Myrmecia dispar
| Myrmecia dispar | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Myrmeciinae |
| Tribe: | Myrmeciini |
| Genus: | Myrmecia |
| Species group: | pilosula |
| Species: | M. dispar |
| Binomial name | |
| Myrmecia dispar (Clark, 1951) | |
Identification
Keys including this Species
Distribution
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: -21.85° to -37.43333333°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Australasian Region: Australia (type locality).
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
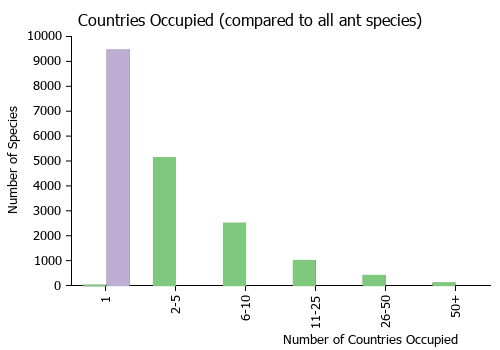
|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |

|
Biology
Life History Traits
- Queen number: monogynous (Rissing and Pollock, 1988; Frumhoff & Ward, 1992)
Castes
Phylogeny
| Myrmecia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Based on Mera-Rodríguez et al. (2023).
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- dispar. Promyrmecia dispar Clark, 1951: 226, fig. 193 (w.) AUSTRALIA (New South Wales).
- Type-material: holotype worker, paratype workers (number not stated).
- Type-localities: Australia: New South Wales, Junee (E.L. Smith), New South Wales, Cowra (W.W. Frogatt).
- [Note: original description gives no indication which series contains the holotype.]
- Type-depository: ANIC.
- Combination in Myrmecia: Taylor & Brown, 1985: 8.
- Status as species: Taylor & Brown, 1985: 8; Taylor, 1987a: 42; Ogata, 1991a: 361; Ogata & Taylor, 1991: 1640 (in key); Bolton, 1995b: 271; Heterick, 2009: 123.
- Distribution: Australia.
Type Material
- Syntype, workers, Cowra and Junee, New South Wales, Australia, Australian National Insect Collection.
Description
Worker Morphology
 Explore: Show all Worker Morphology data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Worker Morphology data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- Caste: monomorphic (Rissing and Pollock, 1988)
References
- Clark, J. 1951. The Formicidae of Australia. 1. Subfamily Myrmeciinae: 230 pp. CSIRO, Melbourne. [(31.xii).1951.]
- Cushing, P.E. 2012. Spider-ant associations: An updated review of myrmecomorphy, myrmecophily, and myrmecophagy in spiders. Psyche: A Journal of Entomology 2012, 1–23 (doi:10.1155/2012/151989).
- Heterick, B.E. 2021. A guide to the ants of Western Australia. Part I: Systematics. Records of the Western Australian Museum, Supplement 86, 1-245 (doi:10.18195/issn.0313-122x.86.2021.001-245).
- Heterick, B.E. 2022. A guide to the ants of Western Australia. Part II: Distribution and biology. Records of the Western Australian Museum, supplement 86: 247-510 (doi:10.18195/issn.0313-122x.86.2022.247-510).
- Mera-Rodríguez, D., Jourdan, H., Ward, P.S., Shattuck, S., Cover, S.P., Wilson, E.O., Rabeling, C. 2023. Biogeography and evolution of social parasitism in Australian Myrmecia bulldog ants revealed by phylogenomics. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 186, 107825 (doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2023.107825).
- Taylor, R. W.; Brown, D. R. 1985. Formicoidea. Zool. Cat. Aust. 2:1- 149: 1-149, 30 (page 8, Combination in Myrmecia)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- CSIRO Collection
- Heterick B. E. 2009. A guide to the ants of south-western Australia. Records of the Western Australian Museum Supplement 76: 1-206.
- Sinclair J. E., and T. R. New. 2004. Pine plantations in south eastern Australia support highly impoverished ant assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Journal of Insect Conservation 8: 277-286.
Categories:
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Pages using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Tropical
- South subtropical
- South temperate
- ANIC specimen
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Myrmeciinae
- Myrmeciini
- Myrmecia
- Myrmecia dispar
- Myrmeciinae species
- Myrmeciini species
- Myrmecia species
- Need Overview
- Need Images
- Need Body Text