Formica truncorum
| Formica truncorum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Formicini |
| Genus: | Formica |
| Species: | F. truncorum |
| Binomial name | |
| Formica truncorum Fabricius, 1804 | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
| Common Name | |
|---|---|
| Kezune-akayama-ari | |
| Language: | Japanese |
This species builds discrete nests in well insolated situations. Mounds are up to 1m in diameter and constructed from dead grass or conifer needles. According to Kupianskaja (pers. com.) there are differences in nest site preference and nesting habits between F. truncorum and Formica yessensis in the Maritime Province of Siberia (Japanese Ant Image Database).
| At a Glance | • Polygynous • Supercolonies • Temporary parasite • Diploid male |
Photo Gallery
Identification
Large workers with head, mesosoma and base of first gaster tergite bright yellowish red, gaster greyish brown covered with long pubescence; smaller workers are usually darker but never with clearly marked black patches as in Formica pratensis. Eyes, occiput, genae, gula, scapes and tibiae as well as whole body covered in short erect hairs. Frons with large shallow punctures; frontal triangle shining without punctures or sculpture. Funiculus in larger workers slender with segments two and three twice as long as wide. Lateral clypeal pits deep and rounded. Length: 3.5-9.0 mm (Collingwood 1979).
Keys including this Species
Distribution
Jura Alps to North Japan, Italy to North Norway (Collingwood 1979). In Japan the known geographical range of F. truncorum is nearly separate from that of F. yessensis, but further distributional analysis is desirable (Japanese Ant Image Database).
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 70.377854° to 32.48611°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Oriental Region: India, Pakistan.
Palaearctic Region: Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, China (type locality), Croatia, Czechia, Democratic Peoples Republic of Korea, Denmark, Estonia, Finland (type locality), Germany (type locality), Hungary, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Mongolia, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Republic of Korea, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Russian Federation (type locality), Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland (type locality), Türkiye, Ukraine.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
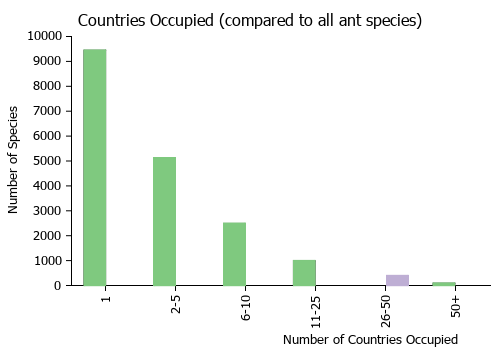
|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |
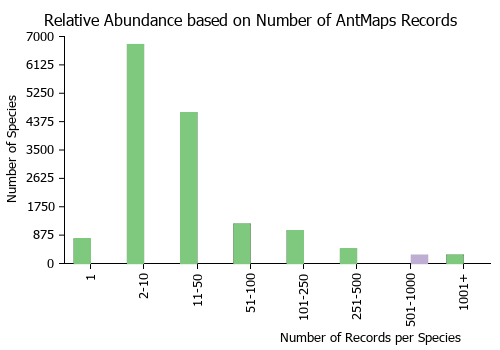
|
Biology
Collingwood (1979) - This species has large spreading colonies among stones or in tree stumps with loose surface leaf litter sometimes built into a shallow loose mound. This is an aggressive acid squirting species found at the borders of woodland and in stony banks and often particularly abundant on offshore islands. F. truncorum is normally polygynous, sometimes with many small dark headed queens. New colonies may be formed by nest splitting or by the adoption of single large red headed queens by Formica fusca and allied species. Males and queens occur in July and August, latter than with most members of the F. rufa group.
Nesting Habits
Rybnikova and Kuznetsov (2015) studied nest complexes of wood ants in the Darwin Nature Reserve (Rybinsk Reservoir basin, Vologda and Yaroslavl Provinces, Russia). Their work assessed, in part, how wild boars and seasonal flooding may influence the survival and viability of wood ant colonies.
Silon Island is a tall ridge of glacial origin. The ant communities of the island were studied in the late 1990s (Rybnikova and Kuznetsov, 1998). The greatest part of the island is occupied by a lichen pine forest which provides little food for red wood ants; therefore, foraging mostly takes place in the riparian zone.
The complex of Silon Island—North. A complex of F. truncorum exists in the northern part of the island. In 1997–1998 it comprised 7–8 living nests and 12–15 foraging ones. The living nests of this species concentrated around the inner drainless depression filled with snowmelt water, with hydrophilic vegetation on its periphery. During the low-water periods, when the exposed inundation zone of the reservoir was overgrown with riparian vegetation, the ants built small foraging nests in the shoreline part of the island, at the edge of the precipice. As many as 15 such nests were present on the shore in some years. The foragers traveled down the precipice into the inundation zone, where aphid colonies developed on the riparian and periaquatic vegetation. After the long sequence of high-water years, four living nests remained on the shore, in the willow shrubs at the edge of the inundation zone. Five more living nests remained on the shores of the inner drainless depression. The mean nest size increased due to the disappearance of more than half of the small, mostly foraging nests. Every year, nests of this complex are destroyed by the bear which migrates to the island in the second half of summer. In some years, occasional wild boars also visit the island.
Flight Period
| X | X | X | |||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
Source: antkeeping.info.
- Check details at Worldwide Ant Nuptial Flights Data, AntNupTracker and AntKeeping.
 Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Flight Month data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- This species is a temporary parasite which uses these species as hosts: Formica fusca (Chernenko et al., 2011; de la Mora et al., 2021; Ruano et al., 2018; Seifert, 2018), Formica lemani (de la Mora et al., 2021; Ruano et al., 2018), Formica polyctena (de la Mora et al., 2021; Seifert, 2018) (single observation), Formica pratensis (de la Mora et al., 2021; Ruano et al., 2018) and Formica rufibarbis (Chernenko et al., 2011; de la Mora et al., 2021; Ruano et al., 2018).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formica fusca (a xenobiont) in Finland (Czechowski, 2004; Kanizsai et al., 2013) (Different successional series of rocky habitats. In rock crevice).
- This species is a xenobiont for the ant Formicoxenus nitidulus (a xenobiont) (Holldobler & Wilson 1990; Busch 2001; Martin et al. 2007).
The record of Formica sanguinea being enslaved by this species (Ruano et al., 2018) is unlikely based on biology (Seifert, pers. comm., in de la Mora et al., 2021).
Fungi
- This species is a host for the fungus Aegeritella superficialis (a pathogen) (Espadaler & Santamaria, 2012).
Life History Traits
- Queen number: polygynous (Rosengren et al., 1985; Frumhoff & Ward, 1992)
Castes
Male
Diploid males are known to occur in this species (found in 9.8% of 1120 examined nests) (Pamilo et al., 1994; Cournault & Aron, 2009).
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- truncorum. Formica truncorum Fabricius, 1804: 403 (q.) CZECHOSLOVAKIA. Subspecies of rufa: Emery & Forel, 1879: 450; Santschi, 1925g: 351; Karavaiev, 1936: 247. Status as species: Bondroit, 1917a: 174; Stitz, 1939: 344; Novak & Sadil, 1941: 105; Holgersen, 1942: 13; Dlussky, 1967a: 81; Tarbinsky, 1976: 192; Kutter, 1977c: 274; Gösswald, 1989: 21; Kupyanskaya, 1990: 192; Atanassov & Dlussky, 1992: 270. Senior synonym of truncicola: Roger, 1863b: 13; Bondroit, 1918: 60; Dlussky, 1967a: 81; Radchenko, 2007: 36; of truncicolopratensis: Dlussky, 1967a: 81; Bernard, 1967: 307; of menozzii, rufotruncicola, staegeri and material of the unavailable name stitzi referred here: Dlussky, 1967a: 81. Current subspecies: nominal plus finzii, frontalis.
- truncicola. Formica truncicola Nylander, 1846a: 907 (w.q.) FINLAND. Nylander, 1849: 29 (m.). Subspecies of rufa: Forel, 1874: 52; André, 1903: 128; Ruzsky, 1905b: 330; Wheeler, W.M. 1908g: 406; Emery, 1909b: 187; Forel, 1915d: 57; Emery, 1916b: 256; Santschi, 1925f: 96. Status as species: Bingham, 1903: 334; Wheeler, W.M. 1913f: 434. Senior synonym of simulata: Forel, 1894c: 403. Junior synonym of truncorum: Roger, 1863b: 13; Bondroit, 1918: 60; Emery, 1925b: 255; Bernard, 1967: 307; Dlussky, 1967a: 81; Dlussky & Pisarski, 1971: 174; Tarbinsky, 1976: 192; Kutter, 1977c: 274; Radchenko, 2007: 36.
- truncicolopratensis. Formica rufa var. truncicolopratensis Forel, 1874: 53 (w.q.m.) SWITZERLAND. Subspecies of pratensis: Dalla Torre, 1893: 205; of rufa: Karavaiev, 1912b: 589; of truncorum: Stitz, 1939: 346; Holgersen, 1942: 14. Raised to species: Bondroit, 1918: 61. Junior synonym of truncorum: Bernard, 1967: 307; Dlussky, 1967a: 81; Dlussky & Pisarski, 1971: 174.
- simulata. Formica simulata Smith, F. 1878b: 10 (w.) CHINA. Junior synonym of truncicola: Forel, 1894c: 403.
- rufotruncicola. Formica rufa var. rufotruncicola Ruzsky, 1896: 68 (w.) RUSSIA. [First available use of Formica rufa subsp. pratensis form. rufotruncicola Ruzsky, 1895: 11; unavailable name.] Junior synonym of truncorum: Dlussky, 1967a: 81.
- menozzii. Formica truncorum var. menozzii Stitz, 1939: 347 (w.) GERMANY. [First available use of Formica rufa subsp. truncicola var. menozzii Krausse, 1926c: 336; unavailable name. Note: truncicola is misspelled aruncicola in this paper.] Junior synonym of truncorum: Dlussky, 1967a: 81.
- staegeri. Formica truncorum var. staegeri Stitz, 1939: 347 (w.) GERMANY. [First available use of Formica rufa subsp. truncicola ab. staegeri Krausse, 1926d: 264; unavailable name.] Subspecies of truncorum: Betrem, 1960b: 76. Junior synonym of truncorum: Dlussky, 1967a: 81; Dlussky & Pisarski, 1971: 174.
Description
Karyotype
- See additional details at the Ant Chromosome Database.
 Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- n = 28 (Finland) (Rosengren et al., 1980) (Only one pupa analyzed was n=27).
- n = 26, 2n = 52 (Finland; Japan; Switzerland) (Imai & Yosida, 1964; Imai, 1969; Hauschteck-Jungen & Jungen, 1976; Rosengren et al., 1980).
References
- Antonov, I.A., Bukin, Yu.S. 2016. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the ant genus Formica L. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Palearctic region. Russian Journal of Genetics 52(8), 810–820 (doi:10.1134/s1022795416080020).
- Atanassov, N.; Dlussky, G. M. 1992. Fauna of Bulgaria. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Fauna Bûlg. 22: 1-310 (page 270, Status as species)
- Baty, J.W., Bulgarella, M., Dobelmann, J., Felden, A., Lester, P.J. 2020. Viruses and their effects in ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News 30: 213-228 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_030:213).
- Berkelhamer, R.C. 1980. Reproductive strategies in ants: A comparison of single-queened versus multiple-queened species in the subfamily Dolichoderinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
- Bernard, F. 1967a [1968]. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp. (page 307, Senior synonym of truncicolopratensis)
- Bondroit, J. 1917a. Notes sur quelques Formicidae de France (Hym.). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1917: 174-177 (page 174, Status as species)
- Bondroit, J. 1918. Les fourmis de France et de Belgique. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 87: 1-174 (page 60, Senior synonym of truncicola)
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Borowiec, M.L., Cover, S.P., Rabeling, C. 2021. The evolution of social parasitism in Formica ants revealed by a global phylogeny. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118, e2026029118 (doi:10.1073/pnas.2026029118).
- Boulay, R., Hefetz, A., Soroker, V., Lenoir, A. 2000. Camponotus fellah colony integration: worker individuality necessitates frequent hydrocarbon exchanges. Animal Behaviour 59, 1127–1133 (doi:10.1006/ANBE.2000.1408).
- Bracko, G., Wagner, H.C., Schulz, A., Gioahin, E., Maticic, J., Trantnik, A. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10: 10-24.
- Brelsford, A., Purcell, J., Avril, A., Tran Van, P., Zhang, J., Brütsch, T., Sundström, L., Helanterä, H., Chapuisat, M. 2020. An ancient and eroded social supergene is widespread across Formica ants. Current Biology 30, 304–311 (doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.032).
- Bulter, I. 2020. Hybridization in ants. Ph.D. thesis, Rockefeller University.
- Chernenko, A., Vidal‐Garcia, M., Helantera, H., Sundstrom, L. 2013. Colony take‐over and brood survival in temporary social parasites of the ant genus Formica. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 67: 727‐735 (doi:10.1007@s00265-013-1496-7).
- Collingwood, C. A. 1979. The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark. Fauna Entomol. Scand. 8:1-174.
- Cournault, L., Aron, S. 2009. Diploid males, diploid sperm production, and triploid females in the ant Tapinoma erraticum. Naturwissenschaften 96: 1393–1400 (doi:10.1007/s00114-009-0590-1).
- Csősz, S., Báthori, F., Gallé, L., Lőrinczi, G., Maák, I., Tartally, A., Kovács, É., Somogyi, A.Á., Markó, B. 2021. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: Survey of ant species with an annotated synonymic inventory. Insects 16;12(1):78 (doi:10.3390/insects12010078).
- Csosz, S., Marko, B., Galle, L. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski, W., Radchenko, A., Czechowska, W. 2002. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Poland. MIZ PAS Warsaw.
- de Bekker, C., Will, I., Das, B., Adams, R.M.M. 2018. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and their parasites: effects of parasitic manipulations and host responses on ant behavioral ecology. Myrmecological News 28: 1-24 (doi:10.25849/myrmecol.news_028:001).
- de la Mora, A., Sankovitz, M., Purcell, J. 2020. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) as host and intruder: recent advances and future directions in the study of exploitative strategies. Myrmecological News 30: 53-71 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_030:053).
- Dekoninck, W., Ignace, D., Vankerkhoven, F., Wegnez, P. 2012. Verspreidingsatlas van de mieren van België. Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 148: 95-186.
- Dlussky, G. M. 1967a. Ants of the genus Formica (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, g. Formica). Moskva: Nauka Publishing House, 236 pp. (page 81, Status as species, Senior synonym of truncicola, Senior synonym of truncicolopratensis, Senior synonym of menozzii, rufotruncicola, staegeri, stitzi)
- Dubovikoff, D.A., Yusupov, Z.M. 2017. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Emery, C.; Forel, A. 1879. Catalogue des Formicides d'Europe. Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 5: 441-481 (page 450, Subspecies/race of rufa)
- Espadaler, X., Santamaria, S. 2012. Ecto- and Endoparasitic Fungi on Ants from the Holarctic Region. Psyche Article ID 168478, 10 pages (doi:10.1155/2012/168478).
- Fabricius, J. C. 1804. Systema Piezatorum secundum ordines, genera, species, adjectis synonymis, locis, observationibus, descriptionibus. Brunswick: C. Reichard, xiv + 15-439 + 30 pp. (page 403, queen described)
- Goropashnaya, A.V., Fedorov, V.B., Seifert, B., Pamilo, P. 2012. Phylogenetic relationships of Palaearctic Formica species (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) based on mitochondrial Cytochrome b sequences. PLoS ONE 7, e41697 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041697).
- Gösswald, K. 1989. Die Waldameise. Band 1. Biologische Grundlagen, Ökologie und Verhalten. Wiesbaden: AULA-Verlag, xi + 660 pp. (page 21, Status as species)
- Helantera, H., Sundstrom, L. 2007. Worker reproduction in Formica ants. The American Naturalist 170: E15-E25.
- Holgersen, H. 1942b. Ants of northern Norway (Hym., Form.). Tromso Mus. Årsh. 63(2 2: 1-34 (page 13, Status as species)
- Imai, H.T., Kihara, A., Kondoh, M., Kubota, M., Kuribayashi, S., Ogata, K., Onoyama, K., Taylor, R.W., Terayama, M., Yoshimura, M., Ugawa, Y. 2003. Ants of Japan. 224 pp, Gakken, Japan.
- Jacobs, S. 2020. Population genetic and behavioral aspects of male mating monopolies in Cardiocondyla venustula (Ph.D. thesis).
- Johnson, C.A. 2000. Mechanisms of dependent colony founding in the slave-making ant, Polyergus breviceps Emery (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ph.D. thesis, City University of New York.
- Kanizsai, O., Lőrinczi, G., Gallé, L. 2013. Nesting associations without interdependence: A preliminary review on plesiobiosis in ants. Psyche 2013, 238602 (doi:10.1155/2013/238602).
- Karavaiev, V. 1936. The fauna of the family Formicidae (ants) of the Ukraine. Part II (conclusion). Tr. Inst. Zool. Biol. Ukr. Akad. Nauk Ser. 1 Pr. Syst. Faun. 1936: 161-316 (page 247, Subspecies/race of rufa)
- Kiran, K., Karaman, C. 2020. Additions to the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Zoosystema 42(18), 285-329 (doi:10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a18).
- Kupyanskaya, A. N. 1990a. Ants of the Far Eastern USSR. Vladivostok: Akademiya Nauk SSSR, 258 pp. (page 192, Status as species)
- Kutter, H. 1977c. Hymenoptera, Formicidae. Insecta Helv. Fauna 6: 1-298 (page 274, Status as species)
- Mabelis, A. A. 2007. Do ants need protecting? Entomologische Berichten (Amsterdam). 67(4):145-149.
- Mabelis, A. A. and J. Korczyńska. 2001. Dispersal for survival: some observations on the trunk ant Formica truncorum Fabricius. Netherlands Journal of Zoology. 51(3):299-321.
- Mabelis, A. A. and J. P. Chardon. 2006. Survival of the trunk ant (Formica truncorum Fabricius, 1804; Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in a fragmented habitat. Myrmecologische Nachrichten. 9:1-11.
- Novák, V.; Sadil, J. 1941. Klíc k urcování mravencu strední Evropy se zvlástním zretelem k mravencí zvírene Cech a Moravy. Entomol. Listy 4: 65-115 (page 1941, Status as species)
- Novgorodova, T.A., Biryukova, O.B. 2011. Some ethological aspects of the trophobiotic interrelations between ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and larvae of the sawfly Blasticotoma filiceti (Hymenoptera: Blasticotomidae), European Journal of Entomology 108, 47-52.
- Pamilo, P., Sundström, L., Fortelius, W., Rosengren, R. 1994. Diploid males and colony-level selection in Formica ants. Ethology Ecology, Evolution 6, 221–235 (doi:10.1080/08927014.1994.9522996).
- Pulliainen, U., Helantera, H., Sundstrom, L., Schultner, E. 2019. The possible role of ant larvae in the defence against social parasites. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 286: 20182867 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2018.2867).
- Ramalho, M.de O., Kim, Z., Wang, S., Moreau, C.S. 2021. Wolbachia Across Social Insects: Patterns and Implications. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 114, 206–218 (doi:10.1093/aesa/saaa053).
- Rasheed, M.T., Bodlah, I., Fareen, A.G., Wachkoo, A.A., Huang, X., Akbar, S.A. 2019. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Pakistan. Sociobiology 66(3), 426-439 (doi:10.13102/sociobiology.v66i3.4330).
- Reznikova, Z. 2020. Spatial cognition in the context of foraging styles and information transfer in ants. Animal Cognition. (doi:10.1007/s10071-020-01423-x).
- Roger, J. 1863b. Verzeichniss der Formiciden-Gattungen und Arten. Berl. Entomol. Z. 7(B Beilage: 1-65 (page 13, Senior synonym of truncicola)
- Ruano, F., Lenoir, A., Silvestre, M., Khalil, A., Tinaut, A. 2018. Chemical profiles in Iberoformica subrufa and Formica frontalis, a new example of temporary host–parasite interaction. Insectes Sociaux 66, 223–233 (doi:10.1007/S00040-018-00677-6).
- Rybnikova, I. A. and A. V. Kuznetsov. 2015. Complexes of Formica s. str. nests in the Darwin Nature Reserve and causes of their degradation. Entomological Review. 95:947-952. doi:10.1134/s0013873815080023
- Santschi, F. 1925g. Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espèces paléarctiques (Hymenopt.). EOS. Rev. Esp. Entomol. 1: 339-360 (page 351, Subspecies/race of rufa)
- Schifani, E. (2022). The new checklist of the Italian fauna: Formicidae. Biogeographia – The Journal of Integrative Biogeography 37, ucl006 (doi:10.21426/b637155803).
- Seifert, B. 2021. A taxonomic revision of the Palaearctic members of the Formica rufa group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) – the famous mound-building red wood ants. Myrmecological News 31: 133-179 (doi:10.25849/MYRMECOL.NEWS_031:133).
- Stitz, H. 1939. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der angrenzenden Meersteile nach ihren Merkmalen und nach ihrer Lebensweise. 37. Theil. Hautflüger oder Hymenoptera. I: Ameisen oder Formicidae. Jena: G. Fischer, 428 pp. (page 344, Status as species)
- Subedi, I.P., Budha, P.B., Bharti, H., Alonso, L. 2020. An updated checklist of Nepalese ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). ZooKeys 1006, 99–136 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.1006.58808).
- Sundstrom, L. 1993. Genetic population structure and sociogenetic organisation in Formica truncorum (Hymenoptera; Formicidae). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 33:345-354
- Tarbinsky, Y.S. 1976. The ants of Kirghizia. Frunze: Ilim, 217 pp. (page 192, Status as species)
- Tinaut, A., Ruano, F. 2021. Biogeography of Iberian ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Diversity 13, 88. (doi:10.3390/d13020088).
- Walin, L., Sundstrom, L., Seppa, P., Rosengren, R. 1998. Worker reproduction in ants — a genetic analysis. Heredity 81, 604–612.
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Alvarado M., and L. Galle. 2000. Ant assemblages associated with lowland forests in the southern part of the great Hungarian plain. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientarum Hungaricae 46(2): 79-102.
- AntArea. Accessed on February 5th 2014 at http://antarea.fr/fourmi/
- Antarea (Personal Communication - Rumsais Blatrix- 27 April 2018)
- Antarea (at www.antarea.fr on June 11th 2017)
- ArtDatabanken Bugs (via GBIG)
- Azuma M. 1955. A list of ants (Formicidae) from Hokkaido Is. Hyogo Biology 3:79-80.
- Baroni Urbani C., and C. A. Collingwood. 1977. The zoogeography of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Northern Europe. Acta Zoologica Fennica 152: 1-34.
- Barrett K. E. 1967. Ants in South Brittany. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 79:112-116.
- Bernard F. 1967. Faune de l'Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen. 3. Les fourmis (Hymenoptera Formicidae) d'Europe occidentale et septentrionale. Paris: Masson, 411 pp.
- Bezdecka P. 1996. The ants of Slovakia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomofauna carpathica 8: 108-114.
- Bezdeckova K., and P. Bezdecka. 2009. Nejvetsi polykalicka kolonie Formica foreli (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) y Ceské republice. Acta rerum naturalium 7: 121126.
- Bharti H., Y. P. Sharma, M. Bharti, and M. Pfeiffer. 2013. Ant species richness, endemicity and functional groups, along an elevational gradient in the Himalayas. Asian Myrmecology 5: 79-101.
- Bharti H., and Y. P. Sharma. 2009. Diversity and abundance of ants along an elevational gradient in Jammu-Kasmir Himalaya -I. Halteres 1(1): 10-24.
- Boer P. 2019. Species list of the Netherlands. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/specieslist.html
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. Van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten (Amsterdam) 63: 54-58.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. Lijst van mieren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) van Belgie en Nederland, hun Nederlandse namen en hun voorkomen. Entomologische Berichten 63(3): 54-57.
- Boer P., W. Dekoninck, A. J. van Loon, and F. Vankerkhoven. 2003. List of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Belgium and The Netherlands, their status and Dutch vernacular names. Entomologische Berichten 63 (3): 54-58.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Bracko G. 2007. Checklist of the ants of Slovenia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Natura Sloveniae 9: 15-24
- Bracko G., H. C. Wagner, A. Schulz, E. Gioahim, J. Maticic, and A. Tratnik. 2014. New investigation and a revised checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Republic of Macedonia. North-Western Journal of Zoology 10(1): 10-24.
- Bracko, G. 2006. Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) of Croatia. Acta Entomologica Slovenica 14(2): 131-156.
- Bracko, G.. "Review of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Croatia." Acta Entomologica Slovenica Vol 14 st (2006): 131-156.
- Carniel A. 1998. Ricerche sulla mirmecofauna delle Prealpi Orobiche (Lombardia) (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Atti. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Morbegno 9: 29-39.
- Casevitz-Weulersse J., and C. Galkowski. 2009. Liste actualisee des Fourmis de France (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 114: 475-510.
- Choi B.M., Kim, C.H., Bang, J.R. 1993. Studies on the distribution of ants (Formicidae) in Korea (13). A checklist of ants from each province (Do), with taxonomic notes. Cheongju Sabom Taehakkyo Nonmunjip (Journal of Cheongju National University of Education) 30: 331-380.
- Collingwood C. A. 1963. Three ant species new to Norway. Entomologist's Record and Journal of Variation 75: 225-228.
- Collingwood C. A. 1971. A synopsis of the Formicidae of north Europe. Entomologist 104: 150-176
- Collingwood C., and H. Heatwole. 2000. Ants from Northwestern China (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Psyche 103 (1-2): 1-24.
- Collingwood C.A. 1959. Scandinavian Ants. Entomol. Rec. 71: 78-83
- Collingwood C.A. 1961. Ants in Finland. Entomol. Rec. 73: 190-195
- Collingwood, C. A. 1974. A revised list of Norwegian ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Norsk Entomologisk Tidsskrift 21: 31-35.
- Collingwood, C. A.. "The Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark." Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 8 (1979): 1-174.
- Csősz S. and Markó, B. 2005. European ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the ant collection of the Natural History Museum of Sibiu (Hermannstadt/Nagyszeben), Romania II. Subfamily Formicinae. Annales Historico-Naturales Musei Nationalis Hungarici 97: 225-240.
- Csősz S., B. Markó, and L. Gallé. 2011. The myrmecofauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Hungary: an updated checklist. North-Western Journal of Zoology 7: 55-62.
- Czechowski W., A. Radchenko, W. Czechowska and K. Vepsäläinen. 2012. The ants of Poland with reference to the myrmecofauna of Europe. Fauna Poloniae 4. Warsaw: Natura Optima Dux Foundation, 1-496 pp
- Dlussky G. M., and B. Pisarski. 1970. Formicidae aus der Mongolei. Ergebnisse der Mongolisch-Deutschen Biologischen Expeditionen seit 1962, Nr. 46. Mitteilungen aus dem Zoologischen Museum in Berlin 46: 85-90.
- Dubovikoff D. A., and Z. M. Yusupov. 2018. Family Formicidae - Ants. In Belokobylskij S. A. and A. S. Lelej: Annotated catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Proceedingss of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences 6: 197-210.
- Elias, M., R. Rosengren, L. Sundstrom. 2005. Seasonal Polydomy and Unicoloniality in a Polygynous Population of the Red Wood Ant Formica truncorum. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 57(4):339-349
- Emery C. 1878. Liste des fourmis de la collection de feu Camille van Volxem, avec la description d'une espèce nouvelle. Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 21: viii-x.
- Emery C. 1916. Fauna entomologica italiana. I. Hymenoptera.-Formicidae. Bullettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 47: 79-275.
- Emery, C., and A. Forel. "Catalogue des Formicides d'Europe." Mitteilungen der Schweirzerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft 5 (1879): 441-481.
- Emery, C.. "Catalogo delle formiche esistenti nelle collezioni del Museo Civico di Genova. Parte seconda. Formiche dell'Europa e delle regioni limitrofe in Africa e in Asia." Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 12 (1878): 43-59.
- Entomological Society of Latvia. 2003. http://leb.daba.lv/Formicidae.htm (Accessed on December 1st 2013).
- Fiedler, K., F. Kuhlmann, B. C. Schlick-Steiner, F. M. Steiner and G. Gebauer. 2007. Stable N-isotope signatures of central European ants assessing positions in a trophic gradient. Insectes Sociaux 54(4):393-402.
- Field Museum Collection, Chicago, Illinois (C. Moreau)
- Forel A. 1904. Note sur les fourmis du Musée Zoologique de l'Académie Impériale des Sciences à St. Pétersbourg. Ezheg. Zool. Muz. 8: 368-388.
- Galle L. 1997. Contribution to the ant fauna of Slovenia with special reference to the submediterranean and eudinaric regions. Annals for Istrian and Mediterranean studies 11: 209-214.
- Galle L., and G. Szonyi. 1988. A check list of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea) of a sandy grassland in Kiskunsag National Park (Hungary). Acta Biol. Szeged 34: 167-168.
- Gallé L., B. Markó, K. Kiss, E. Kovács, H. Dürgő, K. Kőváry, and S. Csősz. 2005. Ant fauna of Tisza river basin (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). In: Gallé, L. (szerk.): Vegetation and Fauna of Tisza River Basin I. Tiscia Monograph Series 7; Szeged, pp. 149-197.
- Glaser F. 2009. Die Ameisen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein. (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Amtlicher Lehrmittelverlag, Vaduz, 2009 (Naturkundliche Forschung im Fürstentum Liechtenstein; Bd. 26).
- Guénard B., and R. R. Dunn. 2012. A checklist of the ants of China. Zootaxa 3558: 1-77.
- Hayashida K. 1959. Ecological Distribution of Ants in Mt. Atusanupuri, An Active Volcano in Akan National Park, Hokkaido. Jour. Pac. Sci. Hokkaiao Univ. Ser. 4(14): 252-260.
- Hayashida K. 1959. Ecological distribution of ants in Mt. Atusanupuri, an active volcano in Akan National Park, Hokkaido. Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University. Series VI. Zoology 14:252-260.
- Holgersen H. 1940. Myrmekologiske notiser I. Nor. Entomol. Tidsskr. 5: 183-187.
- Holgersen H. 1942. Ants of northern Norway (Hym., Form.). Tromso Mus. Årsh. 63(2): 1-34.
- Holgersen H. 1943. Ant studies in Rogaland (south-western Norway). Avhandlingar utgitt av det Norske Videnskaps-Akademi i Oslo. I. Matematisk-Naturvidenskapelig Klasse 1943(7): 1-75.
- Holgersen H. 1944. The ants of Norway (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Nytt Magasin for Naturvidenskapene 84: 165-203.
- Karavaiev V. 1912. Ameisen aus dem paläarktischen Faunengebiete. Rus. Entomol. Obozr. 12: 581-596.
- Karavaiev V. 1931. Beitrag zur Ameisenfauna Jakutiens. (Auf Grund der Sammelergebnisse der Expeditionen der Wissenschaften der UdSSR., ausgeführt in den Jahren 1925 und 1926.). Zool. Anz. 94: 104-117.
- Kim B.J. 1996. Synonymic list and distribution of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) in Korea. Entomological Research Bulletin Supplement 169-196.
- Kim et al. 1993. Systematic study of ants from Chejudo Province. Koran Journal of Entomology 23(3): 117-141.
- Kiran K., and C. Karaman. 2012. First annotated checklist of the ant fauna of Turkey (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zootaxa 3548: 1-38.
- Kofler A. 1995. Nachtrag zur Ameisenfauna Osttirols (Tirol, Österreich) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 1: 14-25.
- Korlevic, A.. "Prilozi fauni hrvatskih opnokrilaca." Glasn. Hrv. Narav. Dr. 5 (1890): 189-250.
- Kupianskaia A.N. 1990. Murav'I (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) Dal'nego Vostoka SSSR (1989). Vladivostok. 258 pages.
- Kupianskaya A. N., Lelej, A.S., and Urbain, B. K. 2000. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist. 92:1-21.
- Kupianskaya, A. N., Lelej, A.S., and Urbain, B. K. 2000. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Kuril Islands. Far Eastern Entomologist. 92:1-21.
- Kvamme T. 1982. Atlas of the Formicidae of Norway (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Insecta Norvegiae 2: 1-56.
- Lameere A. 1892. Note sur les fourmis de la Belgique. Annales dr la Société Entomologique de Belgique 36: 61-69.
- Lapeva-Gjonova, L., V. Antonova, A. G. Radchenko, and M. Atanasova. "Catalogue of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Bulgaria." ZooKeys 62 (2010): 1-124.
- Lelej A. S. 2012. Annotated catalogue of the Insects of Russian Far East. Volume 1. Hymenoptera. Dalnauka: Vladivostok. 635 p.
- Lomnicki J. 1928. Spis mrówek Lwowa i okolicy. Ksiegi Pamiatkowej (Lecia Gimn. IV Jana Dlugosza Lwowie) 50: 1-10.
- Maavara V. 1953. Ants of Estonian SSR. ABIKS loodusevaatlejale 10: 1-44.
- Malozemova L. A. 1972. Ants of steppe forests, their distribution by habitats, and perspectives of their utilization for protection of forests (north Kazakhstan). [In Russian.]. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 51: 57-68.
- Mani M. S., and S. Singh. 1962. Entomological survey of Himalaya. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 59(1): 84-85.
- Marikovsky P. I. 1979. Ants of the Semireche Desert. [In Russian.]. Alma Ata: Nauka, 263 pp.
- Markó B., B. Sipos, S. Csősz, K. Kiss, I. Boros, and L. Gallé. 2006. A comprehensive list of the ants of Romania (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecologische Nachrichten 9: 65-76.
- Moscaliuc L. 2008. Notes on the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Rarau mountain. Analele Facult??ii de Biologie, Univ A.I. Cuza Ia?i 54: 53-55.
- Nadig A. 1918. Alcune note sulla fauna dell'alta Valsesia. Formicidae. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 56: 331-341.
- Paik W.H. 1984. A checklist of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) of Korea. Korean J. Plant Prot. 23(3): 193-195.
- Paraschivescu D. 1972. Fauna mirmecologica din zonele saline ale Romaniei. Studii si Cercetari de Biologie. Seria Zoologie 24: 489-495.
- Paraschivescu D. 1978. Elemente balcanice in mirmecofauna R. S. Romania. Nymphaea 6: 463- 474.
- Park S.J., and B.J. Kim. 2002. Faunal comparison of ants among Cheongsando and other islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Journal of Entomology 32(1): 7-12.
- Park, Seong, Joon and Byung, and Kim, Jin. 2002. Faunal Comparison of Ants among Cheongsando and Other Islands of South Sea in Korea. Korean Jornal of Entomology. 32(1):7-12.
- Paukkunen J., and M. V. Kozlov. 2015. Stinging wasps, ants and bees (Hy menoptera: Aculeata) of the Murmansk region, Northwest Russia. — Entomol. Fennica. 26: 53–73.
- Petal J. M. 1963. Faune des fourmis de la reserve de tourbiere en projet a Rakowskie Bagno pres de Frampol (voivodie de Lublin). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sk?odowska 58(7): 143-174.
- Petal J. M. 1967. Contribution a la connaissance des fourmis (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) de la region de Lublin. VII. Associations des fourmis des milieux de tourbieres, de forets et de dunes aux environs de Libiszow (dist. De Parczew). Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Sklodowska Lublin-Polonia 22(9): 117-130.
- Petrov I. Z., and C. A. Collingwood. 1992. Survey of the myrmecofauna (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) of Yugoslavia. Archives of Biological Sciences (Belgrade) 44: 79-91.
- Punttila P., Y. Haila, and H. Tukia. 1996. Ant communities in taiga clearcuts: habitat effects and species interactions. Ecography 19: 16-28.
- Pusvaskyte O. 1979. Myrmecofauna of the Lituanian SSR. Acta Entomologica Lituanica 4: 99-105.
- Radchenko A. G. 2007. The ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in the collection of William Nylander. Fragmenta Faunistica (Warsaw) 50: 27-41.
- Radchenko, A. 2005. Monographic revision of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of North Korea. Annales Zoologici (Warsaw) 55: 127-221.
- Radchenko, A. 2005. Monographic revision of the ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of North Korea. Annales Zoologici 55(2): 127-221.
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.
- Rasheed M. T., I. Bodlah, A. G. Fareen, A. A. Wachkoo, X. Huang, and S. A. Akbar. 2019. A checklist of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Pakistan. Sociobiology 66(3): 426-439.
- Roger, J.. "Verzeichniss der Formiciden-Gattungen und Arten." Berliner Entomologische Zeitschrift 7 (1863): 1-65.
- Ruzsky M. 1920. Ants of Kamchatka. Izv. Inst. Issled. Sib. 2: 76-80
- Röszler P. 1950. Die Ameisenwelt des Nagy Pietrosz, 2305 m (Ungarn) und Umgebung. Zool. Anz. 145: 210-225.
- Salata S. 2014. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the National Park of the Stołowe Mts. Przyroda Sudetow 17: 161-172.
- Santschi F. 1925. Fourmis d'Espagne et autres espéces paléartiques EOS (Revista española de entomología) 1: 339-360.
- Saure C. 2005. Rote Liste und Gesamtartenliste der Bienen und Wespen (Hymenoptera part.) von Berlin mit Angaben zu den Ameisen. In: DER LANDESBEAUFTRAGTE FÜR NATURSCHUTZ UND LANDSCHAFTSPFLEGE / SENATSVERWALTUNG FÜR STADTENTWICKLUNG (Hrsg.): Rote Listen der gefährdeten Pflanzen und Tiere von Berlin. CD-ROM.
- Schlick-Steiner B. C., and F. M. Steiner. 1999. Faunistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen an den freilebenden Ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Wiens. Myrmecologische Nachrichten 3: 9-53.
- Schultz, R., A. G. Radchenko, and B. Seifert. "A critical checklist of the ants of Kyrgyzstan (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)." Myrmecologische Nachrichten 8 (2006): 201-207.
- Seifert B. 1994. Die freilebenden Ameisenarten Deutschlands (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) und Angaben zu deren Taxonomie und Verbreitung. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Naturkundemuseums Görlitz 67(3): 1-44.
- Seifert B. 1998. Rote Liste der Ameisen. - in: M. Binot, R. Bless, P. Boye, H. Gruttke und P. Pretscher: Rote Liste gefährdeter Tiere Deutschlands. Bonn-Bad Godesberg 1998: 130-133.
- Sonnenburg H. 2005. Die Ameisenfauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Niedersachsens und Bremens. Braunschweiger Naturkundliche Schriften 7: 377-441.
- Steiner F. M., S. Schödl, and B. C. Schlick-Steiner. 2002. Liste der Ameisen Österreichs (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Stand Oktober 2002. Beiträge zur Entomofaunistik 3: 17-25.
- Stumper R. 1953. Etudes myrmecologiques. XI. Fourmis luxembourgeoises. Bulletin Soc. Nat. luxemb. 57: 122-135.
- Sturm P., and H. Distler. 2003. Rote liste gefahrdeter ameisen (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea) Bayerns. In: Bayrisches Landesamt für Umweltschutz (Ed.). Rote Liste gefährdeter Tiere Bayerns. 208-212.
- Terayama M. 1992. Structure of ant communities in East Asia. A. Regional differences and species richness. Bulletin of the Bio-geographical Society of Japan 47: 1-31.
- Terayama M., K. Ogata, and B.M. Choi. 1994. Distribution records of ants in 47 prefectures of Japan. Ari (report of the Myrmecologists Society of Japan) 18: 5-17.
- Terayama M., S. Kubota, and K. Eguchi. 2014. Encyclopedia of Japanese ants. Asakura Shoten: Tokyo, 278 pp.
- Terayama. M. 2004. Geological and ecological distribution of Japanese ants communities. (translated from Japanese) Reports of the Saitama Prefecture Animal Research Association. 48:24
- Vele A., J. Holusa, J. Frouz, and O. Konvicka. 2011. Local and landscape drivers of ant and carabid beetle communities during spruce forest succession. European Journal of Soil Biology 47: 349-356.
- Vele A., J. Holusa, and J. Frouz. 2009. Sampling for ants in different-aged spruce forests: A comparison of methods. European Journal of Soil Biology 45(4): 1-6.
- Vepsalainen K., H. Ikonene, and M. J. Koivula. 2008. The structure of ant assembalges in an urban area of Helsinki, southern Finland. Ann. Zool. Fennici 45: 109-127.
- Vogrin, V.. "Prilog fauni Hymenoptera - Aculeata Jugoslavije." Zast. Bilja 31(suppl.) (1955): 1-74.
- Wegnez P., and A. Ronk. 2017. Découverte de Camponotus herculeanus (Linnaeus, 1758) et signalement de quelques autres espèces rares de fourmis au Luxembourg (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société des naturalistes luxembourgeois 119 : 153–159.
- Wegnez P., and F. Mourey. 2016. Formica uralensis Ruzsky, 1895 une espèce encore présente en France mais pour combien de temps ? (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 152: 72-80.
- Wegnez P., and M. Fichaux. 2015. Liste actualisee des especes de fourmis repertoriees au Grand-Duche de Luxembourg (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société royale belge d’Entomologie 151: 150-165
- Wheeler W. M. 1906. The ants of Japan. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 22: 301-328.
- Wheeler W. M. 1913. A revision of the ants of the genus Formica (Linné) Mayr. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 53: 379-565.
- Wheeler, William Morton. 1928. Ants of Nantucket Island, Mass. Psyche. 35(1):10-11.
- Wiezik M. 2007. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of mountain and alpine ecosystems at Southern part of Krá?ovoho?ské Tatry Mts. Naturae Tutela 11: 85-90.
- Yamane S. 2007. Ants of Mongolia. The Nature and Insects. 42: 20-25
- Yoshimura M. 1998. Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 1, Risiri Island). Rishiri Studies 17:33-38.
- Yoshimura M. 1999. Ants in the island of Hokkaido (Part 2, Part Rebun) Ants from Islands in Hokkaido, Northern Japan (No. 2, Rebun-Island). Rishiri Studies 18: 49-54.
- Yoshimura M., T. Hirata, A. Nakajima, and K. Onoyama. 2003. Ants found in scats and pellets taken from the nests of the Japanese Wryneck Jynx torquilla japonica. Ornithol. Sci. 2: 127-131.
- Zryanin V. A., and T. A. Zryanina. 2007. New data on the ant fauna Hymenoptera, Formicidae in the middle Volga River Basin. Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii 127(2): 226-240.
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Common Name
- Polygynous
- Supercolonies
- Temporary parasite
- Diploid male
- Photo Gallery
- North temperate
- North subtropical
- Nesting Notes
- FlightMonth
- Ant Associate
- Host of Formica fusca
- Host of Formica lemani
- Host of Formica polyctena
- Host of Formica pratensis
- Host of Formica rufibarbis
- Host of Formicoxenus nitidulus
- Fungus Associate
- Host of Aegeritella superficialis
- Karyotype
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Formicini
- Formica
- Formica truncorum
- Formicinae species
- Formicini species
- Formica species
- Need Overview
- Need Body Text




