopogonis
- Host of Brachycaudus cardui
- Host of Capitophorus hippophaes
- Host of Chaitophorus kapuri
- Host of Cinara atlantica
- Host of Cinara palaestinesis
- Host of Cinara pini
- Host of Dysaphis foeniculus
- Host of Dysaphis pyri
- Host of Myzus cerasi
- Host of Neobetulaphis pusilla
- Host of Periphyllus bulgaricus
- Host of Rhopalosiphum cerasifoliae
- Host of Rhopalosiphum maidis
- Host of Rhopalosiphum nymphaeae
- Host of Sipha maydis
- Host of Toxoptera aurantii
- Butterfly Associate
- Host of Glaucopsyche alexis
- Ichneumonid wasp Associate
- Host of Hybrizon buccatus
- Host of Hybrizon rileyi
- Phorid fly Associate
- Host of Pseudacteon formicarum
- Tachinid fly Associate
- Host of Strongylogaster globula
- ''Microdon'' fly Associate
- Host of Microdon ruficrus
- Mite Associate
- Host of Imparipes obsoletus
- Host of Petalomium carelitschensis
- Host of Scutacarus longisetus
- Nematode Associate
- Host of "Mermis"
- Host of Mermithidae (unspecified "Mermix")
- Host of Mermis myrmecophila
- Fungus Associate
- Host of Laboulbenia formicarum
- Photo Gallery
- Karyotype
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Lasiini
- Lasius
- Lasius alienus
- Formicinae species
- Lasiini species
- Lasius species
- Ssr


