Linguamyrmex vladi
| †Linguamyrmex vladi Temporal range: Early Cenomanian, Late Cretaceous Burmese amber, Kachin State, Myanmar | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | †Haidomyrmecinae |
| Genus: | †Linguamyrmex |
| Species: | †L. vladi |
| Binomial name | |
| †Linguamyrmex vladi Barden & Grimaldi, 2017 | |
Photo Gallery
Identification
Distribution
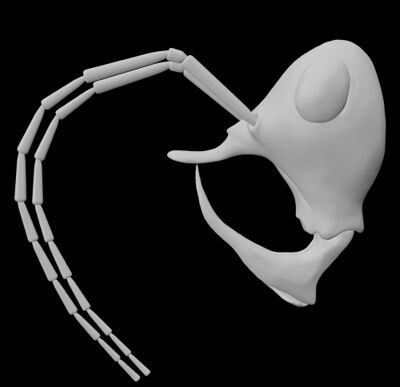
This taxon was described from Burmese amber, Kachin State, Myanmar (Early Cenomanian, Late Cretaceous). Linguamyrmex vladi gen.n. sp.n. is distinguished by an unusual suite of morphological characters indicating specialized predatory behaviour and an adaptive strategy no longer found among modern ant lineages. The clypeus, highly modified as in other closely related haidomyrmecine hell ants, is equipped with a paddle-like projection similar to Ceratomyrmex. X-ray imaging reveals that this clypeal paddle is reinforced, most probably with sequestered metals. Presumably this fortified clypeal structure was utilized in tandem with scythe-like mandibles to pin and potentially puncture soft-bodied prey. This unique taxon, which stresses the diversity of stem-group ants, is discussed in the context of modern and other Cretaceous trap jaw ant species.
Castes
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- †vladi. †Linguamyrmex vladi Barden & Grimaldi, 2017: 839, figs. 1, 2A, 3F-I, 5 (w.) MYANMAR (Burmese amber).
- See also: Perrichot, Wang & Barden, 2020.
Description
Description. Head: measuring 0.90mm postero-anteriorly along dorsal margin, 0.96mm in length/depth from vertex of head to anterior margin of clypeus. Occipital foramen positioned highly dorsad, just under vertex of head. Postgena broadly depressed; postgenal suture visible, deeply furrowed. Vertex broadly rounded and glabrous with gena gradually tapered ventrally towards mandibular socket and oral opening with fine, sparse setae. Ocelli faintly visible on vertex, positioned dorsally. Eye situated high on head capsule and bulging in frontal view, ovoid, measuring 0.38mm in length and 0.25mm in width when viewed laterally. Three antennal segments fully preserved (scape 0.94mm in length; pedicel 0.12 mm; flagellomere I 0.55 mm). Antennal socket approximately in line with ventral margin of eye; socket exposed and immediately flanking a medial frontal triangle (sensu Perrichot et al., 2016). Frontal triangle extends the vertex, contrasted with antennal sockets, which are present within cuticular depressions. Clypeal horn originating at both frontal triangle and clypeal stalk, both structures heavily sclerotized with cleared, membrane-like cuticle connecting from frontal triangle to stalk. Horn paddle-shaped, total length 0.64 mm, diameter 0.49 at greatest; narrow (0.04 mm) glabrous stalk 0.22mm in length leading to setose pad; setose pad (0.42 in length) with long trigger hairs originating at pad base; dorsal margin of setose pad glabrous, underside coated in a large number of stout setae in centre and longer, more tapered setae along edges. Anterior margin of clypeus medially triangulate; distinct medial ridge extending to clypeal horn; lateral margins, beginning just above mandibular insertion, extending diagonally toward clypeal horn. Cheek-like lobes projecting anteroventrally above mandible insertion. Mandible scythe-like, comprise a linear basal margin (0.55mm in length) and curved apical tooth (0.92mm measured as a straight line from base to tip, ignoring curvature) meeting nearly at right angle; preserved with apical teeth in parallel, nearly touching. Basal portion of mandible with anterior flange-like expansion, concave inner margin coated with pointed setae; leading edge of anterior flange expansion smooth; apical tooth rounded broadly with slight point. Maxillary and labial palps not visible.
References
- Barden, P., Engel, M.S. 2020. Fossil social insects. Encyclopedia of Social Insects, Springer, Cham (doi:10.1007/978-3-319-90306-4_45-1).
- Barden, P., Hollister W.H., Grimaldi, D.A. 2017. A new genus of hell ants from the Cretaceous (Hymenoptera:Formicidae: Haidomyrmecini) with a novel head structure. Systematic Entomology 42:837-846.
- Boudinot, B.E., Perrichot, V., Chaul, J.C.M. 2020. †Camelosphecia gen. nov., lost ant-wasp intermediates from the mid-Cretaceous (Hymenoptera, Formicoidea). ZooKeys 1005, 21–55 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.1005.57629).
- Perfilieva, K.S. 2023. Cretaceous-Burmese-amber ants: Morphological features and community structure. Biology Bulletin Reviews 131, 38–54 (doi:10.1134/s207908642301005x).
- Perrichot, V., Wang, B., Barden, P. 2020. New remarkable hell ants (Formicidae: Haidomyrmecinae stat. nov.) from mid-Cretaceous amber of northern Myanmar. Cretaceous Research 109, 104381 (doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104381).