Lasius meridionalis
| Lasius meridionalis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Lasiini |
| Genus: | Lasius |
| Section: | flavus clade |
| Species group: | umbratus |
| Species: | L. meridionalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Lasius meridionalis (Bondroit, 1920) | |
| Common Name | |
|---|---|
| Higenaga-ameiro-ke-ari | |
| Language: | Japanese |
This species is characteristic of lowland sandy heath in North Europe and is found in forests and at forest margins in Japan. Nests are in the ground, often with low earth mounds and carton lined chambers (Europe) or in tree trunks, near the roots of standing trees (Japan). Flight period August in Europe and July to September in Japan. Fertilised queens start colonies through adoption by established nests of Lasius alienus (unconfirmed), Lasius hayashi, Lasius japonicus, Lasius niger (unconfirmed) and Lasius psammophilus (de la Mora et al., 2021; Janda et al., 2004; Seifert, 2018). Males, which have well toothed mandibles, have been seen to pick up objects and to feed themselves (Collingwood, 1979; Japanese Ant Image Database).
| At a Glance | • Temporary parasite |
Identification
Collingwood (1979) - Clear yellow; pubescence on head rather dilute but close and very fine on gaster. Funiculus segments distinctly longer than wide; scapes and tibiae elliptical in cross section with thin front edge. Petiole sides straight to weakly convex, dorsal margin flat to slightly emarginate. Body and appendage hairs numerous. Length: 3.5-5 mm.
Resembles Lasius umbratus but the different habits, flat appendages and rectangular scale in the queen, shining darker colour and fine sculpture in queen and male clearly distinguish the species from L. umbratus, although workers may be less easy to separate.
Keys including this Species
Distribution
Spain to Japan, ltaly to Scandinavia (Collingwood 1979).
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 61.2996° to 33.01222222°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Palaearctic Region: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Czechia, Democratic Peoples Republic of Korea, Denmark, Finland, France (type locality), Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iberian Peninsula, Japan, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Türkiye, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |

|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |
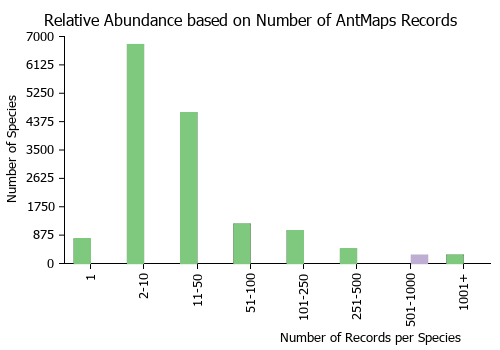
|
Habitat
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - No confirmed or recent data from Greece. In other countries it was noted from sandy xerothermous grassland and grassy parts of open sandy heaths, more rarely in limestone grassland and xerothermous patches on rock. In Greece, most likely is occurs in mountains and inhabits open habitats.
Biology
Flight Period
| X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Source: antkeeping.info.
- Check details at Worldwide Ant Nuptial Flights Data, AntNupTracker and AntKeeping.
 Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
This species is a host for the ant Lasius fuliginosus (a temporary parasite) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018) (as Lasius meridionalis x umbratus).
Castes
Queen
Images from AntWeb
    
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0172711. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- meridionalis. Formicina meridionalis Bondroit, 1920a: 143 (q.) FRANCE. Stärcke, 1937: 52 (w.m.). Combination in Lasius: Emery, 1922b: 13; in L. (Chthonolasius): Emery, 1925b: 234. Subspecies of umbratus: Emery, 1922b: 13; Menozzi, 1925d: 34; Stitz, 1939: 295; Novak & Sadil, 1941: 103. Status as species: Stärcke, 1937: 50. Junior synonym of rabaudi: Wilson, 1955a: 168; Bernard, 1967: 364. Revived from synonymy, status as species: Pisarski, 1975: 37; Collingwood, 1979: 102; Seifert, 1988: 154; Kupyanskaya, 1990: 226; Atanassov & Dlussky, 1992: 247.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - Monomorphic, small to moderately large, HL 0.841-0.952, HW 0.825- 0.921, ML 0.96-1.08. Scape moderately elongate, SL 0.714-0.833. Color. Whole body including appendages pale yellow. Structure and setation. Head slightly longer than wide, sides rounded, occipital margin straight to slightly concave. Eyes very small, head length at least 6.6 times the maximum diameter of eye. Whole frontal head covered with moderately long, appressed and moderately dense pubescence and sparse, long, erected setae, surface well visible, microsculptured but shiny. Occipital part of head with 12-18 long erected setae. Gena and underside of head with numerous erected setae. Mesosomal dorsum with several long erected setae, length of the longest seta 0.135. Below propodeal spiracle1-2 short erected setae. Antennal scapi distinctly flattened, with short appressed and slightly decumbent pubescence and in apical 2/3 length, with suberect hair. Hind tibiae broad and flattened, HTmax/CS up to 0.1449, with 5-40 suberect to erected setae on external surface. Ventral surface of femora with several erected setae, anterior surface of fore coxa with few long erected setae. Pubescence on the whole body and appendages moderately dense and whitish. Pubescence of clypeus sparse, not covering clypeus surface. Surface of gastral tergites with microsculpture but shiny, first gastral tergite on the whole surface with dense, moderately long erected setae. Petiolar scale nearly parallelsided, upper margin with shallow median emargination. Propodeum in lateral view high, slightly conical, metanotal groove deep.
References
- Atanassov, N.; Dlussky, G. M. 1992. Fauna of Bulgaria. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Fauna Bûlg. 22: 1-310 (page 247, Revived from synonymy, status as species)
- Bernard, F. 1967a [1968]. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp. (page 364, Junior synonym of rabaudi)
- Boer, P. 2008. Observations of summit disease in Formica rufa Linnaeus, 1761 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 11. 63-66.
- Bondroit, J. 1920a [1919]. Notes diverses sur des fourmis d'Europe. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 59: 143-158. (page 143, queen described)
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. A monographic review of ants of Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Vol. 1. Introduction and review of all subfamilies except the subfamily Myrmicinae. Part 1: text. Natural History Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum 1: 1-297.
- Collingwood, C. A. 1979. The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Fauna Entomol. Scand. 8: 1-174 (page 102, Revived from synonymy, status as species)
- Csősz, S., Báthori, F., Gallé, L., Lőrinczi, G., Maák, I., Tartally, A., Kovács, É., Somogyi, A.Á., Markó, B. 2021. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: Survey of ant species with an annotated synonymic inventory. Insects 16;12(1):78 (doi:10.3390/insects12010078).
- Csosz, S., Marko, B., Galle, L. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A., Czechowska, W. 2002. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Poland. MIZ PAS Warsaw.
- Dekoninck, W., Boer, P., Maelfait, J.-P. 2004. Lasius platythorax SEIFERT, 1991 as a host of several Chthonolasius species, with remarks on the colony foundation of the parasites (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 6: 5-8.
- Dekoninck, W., Ignace, D., Vankerkhoven, F., Wegnez, P. 2012. Verspreidingsatlas van de mieren van België. Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 148: 95-186.
- Emery, C. 1922b. Il genere Lasius (F.) Mayr e particolarmente le forme mediterranee del gruppo umbratus Nyl. Boll. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 54: 9-15 (page 13, Combination in Lasius)
- Emery, C. 1922b. Il genere Lasius (F.) Mayr e particolarmente le forme mediterranee del gruppo umbratus Nyl. Boll. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 54: 9-15 (page 13, Variety of umbratus)
- Emery, C. 1925d. Hymenoptera. Fam. Formicidae. Subfam. Formicinae. Genera Insectorum 183: 1-302 (page 234, Combination in L. (Chthonolasius))
- Hisasue, Y. 2020. A checklist of the ants of Mt. Hiko-san (Kyushu, Japan). Korasana 93: 31-38.
- Imai, H.T., Kihara, A., Kondoh, M., Kubota, M., Kuribayashi, S., Ogata, K., Onoyama, K., Taylor, R.W., Terayama, M., Yoshimura, M., Ugawa, Y. 2003. Ants of Japan. 224 pp, Gakken, Japan.
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C. 2020. Additions to the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoosystema 42(18), 285-329 (doi:10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a18).
- Kupyanskaya, A. N. 1990a. Ants of the Far Eastern USSR. Vladivostok: Akademiya Nauk SSSR, 258 pp. (page 226, Revived from synonymy, status as species)
- Kwon, T.-S. 2015. Ant assemblages along the Baekdudaegan Mountain Range in South Korea: Human roads and temperature niche. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity 8, 152–157 (doi:10.1016/j.japb.2015.05.001).
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Antonova, V., Ljubomirov, T. 2021. Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Sarnena Sredna Gora Mountains (Bulgaria). Fauna of Sarnena Sredna Gora Mts, Part 2 ZooNotes, Supplement 10: 18-27.
- Menozzi, C. 1925d [1924]. Res mutinenses. Formicidae (Hymenoptera). Atti Soc. Nat. Mat. Modena 55[=(6)3 3: 22-47 (page 34, Variety of umbratus)
- Novák, V.; Sadil, J. 1941. Klíc k urcování mravencu strední Evropy se zvlástním zretelem k mravencí zvírene Cech a Moravy. Entomol. Listy 4: 65-115 (page 103, Variety of umbratus)
- Pisarski, B. 1975. Mrówki Formicoidea. Kat. Fauny Pol. 26: 3-85 (page 37, Revived from synonymy, status as species)
- Ryu, J., Kim, Y.-K., Suh, S.J., Choi, K.S. 2021. The Insect database in Dokdo, Korea: An updated version in 2020. Biodiversity Data Journal 9, e62011 (doi:10.3897/bdj.9.e62011).
- Seifert, B. 1988a. A revision of the European species of the ant subgenus Chthonolasius (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Entomol. Abh. Staatl. Mus. Tierkd. Dres. 51: 143-180 (page 154, Revived from synonymy, status as species)
- Stärcke, A. 1937. Retouches sur quelques fourmis d'Europe. II. Lasius groupe umbratus Nylander. Tijdschr. Entomol. 80: 38-72 (page 50, Status as species)
- Stärcke, A. 1937. Retouches sur quelques fourmis d'Europe. II. Lasius groupe umbratus Nylander. Tijdschr. Entomol. 80: 38-72 (page 52, worker, male described)
- Stitz, H. 1939. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der angrenzenden Meersteile nach ihren Merkmalen und nach ihrer Lebensweise. 37. Theil. Hautflüger oder Hymenoptera. I: Ameisen oder Formicidae. Jena: G. Fischer, 428 pp. (page 295, Variety of umbratus)
- Stukalyuk, S., Radchenko, Y., Gonchar, O., Akhmedov, A., Stelia, V., Reshetov, A., Shymanskyi, A. 2021. Mixed colonies of Lasius umbratus and Lasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae): when superparasitism may potentially develop into coexistence: a case study in Ukraine and Moldova. Halteres 12, 25–48 (doi:10.5281/zenodo.5753121).
- Wilson, E. O. 1955a. A monographic revision of the ant genus Lasius. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 113: 1-201 (page 168, Junior synonym of rabaudi)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Agosti, D. and C.A. Collingwood. 1987. A provisional list of the Balkan ants (Hym. Formicidae) and a key to the worker caste. I. Synonymic list. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, 60: 51-62
- AntArea. Accessed on February 5th 2014 at http://antarea.fr/fourmi/
- Antarea (Personal Communication - Rumsais Blatrix- 27 April 2018)
- Antarea (at www.antarea.fr on June 11th 2017)
- Assing V. 1989. Die Ameisenfauna (Hym.: Formicidae) nordwestdeutscher Calluna-Heiden. Drosera 89: 49-62.
- Bezdecka P. 1996. The ants of Slovakia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomofauna carpathica 8: 108-114.
- Blacker N. C. 1989. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the Gower Peninsula, West Glamorgan, South Wales. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 101: 261-266.
- Blacker N. C. and C. A. Collingwood. 2002. Some significant new records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Salisbury area, south Wiltshire, England, with a key to the British species of Lasius. British Journal of Entomology and Natural History 15: 25-46
- Blacker N.C. 2007. Ants (Hym., Formicidae) in East Anglia-Additional Records from . Entomologist's Monthly Magazine 143: 69-90
- Boer P. 2019. Species list of the Netherlands. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/specieslist.html
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten 63(3): 54-57.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. List of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Belgium and The Netherlands, their status and Dutch vernacular names. Entomologische Berichten 63 (3): 54-58.
- Boer P., and J. Noordijk. 2004. De ruige gaststeekmier Myrmica hirsuta nieuw voor Nederland (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ned. Faun. Meded. 20: 25-32.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2012. Ants of Greece - Checklist, comments and new faunistic data (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus 23(4): 461-563.
- Bracko G. 2007. Checklist of the ants of Slovenia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natura Sloveniae 9: 15-24
- Choi B.M. 1985. Study on distribution of ants (Formicidae) from Korea (1). Formic fauna in Mt. Songni. Cheongju Sabom Taehak Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National Teachers' College) 22:401-437.
- Choi B.M. 1986. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea. Journal of Chongju National Teacher College 23: 317-386.
- Choi B.M. 1996. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (15) -Ant fauna islands Ullungdo and Dokdo. Journal of Chongju National University of Education 33: 201-219.
- Choi B.M., K. Ogata, and M. Terayama. 1993. Comparative studies of ant faunas of Korea and Japan. 1. Faunal comparison among islands of Southern Korean and northern Kyushu, Japan. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Japan 48(1): 37-49.
- Choi B.M., and J. R. Bang. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (12): the analysis of ant communities in 23 islands. Journal of Cheongju National University of Education 30:317-330.
- Collingwood C., and A. Prince. 1998. A guide to ants of continental Portugal (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia. Suplemento 5: 1-49.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "Especies raras de hormigas del género Lasius en España." Boletín de la Asociación Española de Entomología 15 (1991): 215-219.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark." Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 8 (1979): 1-174.
- Consani M., and P. Zangheri. 1952. Fauna di Romagna. Imenotteri - Formicidi. Memorie della Societa Entomologica Italiana 31: 38-48.
- Csosz S., B. Marko, K. Kiss, A. Tartally, and L. Galle. 2002. The ant fauna of the Ferto-Hansag National Park (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Mahunka, S. (Ed.): The fauna of the Fert?-Hanság National Park. Hungarian Natural History Museum, Budapest, pp. 617-629.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski W., A. Radchenko, W. Czechowska and K. Vepsäläinen. 2012. The ants of Poland with reference to the myrmecofauna of Europe. Fauna Poloniae 4. Warsaw: Natura Optima Dux Foundation, 1-496 pp
- Dekoninck W., P. Boer, and J. P. Maelfait. 2004. Lasius platythorax Seifert, 1991 as a host of several Chthonolasius species, with remarks on the colony foundation of the parasites (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 6: 5-8.
- Dubovikoff D. A., and Z. M. Yusupov. 2018. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Else G., B. Bolton, and G. Broad. 2016. Checklist of British and Irish Hymenoptera - aculeates (Apoidea, Chrysidoidea and Vespoidea). Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e8050. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e8050
- Formidabel Database
- Fowles, A.P. 1996. A provisional checklist of the invertebrates recorded from Wales. 2. Aculeate wasps, bees and ants (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Countryside Council for Wales
- Galkowski C. 2008. Quelques fourmis nouvelles ou intéressantes pour la faune de France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux, 143, N.S. 36, 4 : 423-433.
- Galle L. 1997. Contribution to the ant fauna of Slovenia with special reference to the submediterranean and eudinaric regions. Annals for Istrian and Mediterranean studies 11: 209-214.
- Gallé L. 1991. Structure and succession of ant assemblages in a north European sand dune area. Holarctic Ecology 14: 31-37.
- Giacalone I., and M. Moretti. 2001. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) dei castagneti al Sud delle Alpi (ticino, Svizzera). Bollettino della Societa ticinese di Scienze naturali 89(1-2): 51-60.
- Glaser F., A. Freitag, and H. Martz. 2012. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the Münstertal (Val Müstair) a hot spot of regional species richness between Italy and Switzerland. Gredleriana 12: 273 - 284.
- Gouraud C. 2015. Bilan de l’année 2014 : Atlas des fourmis de Loire-Atlantique (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atlas des Formicidae de Loire-Atlantique, compte rendu de la première année d’étude (2014)
- Grandi G. 1935. Contributi alla conoscenza degli Imenotteri Aculeati. XV. Boll. R. Ist. Entomol. Univ. Studi Bologna 8: 27-121.
- Guénard B., and R. R. Dunn. 2012. A checklist of the ants of China. Zootaxa 3558: 1-77.
- Ha S.J, S.J. Park, and B.J. Kim. 2002. Comparative ant faunas between Seonyudo and seven other islands of West Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(2): 75-79.
- Kim B.J. 1996. Synonymic list and distribution of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) in Korea. Entomological Research Bulletin Supplement 169-196.
- Kim B.J., K.G. Kim, D.P. Ryu, J.H. Kim. 1995. Ants of Chindo island in Korea (Hymenoptera; Formicidae). The Korean Journal of Systematic Zoology 11(1): 101-113.
- Kim B.J.; Kim, K.G.; Lim, K.H. 1993. Systematic study of ants from Chejudo province. Korean Journal of Entomology 23: 117-116
- Kim et al. 1993. Systematic study of ants from Chejudo Province. Koran Journal of Entomology 23(3): 117-141.
- Kim, Byung-Jin, Ky-Gyong Kim, Dong-Pyo Ryu and Joong-Hyon Kim. 1995. The Korean Journal of Systematic Zoology. 11(1):101-113.
- Kupianskaia A.N. 1990. Murav'I (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Dal'nego Vostoka SSSR (1989). Vladivostok. 258 pages.
- Kvamme T. 1982. Atlas of the Formicidae of Norway (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Insecta Norvegiae 2: 1-56.
- Kvamme T., and A. Wetas. 2010. Revidert liste over norske maur Inkludert dialektiske navn og forslag til nye norske navn og forslag til norske navn. Norsk institutt for skog og landskap, Ås. 127 pp
- Kwon T. S. 2015. Ant assemblages along the Baekdudaegan Mountain Range in South Korea: Human roads and temperature niche. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity 8: 152-157.
- Kwon T. S., S. S. Kim, and J. H. Chun. 2014. Pattern of ant diversity in Korea: An empirical test of Rapoport's altitudinal rule. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 17: 161167.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, L., V. Antonova, A. G. Radchenko, and M. Atanasova. "Catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Bulgaria." ZooKeys 62 (2010): 1-124.
- Lehouck V., D. Bonte, W. Dekoninck, and J. P. Maelfait. 2004. The distribution of ant nests (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in coastal grey dunes of Flanders (Belgium) and their relationship to myrmecochorous plants. Belg. J. Zool. 134 (2/1) : 89-96.
- Nielsen M. G. 2011. A check list of Danish ants and proposed common names. Ent. Meddr. 79: 13-18.
- Noordijk, J., R. Morssinkhof, P. Boer, A. P. Schaffers, Th. Heijerman and K. V. Sýkora. 2008. How ants find each other; temporal and spatial patterns in nuptial flights. Insectes Sociaux 55(3):266-273.
- Odegaard F. 2013. New and little known ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Norway. Norwegian Journal of Entomology 60, 172175.
- Park S.J., and B.J. Kim. 2002. Faunal comparison of ants among Cheongsando and other islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(1): 7-12.
- Park, Seong, Joon and Byung, and Kim, Jin. 2002. Faunal Comparison of Ants among Cheongsando and Other Islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Jornal of Entomology. 32(1):7-12.
- Petrov I. Z. 2002. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of the Banat Province (Serbia). Archives of Biological Sciences, Belgrade, 54(12): 57-64.
- Petrov I. Z. 2012. Preliminary data on ants (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) on Mountain Avala (Belgrade, Serbia). Bulletin of the Natural History Museum 5: 95-99.
- Petrov I. Z., and C. A. Collingwood. 1992. Survey of the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of Yugoslavia. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade) 44: 79-91.
- Radchenko A., W. Czechowska, W. Czechowski, and E. Siedlar. 1999. Four species of the ant genus Lasius F. new to Poland, with additions to the records for previously reported species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Fragmenta Faunistica 42(11): 115-121.
- Radchenko, A. 2005. Monographic revision of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of North Korea. Annales Zoologici 55(2): 127-221.
- Sato T., N. Tsurusaki, K. Hamaguchi, and K. Kinomura. 2010. Ant fauna of Tottori prefecture, Honshu, Japan. Bulletin of the Tottori Prefectural Museum 47: 27-44.
- Schar S., G Talavera, X. Espadaler, J. D. Rana, A. A. Andersen, S. P. Cover, and R. Vila. 2018. Do Holarctic ant species exist? Trans-Beringian dispersal and homoplasy in the Formicidae. Journal of Biogeography 00: 1-12.
- Schlick-Steiner B. C., and F. M. Steiner. 1999. Faunistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen an den freilebenden Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Wiens. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 3: 9-53.
- Seifert B. 1994. Die freilebenden Ameisenarten Deutschlands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) und Angaben zu deren Taxonomie und Verbreitung. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 67(3): 1-44.
- Seifert B. 1998. Rote Liste der Ameisen. - in: M. Binot, R. Bless, P. Boye, H. Gruttke und P. Pretscher: Rote Liste gefährdeter Tiere Deutschlands. Bonn-Bad Godesberg 1998: 130-133.
- Sonnenburg H. 2005. Die Ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Niedersachsens und Bremens. Braunschweiger Naturkundliche Schriften 7: 377-441.
- Steiner F. M., S. Schödl, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2002. Liste der Ameisen Österreichs (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Stand Oktober 2002. Beiträge zur Entomofaunistik 3: 17-25.
- Stärcke A. 1937. Retouches sur quelques fourmis d'Europe. II. Lasius groupe umbratus Nylander. Tijdschr. Entomol. 80: 38-72.
- Terayama M. 1992. Structure of ant communities in East Asia. A. Regional differences and species richness. Bulletin of the Bio-geographical Society of Japan 47: 1-31.
- Terayama M., Choi, B.M., Kim, C.H. 1992. A check list of ants from Korea, with taxonomic notes. Bulletin of the Toho Gakuen 7:19-54.
- Terayama M., K. Ogata, and B.M. Choi. 1994. Distribution records of ants in 47 prefectures of Japan. Ari (report of the Myrmecologists Society of Japan) 18: 5-17.
- Terayama M., S. Kubota, and K. Eguchi. 2014. Encyclopedia of Japanese ants. Asakura Shoten: Tokyo, 278 pp.
- Tinaut A. 2016. Ants of the Tejeda, Almijara and Alhama Mountains Natural Park (Andalusia, Spain) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boln. Asoc. esp. Ent., 40 (1-2): 125-159.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica en la Cordillera Ibérica." Orsis 6 (1991): 129-126.
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Common Name
- Ant Associate
- Host of Lasius alienus
- Host of Lasius hayashi
- Host of Lasius japonicus
- Host of Lasius niger
- Host of Lasius psammophilus
- Temporary parasite
- North temperate
- North subtropical
- FlightMonth
- Host of Lasius fuliginosus
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Lasiini
- Lasius
- Lasius meridionalis
- Formicinae species
- Lasiini species
- Lasius species
- Ssr

