Lasius fuliginosus
| Lasius fuliginosus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Lasiini |
| Genus: | Lasius |
| Section: | niger clade |
| Species group: | fuliginosus |
| Species: | L. fuliginosus |
| Binomial name | |
| Lasius fuliginosus (Latreille, 1798) | |
Arboricolous, nests in living trees, preferably growing near streams or water intakes. This species exhibits temporary social parasitism. Queens found new colonies by infiltrating an established nest of a different ant species, killing the queen and having the host workers care for her initial brood. Hosts include Lasius bicornis, Lasius jensi, Lasius meridionalis, Lasius mixtus, Lasius rabaudi, Lasius sabularum and Lasius umbratus. Lasius fuliginosus form large carton nests commonly in cavities at the base of old trees (oak, birch, willow, pine).
| At a Glance | • Temporary parasite |
Photo Gallery
Identification
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - A very distinct species. Its deep dark brown to black body, short and sparse vestiture, shiny body surface and deeply emarginate occipital part of head distinguishes it from all members of the genus Lasius.
Radchenko (2005) –
| Lasius fuji worker | Lasius fuliginosus worker |
| head usually somewhat longer than wide (CI 0.95-1.01 ); | head length equal to or less than its width (CI 1.00-1.03); |
| scape relatively longer (SI2 0.88-0.95); | scape relatively shorter (SI2 0.82-0.89); |
| standing hairs on the upper margin of petiolar scale longer, the longest hairs distinctly longer than the half of the maximum diameter of the scape; | standing hairs on the upper margin of petiolar scale shorter, the longest hairs shorter than the half of the maximum diameter of the scape; |
| decumbent pubescence on the anterior (vertical) surface of first gastral tergite relatively dense, distance between hairs distinctly shorter than the hairs length | decumbent pubescence on the anterior (vertical) surface of first gastral tergite relatively sparse, distance between hairs not shorter (usually longer) than the hairs length |
| Queen - eyes with somewhat longer hairs, length of the longest ones ≥ 0.040 mm | Queen - eyes with somewhat shorter hairs, length of the longest ones ≤ 0.035 mm |
Collingwood (1979) - Shining black, legs brownish yellow; pubescence sparse, scattered erect hairs over dorsum. Head broadly cordate, emarginate posteriorly with rounded occipital lobes; genital margins incurving towards mandibular insertions. Maxillary palps short with segments 4, 5 and 6 subequal. Petiole thickened wedge shaped in profile, with feebly convex faces, dorsal margin narrow, convex or straight. Length: 4.0-6.0 mm.
Keys including this Species
Distribution
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 65.090646° to 37.5°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Palaearctic Region: Albania, Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Channel Islands, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France (type locality), Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iberian Peninsula, Isle of Man, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, North Macedonia, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
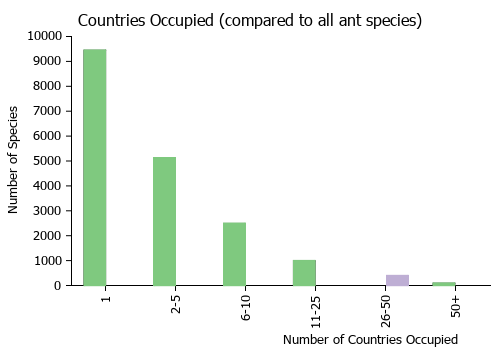
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
|
Habitat
Borowiec and Salata (2022) – Rare in Greece rare where it inhabits mountain deciduous forests and occasionally coniferous forests. Prefers shady and humid habitats. Absent in high mountains, collecting sites were noted from low to mid altitude between 100 to 1200 m.
Biology
Donisthorpe (1927) - This distinctive species is easily recognised by its shining black colour and broad head. Carton nests are constructed at the base of old trees, hedgerows and sometimes in sand dunes and in old walls. Colonies are populous, often polycalic with more than one focal nest and several queens. Workers forage above ground in narrow files throughout the day and night during warm weather, ascending trees and shrubs to tend aphids. The mandibles are relatively weak but small insects may be taken as food. Other competing ant species are repelled by aromatic anal secretions. Fertilised queens may be retained in the old nest or found fresh colonies through adoption by the members of the umbratus species group; mixed colonies with Lasius umbratus or Lasius mixtus have often been observed. Flight periods are irregular and have been recorded in all months from May to October. A number of local beetles occur with this species including members of the genus Zyras which exhibit protective mimicry. Waldén (1964), records an enormous nest measuring 63 x 55 x 55 cm found in a cellar near Göteborg and there are similar reports from outbuildings and cellars in England.
Wilson (1955) - Many European observers have reported independently on various aspects of the ecology of this ant, and together they present a reassuringly consistent picture. Lasius fuliginosus nests primarily in standing tree trunks and rotting stumps, and only occasionally in and around the roots of trees, under stones, and in open soil. In a random field survey in Germany, Gosswald (1932) recorded 63 nests in wood, 2 under stones, and 5 in open soil. He found the species nesting most commonly in old poplars and willows in dry meadows. It is often locally abundant; O'Rourke (1950) notes that in Ireland it may become the dominant ant in oak woods.
Lasius fuliginosus almost invariably constructs a carton nest. The composition of the carton has been analyzed by Stumper (1950), who finds that it consists primarily of macerated wood hardened with secretions from the mandibular glands. There may be some soil particles mixed in, especially in subterranean nests, but these constitute a very minor fraction. Stumper was unable to find supporting evidence for the old contention that several species of symbiotic fungi are normally grown in the carton walls.
Lasius fuliginosus forages during both the day and night, forming long, conspicuous columns which usually lead to trees infested with aphids or eoceids , the excreta of these latter insects forms a principal food source for the ant. In addition, many authors have observed workers carrying dead or crippled insects back to the nests.
Eidmann (1943) has studied overwintering in this species. A colony which he kept under observation through the autumn moved from a position in a tree bole to subterranean quarters directly beneath the tree. The winter carton nest had chambers twice the size of those in the summer nest, and its walls were conspicuously studded with grains of sand. Medium-sized and full grown larvae were found hibernating with the adults.
Winged reproductives have been taken in the nests from May to September. The nuptial flights apparently take place earlier than in other members of the genus; literature records span the period May 4 to July 27. The flights occur mostly in the afternoon, although some authors, such as Escherich and Ludwig (1906), have suggested that they occur at night also. According to Donisthorpe (1927), the mating behavior shows early signs of parasitic degeneration. There is a marked decrease in the size difference between the two sexes, and the nuptial flight appears to have been partly suppressed. In one case Donisthorpe observed nestmates copulating on vegetation in the immediate vicinity of the parent nest.
Donisthorpe (1922) has also reviewed the extensive literature on colony founding in this species. It has been proven without any doubt to be a temporary social parasite on Lasius umbratus (= Lasius mixtus), which species was defined in the old sense and may well include Lasius rabaudi also. Numerous mixed colonies have been found in nature, and successful adoptions of dealate queens by host colonies have been repeatedly obtained under artificial conditions. This habit places fuliginosus in the extraordinary position of being a social hyperparasite, since Lasius umbratus is parasitic itself on members of the subgenus Lasius. In more recent years, Stareke (1944) has obtained the experimental adoption of fuliginosus queens by colonies of rabaudi (= Lasius meridionalis), Lasius niger, and Lasius alienus.
Liu et al. (2000) discuss nestmate discrimination and cuticular profiles of a temporary parasitic Lasius sp. that this species is a host for.
Foraging/Diet
See the general biology discussion above for an overview of diet and foraging. Novgorodova (2015b) investigated ant-aphid interactions of a dozen honeydew collecting ants in south-central Russia. All of the ants studied had workers that showed high fidelity to attending particular aphid colonies, i.e, individual foragers that collect honeydew tend to return to the same location, and group of aphids, every time they leave the nest. Lasius fuliginosus showed no specialization beyond this foraging site fidelity. Foragers tended Chaitophorus populeti (Panzer), Cinara laricis (Hartig) and Stomaphis quercus (Linnaeus).
Known Hosts
Lasius fuliginosus is known to use the following species as temporary hosts:
- Lasius bicornis (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018)
- Lasius jensi (as Lasius jensi x umbratus) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018)
- Lasius meridionalis (as Lasius meridionalis x umbratus) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018)
- Lasius mixtus (unconfirmed) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Janda et al., 2004)
- Lasius rabaudi (unconfirmed) (de la Mora et al., 2021; Janda et al., 2004)
- Lasius sabularum (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018)
- Lasius umbratus (de la Mora et al., 2021; Janda et al., 2004; Seifert, 2018)
Reports of Lasius fuliginosus invading nests of Lasius alienus and Lasius brunneus (Janda et al., 2004) are unlikely based on biology (Seifert, pers. comm., in de la Mora et al., 2021), and while it does associate with Lasius niger (Janda et al., 2004), Seifert (2018) states that it does not survive (de la Mora et al., 2021).
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- This species is associated with the aphids Chaitophorus populeti, Chaitophorus vitellinae, Cinara boerneri, Cinara laricis, Cinara pinea, Lachnus tropicalis, Pterocomma pilosum, Pterocomma rufipes, Stomaphis japonica, Stomaphis quercus and Symydobius oblongus (Saddiqui et al., 2019 and included references).
- This species is a host for the eucharitid wasp Pseudometagea sp. (a parasite) (Universal Chalcidoidea Database) (primary host).
- This species is a host for the pteromalid wasp Spalangia crassicornis (a parasite) (Universal Chalcidoidea Database) (associate).
- This species is a host for the pteromalid wasp Spalangia nigripes (a parasite) (Universal Chalcidoidea Database) (associate).
- This species is host for the following mites: Formicomotes octipes, Gaeolaelaps glabrosimilis, Imparipes brevibasis, Imparipes fuliginosophilus, Imparipes obsoletus, Imparipes sevastianovi, Petalomium carelitschensis, Petalomium fuliginosum, Petalomium podolicus, Scutacarus flexisetus, Scutacarus longisetus and Unguidispus contematosus (Khaustov, 2015; Joharchi et al., 2020; Sevastianov 1980; Rahiminejad & Hajiqanbar, 2020).
- This species is host for the following milichiid flies: Milichia ludens, Phyllomyza donisthorpei, Phyllomyza equitans, Phyllomyza flavitarsis and Phyllomyza pallida.
- This species is a host for the fungus Beauveria bassiana (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission within nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Eurypterna cremieri (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Ghilaromma fuliginosi (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon arakawae (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon cremieri (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon cremieri (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon cremieri (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hybrizon cremieri (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the ichneumonid wasp Hyrbizon fuliginosi (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a host for the phorid fly Pseudacteon formicarum (a parasitoid) (Quevillon, 2018) (encounter mode primary; direct transmission; transmission outside nest).
- This species is a prey for the Microdon fly Microdon sp. (a predator) (Quevillon, 2018).
Flight Period
| X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Source: antkeeping.info.
- Check details at Worldwide Ant Nuptial Flights Data, AntNupTracker and AntKeeping.
 Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Life History Traits
- Mean colony size: 2,500,000 (Hainaut-Riche et al., 1980; Quinet & Pasteels, 1987; Beckers et al., 1989)
- Foraging behaviour: trunk trail (Hainaut-Riche et al., 1980; Quinet & Pasteels, 1987; Beckers et al., 1989)
Castes
Worker
Queen
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0172764. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
    
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0172765. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by CAS, San Francisco, CA, USA. |
Male
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- fuliginosus. Formica fuliginosa Latreille, 1798: 36 (w.q.m.) FRANCE. Hauschteck, 1962: 219 (k.). Combination in Lasius: Mayr, 1861: 49; in Donisthorpea: Donisthorpe, 1915d: 188; in Formicina: Emery, 1916b: 242; in Acanthomyops: Forel, 1916: 460; in Lasius (Dendrolasius): Ruzsky, 1912: 630; Müller, 1923: 132; Emery, 1925b: 236; Wilson, 1955a: 138. See also: Yamauchi, 1979: 171; Collingwood, 1982: 292; Kupyanskaya, 1989: 783; Atanassov & Dlussky, 1992: 243.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Wilson (1955)
(1) Head usually deeply concave in full face, the depth of the concavity 0.06 mm. or more except in some series from northeastern Asia.
(2) Antennal scapes short-elliptical in cross-section, so that for most of their length the minimum width at any point is 0.8 X the maximum width at that point or greater.
(3) Petiole in frontal view broadest at about the level of the dorsal margin of the anterior foramen, gradually narrowing to the top. The dorsolateral angles broadly and evenly rounded; the dorsal margin narrow, convex to feebly emarginate. In side view the petiole symmetrical, with both faces feebly and evenly convex, tapering together to form a narrow-U-shaped dorsal crest.
(4) The hairs of the exposed gastric tergites shorter than in Lasius spathepus and Lasius crispus, rarely longer than 0.08 mm. and probably never surpassing the longest hairs of the pronotum. The appendages covered with dense appressed-to-decumbent pubescence but with few or no standing hairs.
Borowiec and Salata (2022) - Very large, HL 1.333-1.571 (mean 1.448), HW 1.302-1.540 (mean 1.418), ML 1.33-1.54. Scape moderately elongate, SL 1.167-1.333 (mean 1.243). Color. Body, femora, tibiae concolours dark brown to black. Mandibles reddish, antennae yellowish brown, tarsi yellowish. Structure and setation. Head as wide as long or slightly elongated, with convex sides and deeply concave posterior margin, appears heart-shaped, clypeus without median keel. Maxillary palpi short, not extending to the half-length of ventral side of head. Setation of head short and sparse, occipital part of head with 8-14 short erected setae. Gena lacking erected setae, underside of head with 8-26 short erected setae. Mesosomal dorsum with several short erected setae, length of the longest seta 0.095. Below propodeal spiracle no erected setae. Masticatory border of mandibles with 7-8 teeth. Antennal scapi with smooth pubescence, on ventral space decumbent, erected setae absent. Hind tibiae with slightly decumbent pubescence, on external surface lacking erected setae. Ventral surface of femora lacking erected setae, anterior surface of fore coxa with few short erected setae. Pubescence on head and mesosoma short and sparse, whitish, surface microreticulate but appears smooth and shiny. Pubescence of clypeus short and sparse, hardly visible, Clypeus smooth and shiny. Pubescence of gastral tergites slightly shorter and denser than on mesosoma, surface with microsculpture but shiny, first gastral tergite in central part with sparse, short erected setae. Propodeum in lateral view low and rounded, metanotal groove deep.
Queen
Wilson (1955)
(1) HW 1.41 mm. (Odawara, Japan) to 1.65 mm. (England).
(2) Lacking the "beta" characteristics of the spathepus queen, i.e. the occipital margin in full face is only weakly concave, the head is about as long as broad or longer, and the mandibles are not exceptionally reduced relative to the remainder of the head.
(3) The entire body, exclusive of the appendages and (in European series) the anterior half of the head, covered with abundant, coarse suberect-erect hairs. In occasional specimens these hairs are rather sparse on the gastrict tergites, but this may be due to wear. The entire body is covered with appressed ground pubescence of varying density which partly obscures the smooth, shining cuticular surface.
(4) Petiolar lateral outline as in worker. Frontal outline typically as in worker and dorsal margin showing same degree of variation as in that caste; occasionally the broadest level is well above its usual location at the dorsal margin of the anterior foramen.
(5) Median clypeal carina feebly developed (see Lasius buccatus).
Male
Wilson (1955)
(1) HW 1.00 mm. (Kiev) to 1.24 mm. (Innsbruck).
(2) Scape short-elliptical to circular in cross-section.
(3) Petiolar outline in side view similar to that of the worker, differing only in being generally thicker. In frontal view the broadest point is at the level of the dorsal margin of the anterior foramen or higher; the dorsal margin is convex in all series examined.
(4) Pygostyle similar to that typifying the subgenus Lasius: thumb-shaped, nearly as broad near the tip as at the basal attachment.
Karyotype
- See additional details at the Ant Chromosome Database.
 Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- n = 14, 2n = 28 (Italy; Switzerland) (Hauschteck, 1962; Hauschteck-Jungen & Jungen, 1983).
References
- Atanassov, N.; Dlussky, G. M. 1992. Fauna of Bulgaria. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Fauna Bûlg. 22: 1-310 (page 243, see also)
- Balzani, P., Frizzi, F., Masoni, A., Santini, G. 2022. The effect of the introduced Red Wood Ant Formica paralugubris on the frequency of ant nests and first plesiobiotic association between Myrmica ruginodis (Nylander, 1846) and Lasius flavus (Fabricius, 1782). Sociobiology 69(4), e7901 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v69i4.7901).
- Barsagade, D.D., Nagarkar, D.A., Kirsan, J.R. 2019. Surface ultrastructure of antenna and distribution of sensilla in the Leptogenys chinensis (Mayr) (Fabricus) (Formicidae: Hymenoptera). Journal of Applied Biology, Biotechnology 7, 1–6 (doi:10.7324/jabb.2019.70201).
- Barsagade, D.D., Tembhare, D.B., Kadu, S.G. 2013. Microscopic structure of antennal sensilla in the carpenter ant Camponotus compressus (Fabricius) (Formicidae: Hymenoptera). Asian Myrmecology 5, 113-120.
- Beckers R., Goss, S., Deneubourg, J.L., Pasteels, J.M. 1989. Colony size, communication and ant foraging Strategy. Psyche 96: 239-256 (doi:10.1155/1989/94279).
- Bernadou, A., Fourcassié, V., Espadaler, X. 2013. A preliminary checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Andorra. ZooKeys 277, 13–23 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.277.4684).
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec, L., Salata, S. 2022. A monographic review of ants of Greece (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Vol. 1. Introduction and review of all subfamilies except the subfamily Myrmicinae. Part 1: text. Natural History Monographs of the Upper Silesian Museum 1: 1-297.
- Borowiec, L., van Delft, J.P.L., van Delft, J.J.C.W., Salata, S. 2023. Five ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) new to the Greek fauna with notes on ants from Greek Thrace. Annales of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom, Entomology 32 (online 008), 1-13 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.10101028).
- Boudinot, B.E., Borowiec, M.L., Prebus, M.M. 2022. Phylogeny, evolution, and classification of the ant genus Lasius, the tribe Lasiini and the subfamily Formicinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Systematic Entomology 47, 113-151 (doi:10.1111/syen.12522).
- Bracko, G., Wagner, H.C., Schulz, A., Gioahin, E., Maticic, J., Trantnik, A. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10: 10-24.
- Buschinger, A. 2009. Social parasitism among ants: a review (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 12: 219-235.
- Cantone S. 2017. Winged Ants, The Male, Dichotomous key to genera of winged male ants in the World, Behavioral ecology of mating flight (self-published).
- Castracani, C., Spotti, F.A., Schifani, E., Giannetti, D., Ghizzoni, M., Grasso, D.A., Mori, A. 2020. Public engagement provides first insights on Po Plain ant communities and reveals the ubiquity of the cryptic species Tetramorium immigrans (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insects 11, 678. (doi:10.3390/insects11100678).
- Collingwood, C. A. 1982. Himalayan ants of the genus Lasius (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Syst. Entomol. 7: 283-296 (page 292, see also)
- Csősz, S., Báthori, F., Gallé, L., Lőrinczi, G., Maák, I., Tartally, A., Kovács, É., Somogyi, A.Á., Markó, B. 2021. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: Survey of ant species with an annotated synonymic inventory. Insects 16;12(1):78 (doi:10.3390/insects12010078).
- Csosz, S., Marko, B., Galle, L. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski, W., Marko, B., Radchenko, A., Slipinski, P. 2013. Long-term partitioning of space between two territorial species of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and their effect on subordinate species. European Journal of Entomology 110(2): 327–337.
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A., Czechowska, W. 2002. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Poland. MIZ PAS Warsaw.
- Dekoninck, W., Ignace, D., Vankerkhoven, F., Wegnez, P. 2012. Verspreidingsatlas van de mieren van België. Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 148: 95-186.
- Donisthorpe, H. 1915f. British ants, their life-history and classification. Plymouth: Brendon & Son Ltd., xv + 379 pp. (page 188, Combination in Donisthorpea)
- Dubovikoff, D.A., Yusupov, Z.M. 2017. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Emery, C. 1916a [1915]. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 47: 79-275 (page 242, Combination in Formicina)
- Emery, C. 1925d. Hymenoptera. Fam. Formicidae. Subfam. Formicinae. Genera Insectorum 183: 1-302 (page 236, Combination in Lasius (Dendrolasius))
- Forel, A. 1916. Fourmis du Congo et d'autres provenances récoltées par MM. Hermann Kohl, Luja, Mayné, etc. Rev. Suisse Zool. 24: 397-460 (page 460, Combination in Acanthomyops)
- Gathalkar, G.B., Barsagade, D.D. 2018. Cephalic microstructure and its role in predation biology of Myrmicaria brunnea on Antheraea mylitta. Journal of Applied Biology, Biotechnology 6: 1-6 (doi:10.7324/jabb.2017.60101).
- Giannetti, D., Schifani, E., Castracani, C., Ghizzoni, M., Delaiti, M., Pfenner, F., Spotti, F.A., Mori, A., Ioriatti, C., Grasso, D.A. 2021. Assessing ant diversity in agroecosystems: the case of Italian vineyards of the Adige Valley. Redia 104, 97–109 (doi:10.19263/redia-104.21.11).
- Glaser, F. 2016. Artenspektrum, Habitatbindung und naturschutzfachliche Bedeutung von Ameisen (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) am Stutzberg (Vorarlberg, Österreich). inatura – Forschung 34: 26 S.
- Haelewaters, D., Boer, P., Noordijk, J. 2015. Studies of Laboulbeniales (Fungi, Ascomycota) on Myrmica ants: Rickia wasmanniii in the Netherlands. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 44, 39–47 (doi:10.3897/jhr.44.4951).
- Hauschteck, E. 1962. Die Chromosomen einiger in der Schweiz vorkommender Ameisenarten. Vierteljahrsschr. Naturforsch. Ges. Zür. 107: 213-220 (page 219, karyotype described)
- Hickling, R., Brown, R.L. 2000. Analysis of acoustic communication by ants. Journal of the Acoustic Society of America 108: 1920-1929.
- Holldobler, B., Kwapich, C.L. 2017. Amphotis marginata (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) a highwayman of the ant Lasius fuliginosus. PLoS ONE 12(8): e0180847 (DOI //doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180847).
- Joharchi, O., Asyamova, O.S., Khaustov, A.A., Uhey, D.A., Issakova, A.K., Tolstikov, A.V. 2020. New data on two myrmecophilous laelapid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata: Laelapidae) in Western Siberia, Russia. International Journal of Acarology, 1–11. (doi:10.1080/01647954.2020.1819410).
- Khaustov, A.A. 2015. Myrmecophilous pygmephoroid mites (Acari: Pygmephoroidea) associated withLasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Western Siberia, Russia. International Journal of Acarology 42(2): 92–105 (doi:10.1080/01647954.2015.1124921).
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C. 2020. Additions to the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoosystema 42(18), 285-329 (doi:10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a18).
- Kirchmair, G., Friess, T. et al. 2017. Zoologischer Bericht vom Tag der Biodiversität 2017 im Naturpark Südsteiermark. Mitteilungen des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereines für Steiermark 147: 99–134.
- Kleineidam, C., Romani, R., Tautz, J., Isidoro, N. 2000. Ultrastructure and physiology of the CO2 sensitive sensillum ampullaceum in the leaf-cutting ant Atta sexdens. Arthropod Structure and Development 29, 43-55.
- Kupyanskaya, A. N. 1989. Ants of the subgenus Dendrolasius Ruzsky, 1912 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, genus Lisius [sic] Fabricius, 1804) of the Far Eastern USSR. Entomol. Obozr. 68: 779-789 (page 783, see also)
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Antonova, V., Ljubomirov, T. 2021. Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Sarnena Sredna Gora Mountains (Bulgaria). Fauna of Sarnena Sredna Gora Mts, Part 2 ZooNotes, Supplement 10: 18-27.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, A., Kiran, K. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Strandzha (Istranca) Mountain and adjacent Black Sea coast. North-Western Journal of Zoology 8(1), 72-84.
- Latreille, P. A. 1798. Essai sur l'histoire des fourmis de la France. Brive: F. Bourdeaux, 50 pp. (page 36, worker, queen, male described)
- Lenoir, A., Chalon, Q., Carvajal, A., Ruel, C., Barroso, Á., Lackner, T., Boulay, R. 2012. Chemical integration of myrmecophilous guests in Aphaenogaster ant nests. Psyche: A Journal of Entomology 2012, 1–12 (doi:10.1155/2012/840860).
- Liu, C., Fischer, G., Hita Garcia, F., Yamane, S., Liu, Q., Peng, Y.Q., Economo, E.P., Guénard, B., Pierce, N.E. 2020. Ants of the Hengduan Mountains: a new altitudinal survey and updated checklist for Yunnan Province highlight an understudied insect biodiversity hotspot. ZooKeys 978, 1–171 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.978.55767).
- Liu, Z., Yanabe, S., Yamamoto, H., Wang, Q. 2000. Nestmate discrimination and cuticular profiles of a temporary parasitic ant Lasius sp. and its host L. fuliginosus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Journal of Ethology 18: 69‐73.
- Mayr, G. 1861. Die europäischen Formiciden. Nach der analytischen Methode bearbeitet. Wien: C. Gerolds Sohn, 80 pp. (page 49, Combination in Lasius)
- Meurville, M.-P., LeBoeuf, A.C. 2021. Trophallaxis: the functions and evolution of social fluid exchange in ant colonies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 31: 1-30 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_031:001).
- Mueller, U.G., Schultz, T.R., Currie, C.R., Adams, R.M.M., Malloch, D. 2001. The origin of the attine ant-fungus mutualism. The Quarterly Review of Biology 76, 169-197.
- Müller, G. 1923b. Le formiche della Venezia Guilia e della Dalmazia. Boll. Soc. Adriat. Sci. Nat. Trieste 28: 11-180 (page 132, Combination in Lasius (Dendrolasius))
- Nakanishi, A., Nishino, H., Watanabe, H., Yokohari, F., Nishikawa, M. 2009. Sex-specific antennal sensory system in the ant Camponotus japonicus: structure and distribution of sensilla on the flagellum. Cell and Tissue Research 338, 79–97 (doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0863-1).
- Nemet, E., Czekes, Z., Tausan, I., Marko, B. 2012. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the Cefa Nature Park (North-Western Romania). Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica Biologia 20, 61-72.
- Novgorodova, T. 2021. Preventing transmission of lethal disease: Removal behaviour of Lasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Towards Fungus Contaminated Aphids. Insects 12, 99. (doi:10.3390/insects12020099).
- Novgorodova, T. A. 2015b. Organization of honeydew collection by foragers of different species of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): Effect of colony size and species specificity. European Journal of Entomology. 112:688-697. doi:10.14411/eje.2015.077
- Parmentier, T. 2020. Guests of Social Insects. In: Encyclopedia of Social Insects (doi:10.1007/978-3-319-90306-4_164-1).
- Parmentier, T., Gaju-Ricart, M., Wenseleers, T., Molero-Baltanás, R. 2021. Chemical and behavioural strategies along the spectrum of host specificity in ant-associated silverfish. Research Square (doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1108003/v1).
- Pekár, S. 2020. Ant-mimicking spider actively selects its mimetic model (Araneae: Gnaphosidae; Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 30, 131-137 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_030:131).
- Radchenko, A.G., Fisher, B.L., Esteves, F.A., Martynova, E.V., Bazhenova, T.N., Lasarenko, S.N. 2023. Ant type specimens (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the collection of Volodymyr Opanasovych Karawajew. Communication 1. Dorylinae, Poneromorpha and Pseudomyrmecinae. Zootaxa, 5244(1), 1–32 (doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5244.1.1).
- Rahiminejad, V., Hajiqanbar, H. 2020. New records of mites of the Heterostigmata (Acari: Prostigmata) associated with insects from Golestan Province, northern Iran. Persian Journal of Acarology 9(3): 233–242 (doi:10.22073/pja.v9i3.61223).
- Ramirez-Esquivel, F., Zeil, J., Narendra, A. 2014. The antennal sensory array of the nocturnal bull ant Myrmecia pyriformis. Arthropod Structure, Development 43, 543–558. (doi:10.1016/j.asd.2014.07.004).
- Reznikova, Z. 2020. Spatial cognition in the context of foraging styles and information transfer in ants. Animal Cognition. (doi:10.1007/s10071-020-01423-x).
- Ruzsky, M. 1912. Myrmecological notes. Uch. Zap. Kazan. Vet. Inst. 29: 629-636 (page 630, Combination in Lasius (Dendrolasius))
- Siddiqui, J. A., Li, J., Zou, X., Bodlah, I., Huang, X. 2019. Meta-analysis of the global diversity and spatial patterns of aphid-ant mutualistic relationships. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 17: 5471-5524 (doi:10.15666/aeer/1703_54715524).
- Snegovaya, N., Shigayev, C. 2021. A checklist of the ants (Insecta, Formicidae) of Azerbaijan Republic. Iranian Journal of Animal Biosystematics 17(2): 179-207 (doi:10.22067/ijab.2022.67343.1000).
- Stukalyuk, S., Goncharenko, I. 2020. SHIFT IN THE STRUCTURE OF Lasius flavus (HYMENOPTERA, FORMICIDAE) NEST COMPLEXES UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS. Serangga 25(3): 160-178.
- Stukalyuk, S., Radchenko, A., Akhmedov, A., Reshetov, A., Netsvetov, M. 2021. Acquisition of invasive traits in ant, Crematogaster subdentata Mayr (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in urban environments. Serangga 26: 1-29.
- Stukalyuk, S., Radchenko, Y., Gonchar, O., Akhmedov, A., Stelia, V., Reshetov, A., Shymanskyi, A. 2021. Mixed colonies of Lasius umbratus and Lasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae): when superparasitism may potentially develop into coexistence: a case study in Ukraine and Moldova. Halteres 12, 25–48 (doi:10.5281/zenodo.5753121).
- Stukalyuk, S.V., Kozyr, M.S., Netsvetov, M.V., Zhuravlev, V.V. 2020. Effect of the invasive phanerophytes and associated aphids on the ant (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) assemblages. Halteres 11: 56-89 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.4192900).
- Stukalyuk, S.V., Radchenko, A., Reshetov, A., Akhmedov, A., Goncharenko, I. 2021. Comparative analysis of the population structure of Crematogaster subdentata and Lasius neglectus in the primary and secondary ranges (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Fragmenta Entomologica 53, 43-51 (doi:10.13133/2284-4880/436).
- Tausan, I., Dauber, J., Trica, M.R., Marko, B. 2017. Succession in ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in deciduous forest clear-cuts - an Eastern European case study. European Journal of Entomology 114, 92–100 (doi:10.14411/eje.2017.013).
- Tinaut, A., Ruano, F. 2021. Biogeography of Iberian ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Diversity 13, 88. (doi:10.3390/d13020088).
- van Elst, T., Gadau, J. 2018. Temporal variation in social structure and worker reproduction in the temporary social parasite Lasius fuliginosus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News, 27: 75-85.
- Wegnez, P. 2017. Découverte de Myrmica lobicornis Nylander, 1846 et Lasius jensi Seifert, 1982, deux nouvelles espèces pour le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie153, 46–49.
- Wiezik, M., Svitok, M., Wieziková, A., Dovčiak, M. 2013. Shrub encroachment alters composition and diversity of ant communities in abandoned grasslands of western Carpathians. Biodiversity and Conservation 22, 2305–2320 (doi:10.1007/s10531-013-0446-z).
- Wilson, E. O. 1955a. A monographic revision of the ant genus Lasius. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 113: 1-201 (page 138, Combination in Lasius (Dendrolasius); Senior synonym of nipponensis and orientalis:)
- Yamauchi, K. 1979 [1978]. Taxonomical and ecological studies on the ant genus Lasius in Japan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). I. Taxonomy. Sci. Rep. Fac. Educ. Gifu Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 6: 147-181 (page 171, see also)
- Zhu, W., Wu, L., Duan, L., Xu, S. 2022. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in northern Shaanxi Province, China, with one new species of genus Proformica Ruzsky, 1902, Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 25, 101875 (doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2022.101875).
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Agosti D. 1983. Zur Insektenfauna der Umgebung der Vogelwarte Sempach, Kanton Luzern. XIII. Hymenoptera 2: Formicidae (Ameisen). Entomologische Berichte Luzern 10: 91-92.
- Agosti, D. and C.A. Collingwood. 1987. A provisional list of the Balkan ants (Hym. Formicidae) and a key to the worker caste. I. Synonymic list. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, 60: 51-62
- Aldawood AS, Sharaf MR (2011) Monomorium dryhimi sp. n., a new ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the M. monomorium group from Saudi Arabia, with a key to the Arabian Monomorium monomorium-group. ZooKeys 106: 4754. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.106.139
- Alvarado M., and L. Galle. 2000. Ant assemblages associated with lowland forests in the southern part of the great Hungarian plain. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientarum Hungaricae 46(2): 79-102.
- Andoni V. 1977. Kontribut mbi Himenopteret e familjes Formicidae te vendit tone. Buletini I Shkencave te Natyres 31(2): 93-101.
- Anonymous. A list of ants collected at Bandai, Fukushima Prefecture by the members of the Myrmecological Society of Japan in 1992. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 18: 31
- AntArea. Accessed on February 5th 2014 at http://antarea.fr/fourmi/
- Antarea (Personal Communication - Rumsais Blatrix- 27 April 2018)
- Antonov I. A. 2013. Ant Assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Cities of the Temperate Zone of Eurasia. Russian Journal of Ecology 44(6): 523526.
- Antonova V., and L. Penev. 2008. Classification of assemblages of ants in the green areas in Sofia City. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 60(2): 103-110.
- ArtDatabanken Bugs (via GBIG)
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2011. List of species collected during the Taxomara Lisboa 2011. Iberomyrmex 3: 30-31.
- Asociacion Iberica de Mirmecologia. 2014. List of species collected during the Taxomara 2014 Oviedo. Iberomyrmex 6: 23-24.
- Assing V. 1989. Die Ameisenfauna (Hym.: Formicidae) nordwestdeutscher Calluna-Heiden. Drosera 89: 49-62.
- Azuma M. 1938. A list of ants found in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Entomol. World Tokyo 6: 238-243.
- Azuma M. 1938. A list of ants found in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Entomological World. Tokyo 6:238-243.
- Azuma M. 1951. On the Myrmecological fauna of Osaka Prefecture, Japan with description of new species (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). Hyogo Biology 1(5): 1-5.
- Azuma M. 1953. On the myrmecological fauna of Mt. Rokko, Hyogo Prefecture. Warera 2:1-7.
- Azuma M. 1955. A list of ants (Formicidae) from Hokkaido Is. Hyogo Biology 3:79-80.
- Azuma M. 1977. On the myrmecological-fauna of Mt. Rokko, Hyogo, with description of a new species (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). Hyogo Biology 7:112-118.
- Baba, K. 1935. Some hymenopterous insects from Sado Island. [In Japanese.]. Mushi 8:83-85.
- Banert P, and B. Pisarski. 1972. Mrówki (Formicidae) Sudetów. Fragmenta Faunistica (Warsaw) 18: 345-359.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1976. A Numerical Analysis of the Distribution of British Formicidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata). Verhandlungen der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Basel 85: 51-91.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1977. The zoogeography of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Northern Europe. Acta Zoologica Fennica 152: 1-34.
- Barrett K. E. 1967. Ants in South Brittany. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 79:112-116.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968. Ants in western France. Entomologist 101: 153-155.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1968b. The distribution of ants in central southern England. Transactions of the Society for British Entomology 17: 235-250.
- Barrett K. E. J. 1970. Ants in France, 1968-69. Entomologist 103: 270-274.
- Baugnee J. Y. 2003. Camponotus piceus (Leach, 1825), fourmi nouvelle pour la faune belge decouverte dans le parc naturel Viroin-Hermeton (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin S. R. B. E./K. B. V. E. 139: 219-225.
- Behr D., S. Lippke, and K. Colln. 1996. Zur kenntnis der ameisen von Koln (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Decheniana-Beihefte (Bonn) 35: 215-232.
- Behr D., and K. Colln. 1993. Zur ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) von Gonnersdorf (Kr. Daun). Dendrocopos 20: 148-160.
- Bernadou A., V. Fourcassié, and X. Espadaler. 2013. A preliminary checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Andorra. Zookeys 277: 13-23.
- Bernadou, A., G. Latil, V. Fourcassié, and X. Espadaler. "Les formigues de la Vall del Madriu-Perafita-Claror : diversitat i distribució." Hàbitats, 13 (2006): 10-21.
- Berville L., C. Santelli, J. Reybaud, M. Renucci, P. Ponel, O. Blight, and E. Provost. 2014. Suivi d’un site atelier dans le golfe de Fos: Une diversite myrmecologique insoupconne. Etudes Vauclusiennes 82: 71-78.
- Blacker N. C. 1989. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the Gower Peninsula, West Glamorgan, South Wales. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 101: 261-266.
- Blacker N. C. and C. A. Collingwood. 2002. Some significant new records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Salisbury area, south Wiltshire, England, with a key to the British species of Lasius. British Journal of Entomology and Natural History 15: 25-46
- Blacker N.C. 2007. Ants (Hym., Formicidae) in East Anglia-Additional Records from . Entomologist's Monthly Magazine 143: 69-90
- Boer P. 2019. Species list of the Netherlands. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/specieslist.html
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. Van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten (Amsterdam) 63: 54-58.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. List of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Belgium and The Netherlands, their status and Dutch vernacular names. Entomologische Berichten 63 (3): 54-58.
- Boer P., and J. Noordijk. 2004. De ruige gaststeekmier Myrmica hirsuta nieuw voor Nederland (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ned. Faun. Meded. 20: 25-32.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec L., and S. Salata. 2012. Ants of Greece - Checklist, comments and new faunistic data (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus 23(4): 461-563.
- Bourne R. A. 1973. A taxonomic study of the ant genus Lasius Fabricius in the British Isles (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Entomol. Ser. B 42: 17-27 .
- Boven J. K. A. 1947. Liste de détermination des principales espèces de fourmis belges (Hymenoptera Formicidae). Bulletin et Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 83: 163-190.
- Bracko G. 2007. Checklist of the ants of Slovenia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natura Sloveniae 9: 15-24
- Bracko G., H. C. Wagner, A. Schulz, E. Gioahim, J. Maticic, and A. Tratnik. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10(1): 10-24.
- Bracko G., K. Kiran, C. Karaman, S. Salata, and L. Borowiec. 2016. Survey of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Greek Thrace. Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e7945. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e7945
- Bracko, G. 2006. Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) of Croatia. Acta Entomologica Slovenica 14(2): 131-156.
- Bracko, G.. "Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Croatia." Acta Entomologica Slovenica Vol 14 st (2006): 131-156.
- Carniel A. 1988. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna del Cansiglio (Prealpi Carniche). Boll. Soc. Ent. Ital., Genova 119(3): 179-190.
- Carniel A. 1998. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna delle Prealpi Orobiche (Lombardia) (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atti. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Morbegno 9: 29-39.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and C. Galkowski. 2009. Liste actualisee des Fourmis de France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 114: 475-510.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and M. Prost. 1991. Fourmis de la Côte-d'Or présentes dans les collections du Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Dijon. Bulletin Scientifique de Bourgogne 44: 53-72.
- Chen Z. L., S. Y. Zhou, D. D. Ye, Y. Chen, and C. W. Lu. 2013. Moleular phylogeny of the ant subfamily Formicinae (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from China based on Mitochondrial genes. Sociobiology 60(2): 135-144.
- Cherix D., and S. Higashi. 1979. Distribution verticale des fourmis dans le Jura vaudois et recensement prelimaire des bourdons (Hymenoptera, Formicidae et Apidae). Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sc. Nat. 356(74): 315-324.
- Choi B.M. 1996. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (15) -Ant fauna islands Ullungdo and Dokdo. Journal of Chongju National University of Education 33: 201-219.
- Choi B.M., K. Ogata, and M. Terayama. 1993. Comparative studies of ant faunas of Korea and Japan. 1. Faunal comparison among islands of Southern Korean and northern Kyushu, Japan. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Japan 48(1): 37-49.
- Choi B.M., Kim, C.H., Bang, J.R. 1993. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (13). A checklist of ants from each province (Do), with taxonomic notes. Cheongju Sabom Taehakkyo Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National University of Education) 30: 331-380.
- Choi B.M., and J. R. Bang. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (12): the analysis of ant communities in 23 islands. Journal of Cheongju National University of Education 30:317-330.
- Choi B.M.; Bang, J.R. 1992. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (10). Ant distribution in Gangweon Do. Journal of the Institute of Science Education (Cheongju National Teachers' College) 14:12-30.
- Colindre L. 2015. Les fourmis en Picardie: bilan 2014 (Hymenoptera/ Formicidae). Entomologiste Picard 26, 15 pages.
- Collingwood C. A. 1956. Ant hunting in France. Entomologist 89: 106-108.
- Collingwood C. A. 1971. A synopsis of the Formicidae of north Europe. Entomologist 104: 150-176
- Collingwood C. A. 1976. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from North Korea. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 68:
- Collingwood C. A. 1982. Himalayan ants of the genus Lasius (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Systematic Entomology 7: 283-296.
- Collingwood C. A., and J. Hughes. 1987. Ant species in Yorkshire, England. Naturalist (Leeds) 112: 95-101.
- Collingwood C.A. 1957. The Species of Ants of the Genus Lasius in Britain. Journal of the Society for British Entomology. 5: 204-214
- Collingwood C.A. 1961. New Vice-County Records for British Ants. Entomologist. 73: 90-93
- Collingwood C.A. and Satchell J.E. 1956. The Ants of the South Lake District. Journal of the Society for British Entomology. 5: 159-164
- Collingwood, C. A. 1958b. A key to the species of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) found in Britain. Trans. Soc. Br. Entomol. 13: 69-96
- Collingwood, C. A. 1964. The Identification of British Ants (Hym. Formicidae). Transactions of the Society for British Entomology. 16:93-121.
- Collingwood, C. A. 1974. A revised list of Norwegian ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Norsk Entomologisk Tidsskrift 21: 31-35.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark." Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 8 (1979): 1-174.
- Collingwood, C.A. 1958. A survey of Irish Formicidae. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy 59B:213-219
- Consani M., and P. Zangheri. 1952. Fauna di Romagna. Imenotteri - Formicidi. Memorie della Societa Entomologica Italiana 31: 38-48.
- Csosz S., B. Marko, K. Kiss, A. Tartally, and L. Galle. 2002. The ant fauna of the Ferto-Hansag National Park (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Mahunka, S. (Ed.): The fauna of the Fert?-Hanság National Park. Hungarian Natural History Museum, Budapest, pp. 617-629.
- Csősz S. and Markó, B. 2005. European ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the ant collection of the Natural History Museum of Sibiu (Hermannstadt/Nagyszeben), Romania II. Subfamily Formicinae. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 97: 225-240.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2001. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Stana Valley (Romania): Evaluation of the effectiveness of a myrmecological survey. Entomologica Romanica 6 : 121-126.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Cuní, M.. "Excursión entomológica y botánica a la Cerdaña española (Cataluña)." Anales de la Sociedad española de Historia Natural (1881): 377.
- Czechowski W., A. Radchenko, W. Czechowska and K. Vepsäläinen. 2012. The ants of Poland with reference to the myrmecofauna of Europe. Fauna Poloniae 4. Warsaw: Natura Optima Dux Foundation, 1-496 pp
- Czechowski W., B. Marko, A. Radchenko, and P. Slipinski. 2013. Long-term partitioning of space between two territorial species of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and their effect on subordinate species. Eur. J. Entomol. 110(2): 327337.
- Dauber, J., J. Bengtsson and L. Lenoir. 2006. Evaluating Effects of Habitat Loss and Land-Use Continuity on Ant Species Richness in Seminatural Grassland Remnants. Conservation Biology 20(4):1150-1160
- Dekoninck W., H. De Koninck, J. Y. Baugnee, and J. P. Maelfait. 2007. Ant biodiversity conservation in Belgian calcareous grasslands: active management is vital. Belg. J. Zool. 137 (2): 137-146.
- Della Santa E. 1994. Guide pour l'identification des principales espèces de fourmis de Suisse. Miscellanea Faunistica Helvetiae 3: 1-124.
- Dewes E. 2005. Ameisenerfassung im Waldschutzgebiet Steinbachtal/Netzbachtal. Abh. Delattinia 31: 89-118.
- Dietrich C. O., B. Schlick, and F. Steiner. 1998. Ameisen bei Hochwasser (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Beobachtungen in Ostösterreich im Juli 1997. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 2: 35-41.
- Dolek M., A. Freese-Hager, H. Bussler, A. Floren, A. Liegl, and J. Schmidl. 2009. Ants on oaks: effects of forest structure on species composition. Journal of Insect Conservation 13: 367-375.
- Donisthorpe H. 1914. Myrmecophilous notes for 1913. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 26: 37-45.
- Dreimanis J. 2015. Occurrences of jet ants Lasius fuliginosus (Latereille, 1798) in Latvia, 2007–2014. Daba un muzejs 10: 57-67
- Dubovikoff D. A., and Z. M. Yusupov. 2018. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Dvorak, L., P. BOGUSCH, I. MALENOVSKÝ, P. BEZDÌÈKA, K. BEZDÌÈKOVÁ, K. HOLÝ, P. LIKA, J. MACEK, L. ROLLER, M. RÍHA et al. "Hymenoptera of Hády Hill, near the city of Brno (Czech Republic), collected during the Third Czech-Slovak Hymenoptera meeting." Acta Musei Moraviae, Scientiae biologicae (Brno) 93 (2008): 53-92.
- Else G., B. Bolton, and G. Broad. 2016. Checklist of British and Irish Hymenoptera - aculeates (Apoidea, Chrysidoidea and Vespoidea). Biodiversity Data Journal 4: e8050. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e8050
- Emery C. 1869. Enumerazione dei formicidi che rinvengonsi nei contorni di Napoli con descrizioni di specie nuove o meno conosciute. Ann. Accad. Aspir. Nat. Secunda Era 2: 1-26.
- Emery C. 1878. Liste des fourmis de la collection de feu Camille van Volxem, avec la description d'une espèce nouvelle. Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 21: viii-x.
- Emery C. 1916. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bullettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 47: 79-275.
- Emery, C.. "Catalogo delle formiche esistenti nelle collezioni del Museo Civico di Genova. Parte seconda. Formiche dell'Europa e delle regioni limitrofe in Africa e in Asia." Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 12 (1878): 43-59.
- Entomological Society of Latvia. 2003. http://leb.daba.lv/Formicidae.htm (Accessed on December 1st 2013).
- Espadaler X., F. Garcia, X. Roig, and R. Vila. 2013. Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from the Castell de Montesquiu park (Osona, north-east of the Iberian Peninsula). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa (S.E.A.) 53: 223-227.
- Espadaler X., T. Akino, and M. Terayama. 2002. Taxonomic status of the ant Lasius nipponensis Forel, 1912 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Nouv. Rev. Entomol. 18: 335-341.
- Espadaler X., X. Roig, K. Gómez, and F. García. 2011. Formigues de les Planes de Son i mata de València (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Treballs de la Institució Catalana d'Història Natural 16: 609-627.
- Espadaler, X., T. Akino, and M. Terayama. "Taxonomic status of the ant Lasius nipponensis Forel, 1912." Nouvelle Revue d'Entomologie (N. S.) 18 (2002): 335-341.
- Espadaler, X., and C. Ascaso. "Adición a las hormigas del Montseny (Barcelona)." Orsis 5 (1990): 141-147.
- Espadaler, X.. "Contribución al conocimiento de los formícidos (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) del Pirineo catalán." Tesis Universida (1979): 285 pp.
- Fiedler, K., F. Kuhlmann, B. C. Schlick-Steiner, F. M. Steiner and G. Gebauer. 2007. Stable N-isotope signatures of central European ants assessing positions in a trophic gradient. Insectes Sociaux 54(4):393-402.
- Field Museum Collection, Chicago, Illinois (C. Moreau)
- Finzi, B.. "Risultati scientifici della spedizione Ravasini-Lona in Albania. III. Formiche." Bollettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 55 (1923): 1-4.
- Forel A. 1892. Die Ameisenfauna Bulgariens. (Nebst biologischen Beobachtungen.). 305-318.
- Forel A. 1902. Variétés myrmécologiques. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 46: 284-296.
- Forel A. 1903. Les Formicides de l'Empire des Indes et de Ceylan. Part X. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 14: 679-715.
- Forel A. 1906. Les fourmis de l'Himalaya. Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles 42: 79-94.
- Forel A. 1907. Formiciden aus dem Naturhistorischen Museum in Hamburg. II. Teil. Neueingänge seit 1900. Mitt. Naturhist. Mus. Hambg. 24: 1-20.
- Forel A. 1912. Quelques fourmis de Tokio. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 56: 339-342
- Forel, A.. "Fourmis d'Espagne récoltées par M. O. Vogt et Mme Cécile Vogt, Docteurs en médecine." Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 53 (1909): 103-106.
- Formidabel Database
- Fowles, A.P. 1996. A provisional checklist of the invertebrates recorded from Wales. 2. Aculeate wasps, bees and ants (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Countryside Council for Wales
- Franch, J., and X. Espadaler. "Ants as colonizing agents of pine stumps in San Juan de la Peña (Huesca, Spain)." Vie et Milieu 38 (1988): 149-154.
- Francois J. 1958. Contribution a l'etude ecologique des Formicides (Insectes, Hymenopteres) de la region Dijonnaise. Travaux du laboratoire de Zoologie et de la Station Aquicole Grimaldi de la Faculte des Sciences de Dijon 25, 39 pages.
- Freitag A. 2013. Biodiversite 2010 en ville de Neuchatel: les fourmis (Hymenopteres, Formicidae). Bulletin de la societe Neuchateloise des sciences naturelles 133: 183-225.
- GRETIA. 2017. Bilan annuel de l'enquete sur la repartition des fourmis armoricaines. 23 pages.
- Gadeau de Kerville H. 1922. Materiaux pour la Faune des Hymenopteres de la Normandie. Bull. Soc. Amis Sc. Nat. Rouen 1916-1921, 1922: 217-225.
- Galkowski C. 2013. Nouvelles données sur la répartition de Strongylognathus huberi Forel, 1874 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en France. Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux (n.s.) 41: 167-174.
- Galkowski C., and C. Foin. 2013. Nouvelles données sur la répartition de Strongylognathus huberi Forel, 1874 (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) en France. Bulletin de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux (n.s.) 41: 167-174.
- Galkowski C., and P Wegnez. 2010. Myrmica constricta Karavaiev 1934, nouvelle espece pour la France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Ent. Mulhouse 66(3): 41-45.
- Galle L. 1981. The Formicoid fauna of the Hortobagy. Pp. 307-311 in: Mahunka, S. (ed.) 1981. The fauna of the Hortobágy National Park. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó, 415 pp.
- Galle L. 1993. Data to the ant fauna of the Bukk (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natural history of the national parks of Hungary 7: 445-448.
- Galle L. 1997. Contribution to the ant fauna of Slovenia with special reference to the submediterranean and eudinaric regions. Annals for Istrian and Mediterranean studies 11: 209-214.
- Galle L., and G. Szonyi. 1988. A check list of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea) of a sandy grassland in Kiskunsag National Park (Hungary). Acta Biol. Szeged 34: 167-168.
- Gallé L. 1991. Structure and succession of ant assemblages in a north European sand dune area. Holarctic Ecology 14: 31-37.
- Gallé L., B. Markó, K. Kiss, E. Kovács, H. Dürgő, K. Kőváry, and S. Csősz. 2005. Ant fauna of Tisza river basin (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Gallé, L. (szerk.): Vegetation and Fauna of Tisza River Basin I. Tiscia Monograph Series 7; Szeged, pp. 149-197.
- Garcia Garcia F., and A. D. Cuesta-Esgura. 2017. First catalogue of the ants of Burgos province, Spain (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Boletín de la Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa 60: 245–258.
- Gaspar C. 1968. Les fourmis de la Drome et des Basses-Alpes, en France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Naturaliste can. 95: 747-766.
- Gaspar C., and C. Thirion. 1978. Modification des populations d'Hymenopteres sociaux dans les milieux anthropogenes. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 61-77.
- Gaspare Charles. 1965. Étude myrmécologique d'une région naturelle de Belgique: la Famenne Survey des Fourmis de la Région (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Institut agronomique de l'Etat a' Gembloux. 32(4): 427-434.
- Giacalone I., and M. Moretti. 2001. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) dei castagneti al Sud delle Alpi (ticino, Svizzera). Bollettino della Societa ticinese di Scienze naturali 89(1-2): 51-60.
- Glaser F. 2009. Die Ameisen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Amtlicher Lehrmittelverlag, Vaduz, 2009 (Naturkundliche Forschung im Fürstentum Liechtenstein; Bd. 26).
- Glaser F., A. Freitag, and H. Martz. 2012. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the Münstertal (Val Müstair) a hot spot of regional species richness between Italy and Switzerland. Gredleriana 12: 273 - 284.
- Glaser F., T. Kopf, and K. H. Steiberger. 2003. Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) im Frastanzer Ried und den Illauen (Vorarlberg, Österreich) Artenspektrum, Gefährdung und Schutzempfehlungen. Vorarlberger Naturschau 13: 287-310.
- Gouraud C. 2015. Bilan de l’année 2014 : Atlas des fourmis de Loire-Atlantique (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atlas des Formicidae de Loire-Atlantique, compte rendu de la première année d’étude (2014)
- Grandi G. 1935. Contributi alla conoscenza degli Imenotteri Aculeati. XV. Boll. R. Ist. Entomol. Univ. Studi Bologna 8: 27-121.
- Gratiashvili N., Barjadze S. 2008. Checklist of the ants (Formicidae Latreille, 1809) of Georgia. Proceedings of the Institute of Zoology (Tbilisi) 23: 130-146.
- Groc S., J. H. C. Delabie, R. Cereghino, J. Orivel, F. Jaladeau, J. Grangier, C. S. F. Mariano, and A. Dejean. 2007. Ant species diversity in the Grands Causses (Aveyron, France): In search of sampling methods adapted to temperate climates. C. R. Biologies 330: 913922.
- Hauschteck-Jungen E., and H. Jungen. 1983. Ant chromosomes. II. Karyotypes of western palearctic species. Insectes Soc. 30: 149-164.
- Hayashida K. 1957. Ecological distribution of ants in Sapporo and vicinity. (Preliminary report.). Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University. Series VI. Zoology 13:173-177.
- Hayashida K. 1961. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Sapporo and its vicinity (1 et 2). Insectes Sociaux 7: 125-162.
- Hayashida K. 1964. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Kutchan and its adjacent area. Journal of the Sapporo Otani Junior College 2: 107-129.
- Hayashida K. 1971. Vertical distribution of ants in the southern part of the Hidaka mountains. [In Japanese.]. Memoirs of the National Science Museum (Tokyo) 4:29-38.
- Hayashida K. 1972. Ecological survey on ants in Nakagawa Experiment Forest of Hokkaido University. Res. Bull. Exper. Forests, Coll. Agr., Hokkaido Univ. 29: 25-36.
- Hayashida K., and S. Maeda. 1960. Studies on the ecological distribution of ants in Akkeshi. Journ. Sc. Hokkaido Univ., IV. Zool., 14 (3) : 305-319.
- Hisamatsu M. 2004. List of Hymenoptera Recorded in Ibaraki Prefecture. Bulletin of Ibaraki Nature Museum 7: 125-164.
- Hou J.H., D.W. Zhou, and S.C. Jiang. 2002. Species Composition and Spatial Distribution 0f Ants in the Grassland Region in the West of Jilin Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica 22(10): 1781-1787.
- IZIKO South Africa Museum Collection
- Ichinose K. 1990. The Ant Fauna of the Tomakomai Experiment Forest, Hokkaido University (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with Notes on the Nuptial Season. Research Bulletins of College Experiment Forests 47(1) 137-144.
- Ihnatiuk O. A., and S. V. Stukalyuk. 2015. Degradation changes in the structure of multispecies associations of ants in urbanized areas. Russian Journal of Ecology 46(1): 109–115.
- Ito F. 2001. Notes on the distribution of the subgenus Dendrolasius in Kagawa Prefecture. Ari 25: 7-8.
- Jakubzik A., H. Kinkler, and K. Colln. 2010. Aculeate Hymenoptera from a Humid Biotope in Leverkusen-Steinbüchel. Decheniana (Bonn) 163: 145158.
- Jeffery H. G. 1931. The Formicidae (or ants) of the Isle of Wight. Proceedings of the Isle of Wight Natural History and Archaeological Society 2: 125-128.
- Kalnins M., and J. Dreimanis. 2007. Protected Insects of Latvia - Lasius fuliginosus (LATREILLE, 1798) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Latvijas entomologs 44: 95-102.
- Karaman M. G. 2009. An introduction to the ant fauna of Macedonia (Balkan Peninsula), a check list (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Natura Montenegrina 8(3): 151-162.
- Karaman M. G. 2011. A catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Montenegro. Podgorica: Catalogues 3, Volume 2, Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts, 140 pp.
- Karaman M. G., and G. S. Karaman. 2003. Contribution to the knowledge of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Serbia. The Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts. Glasnik of the Section of Natural Sciences 15: 39-58.
- Karaman M. G., and G. S. Karaman. 2007. Contribution to the Knowledge of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) from Special nature reserve Zasavica , Serbia. Zbornik “Naucno-strucni skup Zasavica 2007, Sremska Mitrovica, 67-75.
- Karavaiev V. 1927. Übersicht der Ameisenfauna der Krim nebst einigen Neubeschreibungen. Konowia 5: 281-303.
- Kholin S. K., and A. N. Kupianskaya. 2006. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula. A.I. Kurentsov's Annual Memorial Meetings 17: 114-119.
- Kim B.J. 1986. A systematic study of ants in Island Ullungdo of Korea on the basis of external fine features. The journal of Natural Science 5(2): 84-94.
- Kim B.J. 1996. Synonymic list and distribution of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) in Korea. Entomological Research Bulletin Supplement 169-196.
- Kiran K., and C. Karaman. 2012. First annotated checklist of the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zootaxa 3548: 1-38.
- Kiran K., and N. Aktac. 2006. The vertical distribution of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Samanh Mountains, Turkey. Linzer Biol. Beitr. 38(2): 1105-1122.
- Kofler A. 1995. Nachtrag zur Ameisenfauna Osttirols (Tirol, Österreich) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 1: 14-25.
- Kondoh M. 1961. Ants from Hakone region. Hakone Hakubutsu 1:16-27.
- Korlevic, A.. "Prilozi fauni hrvatskih opnokrilaca." Glasn. Hrv. Narav. Dr. 5 (1890): 189-250.
- Kubota S., and M. Terayama. 1982. Ant fauna of Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan (IV) Ants of Kakio. Kanagawa-chuho (Journal of the Kanagawa Entomologists Association) 21-28.
- Kubota S.; Terayama, M. 1989. Ant fauna of Tokyo. (1) A list of ants collected at the parks. Ari 16:14-16.
- Kubota. S., and M. Terayama. 1988. Ant fauna of Tokyo. (1) A list of ants collected at the parks. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 16: 14-16
- Kupianskaia A.N. 1990. Murav'I (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Dal'nego Vostoka SSSR (1989). Vladivostok. 258 pages.
- Kupianskaya A. N., Lelej, A.S., and Urbain, B. K. 2000. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist. 92:1-21.
- Kupianskaya A. N., and A. S. Lelej. 2000. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) collected in the Habomai and Shikotan (Kuril Islands) in 1998. Far Eastern entomologist 92: 22-24.
- Kupianskaya, A. N., Lelej, A.S., and Urbain, B. K. 2000. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist. 92:1-21.
- Kvamme T. 1982. Atlas of the Formicidae of Norway (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Insecta Norvegiae 2: 1-56.
- Kvamme T., and A. Wetas. 2010. Revidert liste over norske maur Inkludert dialektiske navn og forslag til nye norske navn og forslag til norske navn. Norsk institutt for skog og landskap, Ås. 127 pp
- Lapeva-Gjonova, L., V. Antonova, A. G. Radchenko, and M. Atanasova. "Catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Bulgaria." ZooKeys 62 (2010): 1-124.
- Le Moli F., and A. Zaccone. 1995. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna del Cansiglio (Prealpi Carniche). Soc. Ven. Sc. Nat. 20: 33-52.
- Lebas C., C. Galkowski, P. Wegnez, X. Espadaler, and R. Blatrix. 2015. The exceptional diversity of ants on mount Coronat (Pyrénées-Orientales), and Temnothorax gredosi(Hymenoptera, Formicidae) new to France. R.A.R.E., T. XXIV (1): 24 33
- Lehouck V., D. Bonte, W. Dekoninck, and J. P. Maelfait. 2004. The distribution of ant nests (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in coastal grey dunes of Flanders (Belgium) and their relationship to myrmecochorous plants. Belg. J. Zool. 134 (2/1) : 89-96.
- Li Z.h. 2006. List of Chinese Insects. Volume 4. Sun Yat-sen University Press
- Lillig M., and E. Dewes. 2015. The former Siegfried Line as habitats for ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Abh. Delattinia 37: 117 - 136
- Livory A. 2003. Les fourmis de la Manche. L'Argiope 39: 25-49.
- Lomnicki J. 1928. Spis mrówek Lwowa i okolicy. Ksiegi Pamiatkowej (Lecia Gimn. IV Jana Dlugosza Lwowie) 50: 1-10.
- Lorinczi G. 2011. Lasius (Chthonolasius) nitidigaster Seifert, 1996 -a new ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) for the Hungarian fauna. Natura Somogyiensis 19: 223-228.
- Ma Yonglin, Xin Ming, Song Lingying, He Dahan. 2008. A survey of ants(Hymenoptera:Formicidae) species and distribution in Ningxia. Journal of Agricultural Sciences 29(1): 35-38.
- Maavara V. 1953. Ants of Estonian SSR. ABIKS loodusevaatlejale 10: 1-44.
- Majzlan O., and P. Devan. 2009. Selected insect groups (Hymenoptera, Neuroptera, Mecoptera, Raphidioptera) of the Rokoš Massif (Strážovské vrchy Mts.). Rosalia (Nitra), 20, p. 63–70.
- Marko B. 2008. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Sand Dunes of Foieni Protected Area and Its Surroundings (Satu Mare County, Romania), and a New Species for the Romanian Fauna. Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica 16(3): 87-99.
- Markó B. 1997. Contribution to the Knowledge of the Ant-Fauna (Hymenoptera: Fromicoidea) of the Cri?ul-Repede River-Valley. In: Sárkány-Kiss, A., Hamar, J. (szerk.): The Cri?/Körös Rivers' Valleys. A study of the geography, hydrobiology and ecology of the river system and its environment. Tiscia Monograph Series 2, Szolnok-Szeged-Tîrgu Mure?, pp. 345-352.
- Markó B., B. Sipos, S. Csősz, K. Kiss, I. Boros, and L. Gallé. 2006. A comprehensive list of the ants of Romania (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 9: 65-76.
- Martínez Ibáñez, M. D., and A. Tinaut. "Nuevas especies de formícidos (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) para la Sierra de Albarracín (Teruel)." Real Sociedad Española de Historia Natural Tomo extra (1996): 174-177.
- Masuko K., H. Yamaoka, T. Kannari, and S. Usuba. 1985. Ants of Mt. Kiyosumi (4). Kiyosumi 11: 9-12.
- Mei, M.. "Nuovi reperti de formicidi per l'Italia centrale (Hymenoptera, Formicidae)." Bollettino dell'Associazione Romana di Entomologia 37 (1984): 49-58.
- Menozzi C. 1918. Primo contributo alla conoscenza della fauna mirmecologica del Modenese. Atti della Società dei Naturalisti e Matematici di Modena. (5)4: 81-88.
- Minato M., T. Kameyama, F. Ito, and T. Itino. 1996. A preliminary report of ant fauna in Gagawa Prefecture. Ari 20: 9-13.
- Mizota K. 2002. A check list of insects in Kinkazan Island, Miyagi Pref., Northeastern Japan: A bibliographical Survey. Bulletin of Miyagi University of Education Environmental Education 5: 69-78.
- Mizutani A. 1979. A myrmecofaunal survey at Hiyama Experiment Forest, Hokkaido University. Research Bulletin of the College Experiment Forests, Hokkaido University 36:509-516.
- Mizutani A. 1979. A myrmecofaunal survey at Hiyama Experiment Forest, Hokkaido University. Research Bulletins of the College Experiment Forests Hokkaido University 36(2): 509-516.
- Morisita M. 1945. Ants of the southern part of Hokkaido, Japan. [In Japanese.] Mushi 16:21-28.
- Morisita, M. 1941. Notes on Camponotus herculeanus subsp. vagus var. yessensis Teranishi (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). [In Japanese.]. Mushi 13:94. [1941-02-28] PDF 127445
- Moscaliuc L. 2008. Notes on the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Rarau mountain. Analele Facult??ii de Biologie, Univ A.I. Cuza Ia?i 54: 53-55.
- Murata K. 1990. Ant fauna of Yamizo Mountains. Memoirs of Tochigi Prefectural Museum 8: 86-103.
- Müller, G.. "Le formiche della Venezia Guilia e della Dalmazia." Bollettino della Società Adriatica di Scienze Naturali in Trieste 28 (1923): 11-180.
- Nadig A. 1918. Alcune note sulla fauna dell'alta Valsesia. Formicidae. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 56: 331-341.
- Nagy C., A. Tartally, F. Villisics, O. Merkl, E. Szita, A. Podlussany, D. Redei, S. Csosz, G. Pozgai, A. Orosz, G. Szovenyi, and V. Marko. 2009. Effects of the invasive garden ant, Lasius neglectus VAN LOON, BOOMSMA & ANDRÁS-FALVY, 1990 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), on arthropod assemblages: pattern analyses in the type supercolony. Myrmecological News 12: 171-181.
- Natuhara Y. 1998. Ant faunae in Osaka City and three other sites in Osake Prefecture. Bulletin of Myrmecological Society of Japan 22: 1-5.
- Negoro H. 1994. Ants from Toyama Prefecture, Hokuriku. Bulletin of the Toyama Science Museum 17: 35-47.
- Nemet E., Z. Czekes, I. Tausan, and B. Marko. 2012. Contribution to the knowledge of the myrmecofauna of the Cefa Nature Park (North-Western Romania). Acta Scientiarum Transylvanica 20(1): 61-72.
- Neumeyer R., and B. Seifert. 2005. Commented check list of free living ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species of Switzerland. Bulletin de la Societe Entomologique Suisse 78: 1-17.
- Nielsen M. G. 2011. A check list of Danish ants and proposed common names. Ent. Meddr. 79: 13-18.
- Novgorodova T. A., A. S. Ryabinin. 2015. Trophobiotic associations between ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) and aphids (Hemiptera, Aphidomorpha) in South Zauralye. News of Saratov University. Chemistry Series, Biology, Ecology 2(15): 98-107.
- Nylander, W.. "Synopsis des Formicides de France et d'Algérie." Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie (4)5 (1856): 51-109.
- O'Rourke F. J. 1948. The distribution and general ecology of the Irish Formicidae. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy. Section B: Biological, Geological, and Chemical Science 52: 383-410.
- Ochi K. 1983. Distribution pattern of ants in pine stands, with special reference to Monomorium nipponense Wheeler (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Gensei 44:1-6.
- Ohkawara K., and Y. Fukushima. 1998. A Preliminary report of ant fauna in Ishikawa Prefecture, Central Japan. Ari 22: 6-9.
- Ottonetti L., L. Tucci, and G. Santini. 2006. Recolonization Patterns of Ants in a Rehabilitated Lignite Mine in Central Italy: Potential for the Use of Mediterranean Ants as Indicators of Restoration Processes. Restoration Ecology 14(1): 6066.
- Paraschivescu D. 1972. Fauna mirmecologica din zonele saline ale Romaniei. Studii si Cercetari de Biologie. Seria Zoologie 24: 489-495.
- Paraschivescu D. 1978. Elemente balcanice in mirmecofauna R. S. Romania. Nymphaea 6: 463- 474.
- Park S.J., K.G. Kim, J.H. Kim, and B.J. Kim. 1998. Ants from the Seoraksan National Park. The Korean Journal of Systematic Zoology 14(4): 429-439.
- Park, Seong, Joon and Byung, and Kim, Jin. 2002. Faunal Comparison of Ants among Cheongsando and Other Islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Jornal of Entomology. 32(1):7-12.
- Pavlova N. S. 2014. To ant fauna (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the floodplain of Medvedista River (Saratov Province). Entomological and parasitological studies in the Volga region 11: 145-147.
- Peng Y. 2008. Ants resources in Heilongjiang Province and Flora (Hymenoptera). Master's Thesis Northeast Normal University, China. 90 Pages.
- Petal J. M. 1967. Contribution a la connaissance des fourmis (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) de la region de Lublin. VII. Associations des fourmis des milieux de tourbieres, de forets et de dunes aux environs de Libiszow (dist. De Parczew). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Lublin-Polonia 22(9): 117-130.
- Petrov I. Z. 2002. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of the Banat Province (Serbia). Archives of Biological Sciences, Belgrade, 54(12): 57-64.
- Petrov I. Z. 2010. Contribution to the myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Krusevac and its surroundings. Acta entomologica serbica, 2010, 15(1): 145-148.
- Petrov I. Z., B. Petrov, D. Milicic, T. Karan-Znidarsic. 2007. Contribution to the Myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of East and South Serbia. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 59(3): 295-299.
- Petrov I. Z., and C. A. Collingwood. 1992. Survey of the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of Yugoslavia. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade) 44: 79-91.
- Poldi B., M. Mei, and F. Rigato. 1995. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Vol 102. Checklist delle specie della fauna Italiana: 1-10.
- Punttila P., Y. Haila, and H. Tukia. 1996. Ant communities in taiga clearcuts: habitat effects and species interactions. Ecography 19: 16-28.
- Punttila P., and Y. Haila. 1996. Colonisation of a burned forest by ants in the southern Finnish Boreal forest. Silva Fennica 30(4): 421-435.
- Pusvaskyte O. 1979. Myrmecofauna of the Lituanian SSR. Acta Entomologica Lituanica 4: 99-105.
- Radchenko A., W. Czechowska, W. Czechowski, and E. Siedlar. 1999. Four species of the ant genus Lasius F. new to Poland, with additions to the records for previously reported species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Fragmenta Faunistica 42(11): 115-121.
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.
- Reznikova Z. I. 2003. Distribution patterns of ants in different natural zones and landscapes in Kazakhstan and West Siberia along a meridian trend. Euroasian Entomological Journal 2(4): 235-342.
- Rigato F., and R. Sciaky. 1989. Contributo alla conoscenza della mirmecofauna della Val Gesso (alpi Marittime) (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Boll. Mus. Reg. Sci. Nat. Torino 7(2): 427-442.
- Sakai H. 2002. Reproductive flight season of Japanese ants. Ari 26: 33-39.
- Santschi F. 1926. Travaux scientifiques de l'Armée d'Orient (1916-1918). Fourmis. Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle 32: 286-293.
- Schifani E., and A. Alicata. 2018. Exploring the myrmecofauna of Sicily: thirty-two new ant species recorded, including six new to Italy and many new aliens (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Polish Journal of Entomology 87 (4): 323–348.
- Schlick-Steiner B. C., and F. M. Steiner. 1999. Faunistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen an den freilebenden Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Wiens. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 3: 9-53.
- Seifert B. 1994. Die freilebenden Ameisenarten Deutschlands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) und Angaben zu deren Taxonomie und Verbreitung. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 67(3): 1-44.
- Sellier Y., C. Galkowski, C. Lebas, and P. Wegnez. 2016. Découverte de Temnothorax pardoi (Tinaut, 1987) dans la réserve naturelle nationale du Pinail (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Revue de l’Association Roussillonnaise d’Entomologie 25(2): 106-113.
- Sevastianov, V.D. 1980. New taxa of mites of the family Dolichocybidae (Trombidiformes, Tarsonemina) and phylogenetic relations of its subfamilies. Zoologicheskiy Zhurnal, 59: 1453– 1462 (In Russian).
- Shilenkov V. G., A. A. Pankratov, and E. V. Sofronova. 2012. Preliminirary notes on species composition of Magdansky Reserve. Baikal Zoological Journal 3: 30-34.
- Shlyakhtenok A. S. 2007. Hymenoptera Aculeata of Raised Bogs in Belarus. Entomological Review 87(2): 136147.
- Slipinski P., B. Marko, K. Rzeszowski, H. Babik, and W. Czechowski. 2014. Lasius fuliginosus(Hymenoptera: Formicidae) shapes local ant assemblages. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10(2): 404-412.
- Slipinski P., M. Zmihorski, and W. Czechowski. 2012. Species diversity and nestedness of ant assemblages in an urban environment. Eur. J. Entomol. 109: 197206.
- Sommer F., and H. Cagniant. 1988. Peuplements de fourmis des Albères Orientales (Pyrénées-Orientales, France) (Première partie). Vie Milieu 38: 189-200.
- Sonnenburg H. 2005. Die Ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Niedersachsens und Bremens. Braunschweiger Naturkundliche Schriften 7: 377-441.
- Sonobe R. 1971. Ant survey of the Mt. Daisetsu area. Faunal Survey of the Mt. Daisetsu area. JIBP main area XIV. Annual Report of JIBP/CT-S: 199-210.
- Sonobe R. 1977. Ant fauna of Miyagi prefecture , Japan. Japanese Journal of Ecology 27: 111-116.
- Steffek J., and M. Wiezik. 2008. Exploited peatbog and associated mollusk and ant assemblages: still a reasonable protection? Naturae Tutela 12: 15-19.
- Steiner F. M., S. Schödl, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2002. Liste der Ameisen Österreichs (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Stand Oktober 2002. Beiträge zur Entomofaunistik 3: 17-25.
- Stiprais M. 1973. Materi?li par R?gas kukai?u faunu. - Latvijas Entomologs, 15: 30-32.
- Stukalyuk S. V. 2015. Structure of the ant assemblages (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the broad-leaved forests of Kiev. Entomological Review 95(3): 370–387.
- Stukalyuk S. V. 2017. Stratification of the ant species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the urban broadleaf woodlands of the city of Kiev. Entomological Review 97(3): 320-343.
- Stumper R. 1953. Etudes myrmecologiques. XI. Fourmis luxembourgeoises. Bulletin Soc. Nat. luxemb. 57: 122-135.
- Suvak M. 2007. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the stubble-fields of east Slovakia. Acta Zoologica Universitatis Comenianae. 47: 21-33
- Suñer i Escriche, David. "Contribució al coneixement mirmecologic de Gavarres, Montgrí, Guilleríes i la Serralada Transversal." Tesis Doctoral Universida (1991): 577 pp.
- Szujecki A., J. Szyszko, S. Mazur, and S. Perlinski. 1978. A succession of the ants (Formicidae) on afforested arable land and forest soils. Memorabilia Zoologica 29: 183-189.
- Tamura H., Y. Nakamura, K. Yamauchi, and T. Fujikawa. 1969. An ecological survey of soil fauna in Hidaka-Mombetsu, Southern Hokkaido. Journal of the Faculty of Science Hokkaido University, Zoology 17(1): 17-57.
- Tanaka B., N. Kanie, T. Mano, R. Arita, and A. Shiragane. 1999. The insect fauna between Takabashi bridge and Nomi-kouen Park, margins of the Yahagigawa river. ????? 3: 35-79.
- Tang J., Li S., Huang E., Zhang B. and Chen Y.. 1995. Hymenoptera: Formicidae (1). Economic Insect Fauna of China 47: 1-133.
- Tartally A. 2009. Data on the ant fauna of Gy?r?f? (SW-Hungary) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natura Somogyiensis 13: 155-158.
- Tausan I., J. Dauber, M. R. Tricia, and B. Marko. 2017. Succession in ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in deciduous forest clear-cuts – an Eastern European case study. European Journal of Entomology 114: 92-100.
- Tausan I., M. M. Jerpel, I. R. Puscasu, C. Sadeanu, R. E. Brutatu, L. A. Radutiu, and V. Giurescu. 2012. Ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Sibiu County (Transylvania, Romania). Brukenthal. Acta Musei 7(3): 499-520.
- Tausan I., and B. Marko. 2009. Comparative analysis of ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the surroundings of Sibiu (Romania). Brukenthal. Acta Musei 4(3): 635-644.
- Terayama M. 1977. Checklist of the known ants of Saitama Prefecture. Insects and nature 12(4): 26-27
- Terayama M. 1978. Ants of Bukozan. Nature and insects 13(4): 32-34.
- Terayama M. 1992. Structure of ant communities in East Asia. A. Regional differences and species richness. Bulletin of the Bio-geographical Society of Japan 47: 1-31.
- Terayama M. 1994. Ants of Okushiri-to Island, Hokkaido. Ari 18: 28-29.
- Terayama M., K. Ogata, and B.M. Choi. 1994. Distribution records of ants in 47 prefectures of Japan. Ari (report of the Myrmecologists Society of Japan) 18: 5-17.
- Terayama M., and K. Murata. 1990. Effects of area and fragmentation of forests for nature conservation: Analysis by ant communities. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Japan 45(2): 11-17.
- Terayama M., and R. Sonobe. 2002. Ants from the Nasu Imperial Villa, Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. Flora and fauna of the Tochigi Prefectural Museum research report Nasu Imperial Villa 157-161.
- Terayama M., and S. Kubota. 2002. Ants of Tokyo, Japan. ARI 26: 1-32.
- Terayama. M. 1994. Ants of Okushiri-to Island, Hokkaido. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 18: 28-29
- Terayama. M. 2004. Geological and ecological distribution of Japanese ants communities. (translated from Japanese) Reports of the Saitama Prefecture Animal Research Association. 48:24
- Teruyama. M. 1988. Ant fauna of Saitama Prefecture, Japan. ARI Reports of the Myrmecologists Society (Japan) 16: 4-13
- Tie Ru, and Xu Shengquan. 2004. Variety and distribution of ants in Northwest China. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College 25(3): 4-9.
- Vagalinski B., and A. Lapeva-Gjonova. 2012. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Plana Mountain (Bulgaria). Historia naturalis bulgarica 20: 87-101.
- Vesni? A. 2011: Revidirani sistematski prijegled mrava Bosne i Hercegovine. Unutar : S. Lelo (urednik), Fauna Bosne i Hercegovine Biosistematski pregledi. 7. izmijenjeno i popravljeno interno izdanje Udruenja za inventarizaciju i zatitu ivotinja, Ilija, Kanton Sarajevo, pp: 205-207.
- Vogrin, V.. "Prilog fauni Hymenoptera - Aculeata Jugoslavije." Zast. Bilja 31(suppl.) (1955): 1-74.
- Wang Lu-ling. 2006. Ant resources in Kaifeng region, Henan Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology 25(3): 546-548.
- Wang Wei. 2007. Fauna of Formicidae ants from three nature reserves in southwest Hubei. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology 44(2): 267-270.
- Wegnez P. 2014. Premières captures de Lasius distinguendus Emery, 1916 et de Temnothorax albipennis (Curtis, 1854) au Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 150 (2014) : 168-171.
- Wegnez P. 2017. Découverte de Myrmica lobicornis Nylander, 1846 et Lasius jensi Seifert, 1982, deux nouvelles espèces pour le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 153: 46-49.
- Wegnez P. 2018. Premières decouvertes de Myrmica bibikoffi Kutter, 1963 et de Ponera testacea Emery, 1895, au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 154: 263–272.
- Wegnez P., D. Ignace, E. Lommelen, M. Hardy, J. Bogaert, and C. Nilsson. 2015. Redécouverte de Teleutomyrmex schneideriKutter, 1950 dans les Alpes françaises (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 52-57.
- Wegnez P., and A. Ronk. 2017. Découverte de Camponotus herculeanus (Linnaeus, 1758) et signalement de quelques autres espèces rares de fourmis au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois 119 : 153–159.
- Wegnez P., and M. Fichaux. 2015. Liste actualisee des especes de fourmis repertoriees au Grand-Duche de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 150-165
- Wheeler W. M. 1906. The ants of Japan. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 22: 301-328.
- Wheeler W. M. 1921. Chinese ants. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 64: 529-547.
- Wheeler W. M., and I. W. Bailey. 1920. The feeding habits of pseudomyrmine and other ants. Transactions of the American Philosophical Society (2)22: 235-279.
- Wiezik M. 2007. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of mountain and alpine ecosystems at Southern part of Krá?ovoho?ské Tatry Mts. Naturae Tutela 11: 85-90.
- Wilson E. O. 1955. A monographic revision of the ant genus Lasius. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 113: 1-201
- Wu J. and Wang C.. 1995. The ants of China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. 214 pp.
- Wu W. 2010. The taxonomic and fauna study on the Formicidae of Liaoning Province (Insecta: Hymenoptera). Master's Thesis Northeast Normal University, 75 pages.
- Xin M., Y. Ma, and D. He. 2011. Fauna composition of Formicidae in Ningxia. Journal of Ningxia University (Natural Science Edition) 32(4): 403-412.
- Yamauchi K. 1968. Additional Notes on the Ecological Distribution of Ants in Sapporo and the Vicinity . Journal of the Faculty of Science Hokaido University, series VI, Zoology 16(3): 382-395.
- Yamauchi K. 1979. Taxonomical and ecological studies on the ant genus Lasius in Japan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). I. Taxonomy. Sci. Rep. Fac. Educ. Gifu Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 6: 147-181.
- Yamauchi K., and K. Hayashida. 1968. Taxonomic studies on the genus Lasius in Hokkaido, with ethological and ecological notes (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). I. The subgenus Dendrolasius or Jet Black Ants. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Ser. VI. Zool. 16: 396-412.
- Yasuda N., and M. Sato. 1999. Checklist of insect fauna of Nayoro. Research Records of North Country, Nayoro North Country Museum (in Japanese) 3: 15-36.
- Yoshimura M. 1998. Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 1, Risiri Island). Rishiri Studies 17:33-38.
- Yoshimura M. 1999. Ants in the island of Hokkaido (Part 2, Part Rebun) Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 2, Rebun-Island). Rishiri Studies 18: 49-54.
- Yoshimura M. 2000. Ants in the island of Hokkaido (Part 3, Part ???) Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 3, Teuri Island). Rishiri Studies 19: 27-35.
- Zhang W. and Zheng Z.. 2002. Studies of ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) fauna in Sichuan Province. Entomotaxonomia 24(3): 216-222.
- Zhou S.-Y. 2001. Ants of Guangxi. Guangxi Normal University Press, Guilin, China, Guilin, China. 255 pp.
- Zhuytszyuan D. 2016. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Nizhne-Svirsky reserve and their environmental features. Master's thesis Saint Petersburg State University.
- Zryanin V. A., and T. A. Zryanina. 2007. New data on the ant fauna Hymenoptera, Formicidae in the middle Volga River Basin. Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii 127(2): 226-240.
- de Haro, Andrés, and C. A. Collingwood. "Prospección mirmecológica en la Cordillera Ibérica." Orsis 6 (1991): 129-126.
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Temporary parasite
- Photo Gallery
- North temperate
- Ant Associate
- Host of Lasius bicornis
- Host of Lasius jensi
- Host of Lasius meridionalis
- Host of Lasius mixtus
- Host of Lasius rabaudi
- Host of Lasius sabularum
- Host of Lasius umbratus
- Aphid Associate
- Host of Chaitophorus populeti
- Host of Chaitophorus vitellinae
- Host of Cinara boerneri
- Host of Cinara laricis
- Host of Cinara pinea
- Host of Lachnus tropicalis
- Host of Pterocomma pilosum
- Host of Pterocomma rufipes
- Host of Stomaphis japonica
- Host of Stomaphis quercus
- Host of Symydobius oblongus
- Eucharitid wasp Associate
- Host of Pseudometagea sp.
- Pteromalid wasp Associate
- Host of Spalangia crassicornis
- Host of Spalangia nigripes
- Mite Associate
- Host of Formicomotes octipes
- Host of Gaeolaelaps glabrosimilis
- Host of Imparipes brevibasis
- Host of Imparipes fuliginosophilus
- Host of Imparipes obsoletus
- Host of Imparipes sevastianovi
- Host of Petalomium carelitschensis
- Host of Petalomium fuliginosum
- Host of Petalomium podolicus
- Host of Scutacarus flexisetus
- Host of Scutacarus longisetus
- Host of Unguidispus contematosus
- Milichiid fly Associate
- Host of Milichia ludens
- Host of Phyllomyza donisthorpei
- Host of Phyllomyza equitans
- Host of Phyllomyza flavitarsis
- Host of Phyllomyza pallida
- Fungus Associate
- Host of Beauveria bassiana
- Ichneumonid wasp Associate
- Host of Eurypterna cremieri
- Host of Ghilaromma fuliginosi
- Host of Hybrizon arakawae
- Host of Hybrizon cremieri
- Host of Hyrbizon fuliginosi
- Phorid fly Associate
- Host of Pseudacteon formicarum
- ''Microdon'' fly Associate
- Host of Microdon sp.
- FlightMonth
- Karyotype
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Lasiini
- Lasius
- Lasius fuliginosus
- Formicinae species
- Lasiini species
- Lasius species
- Ssr








