Pheidole metallescens
| Pheidole metallescens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Myrmicinae |
| Tribe: | Attini |
| Genus: | Pheidole |
| Species: | P. metallescens |
| Binomial name | |
| Pheidole metallescens Emery, 1895 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Naves (1985) reports metallescens as common in Florida, preferring to nest in the shade of trees. Nests are in the soil, surrounded by small craters of excavated earth, and comprising small chambers connected by a central vertical gallery to a depth of up to 40 cm. Each colony has a single queen. The minor workers, often accompanied by majors, collect small grass seeds and scavenge for dead arthropods. In Texas, Stefan Cover found the species in similar habitats, nesting variously in the soil and in rotting logs. (Wilson 2003)
Identification
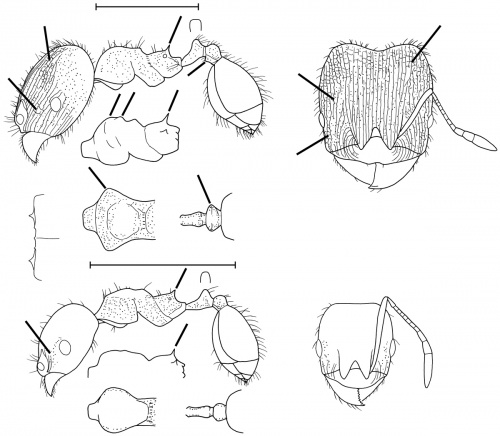
The minors of this species can be easily recognized, as they have abundant bluish or purple reflections, which are especially obvious on the head. The majors rarely have bluish reflections, and are relatively small (about 2 mm total length), with short scapes (extend about 1/2 the length of the head), and the entire dorsum of the head is covered with rugae, and is granulose between the rugae. Only the tops of the posterior lateral lobes are smooth and shining. The lateral connules on the postpetiole are well developed, but blunt and rounded. (Mackay and Mackay 2002)
Also see the description in the nomenclature section.
Keys including this Species
Distribution
From central Florida through the Gulf States to Oklahoma and southern Texas. (Wilson 2003)
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 36.06464° to 26.118713°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Nearctic Region: United States (type locality).
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
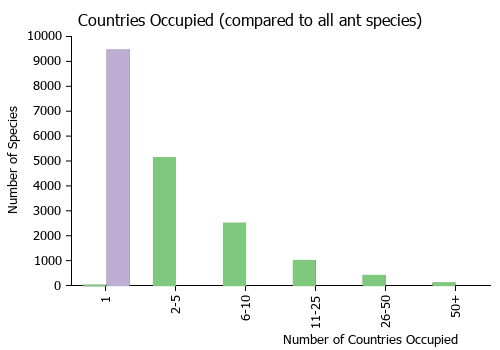
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
|
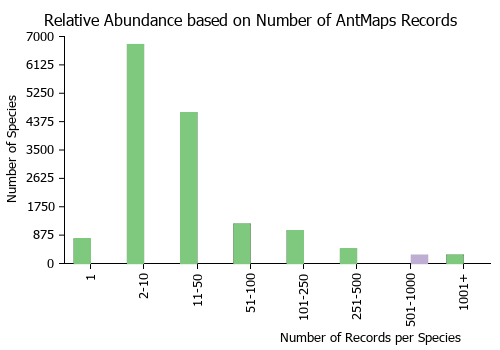
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |
|
Biology
This species is known to remove seeds (Atchison & Lucky, 2022; Stamp & Lucas, 1990).
Castes
Worker
Minor
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Worker. Specimen code casent0104412. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by ABS, Lake Placid, FL, USA. |
Major
   
| |
| . | |
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Worker (major/soldier). Specimen code casent0104411. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by ABS, Lake Placid, FL, USA. |
Queen
Images from AntWeb
    
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0104410. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by ABS, Lake Placid, FL, USA. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- metallescens. Pheidole metallescens Emery, 1895c: 294 (w.) U.S.A. Wheeler, W.M. 1908e: 476 (s.); Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1960b: 12 (l.). Senior synonym of splendidula: Wilson, 2003: 453.
- splendidula. Pheidole metallescens subsp. splendidula Wheeler, W.M. 1908e: 474, pl. 26, figs. 20, 21 (s.w.q.m.) U.S.A. Junior synonym of metallescens: Wilson, 2003: 453.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
DIAGNOSIS From Wilson (2003): A distinctive species, similar in some traits to Pheidole ceibana, Pheidole harrisonfordi and Pheidole lignicola, distinguished as follows.
Major: reddish brown; occiput rugoreticulate, with the reticulum extending partway anteriorly down the side of the head to near the eye, and another, small patch of rugoreticulum occurs between the eye and antennal fossa on each side; humerus prominent, subangulate from above and lobate in dorsal-oblique view; propodeal spine long and thin; postpetiole wide and elliptical from above, and with subangulate anterior ventral margin.
Minor: body blackish with bluish reflections; often most of mesosoma foveolate and opaque.
Minors of some series have entirely foveate heads and may represent a distinct species.
MEASUREMENTS (mm) Major (Archbold Station, Florida): HW 0.84, HL 0.94, SL 0.42, EL 0.12, PW 0.44. Minor (Archbold Station): HW 0.42, HL 0.46, SL 0.40, EL 0.10, PW 0.26.
COLOR Major: bicolored, with head and appendages light reddish brown, and rest of body medium to dark brown.
Minor: body concolorous blackish brown, with metallic bluish reflections; central parts of femora and tibiae medium brown; distal and proximal portions brownish yellow.
Figure. Upper: major. Lower: minor. FLORIDA: Archbold Station, near Sebring, Highlands Co. Scale bars = 1 mm.
Type Material
St. George (Cape or Island), Florida, Museo Civico di Storia Naturale, Genoa - as reported in Wilson (2003)
Etymology
L metallescens, metallic, alluding to the gun-metal blue reflections from the body of the minor. (Wilson 2003)
References
- Atchison, R. A., Lucky, A. 2022. Diversity and resilience of seed-removing ant species in Longleaf Sandhill to frequent fire. Diversity 14, 1012 (doi:10.3390/d14121012).
- Davis, T. 2009. The ants of South Carolina (thesis, Clemson University).
- Emery, C. 1895d. Beiträge zur Kenntniss der nordamerikanischen Ameisenfauna. (Schluss). Zool. Jahrb. Abt. Syst. Geogr. Biol. Tiere 8: 257-360 (page 294, worker described)
- Hill, J.G. 2015. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Big Thicket Region of Texas. Midsouth Entomologist 8: 24-34.
- Ipser, R.M., Brinkman, M.A., Gardner, W.A., Peeler, H.B. 2004. A survey of ground-dwelling ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Georgia. Florida Entomologist 87: 253-260.
- MacGown, J.A., Booher, D., Richter, H., Wetterer, J.K., Hill, J.G. 2021. An updated list of ants of Alabama (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with new state records. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 147: 961-981 (doi:10.3157/061.147.0409).
- Mackay, W. P. and E. Mackay. 2002. The ants of New Mexico (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Edwin Mellen Press, Lewiston, NY.
- Naves, M. A. 1985. A monograph of the genus Pheidole in Florida, USA (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Insecta Mundi 1: 53–90.
- Nielsen, A., Atchison, R., Lucky, A. 2020. Effects of the invasive Little Fire Ant (Wasmannia auropunctata) on ant community composition on UF Campus. University of Florida | Journal of Undergraduate Research | Volume 22
- Stamp, N.E., Lucas, J.R. 1990. Spatial patterns and dispersal distances of explosively dispersing plants in Florida sandhill vegetation. Journal of Ecology 78, 589–600.
- Wheeler, G. C.; Wheeler, J. 1960b. Supplementary studies on the larvae of the Myrmicinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 62: 1-32 (page 12, larva described)
- Wheeler, W. M. 1908h. The ants of Texas, New Mexico and Arizona. (Part I.). Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 24: 399-485 (page 476, soldier described)
- Wilson, E. O. 2003. Pheidole in the New World: A dominant, hyperdiverse ant genus. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA. (page 453, fig. major, minor described, page 453, Senior synonym of splendidula)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Annotated Ant Species List Ordway-Swisher Biological Station. Downloaded at http://ordway-swisher.ufl.edu/species/os-hymenoptera.htm on 5th Oct 2010.
- Atchison R. A., J. Hulcr, and A. Lucky. 2018. Managed fire frequency significantly influences the litter arthropod community in longleaf pine flatwoods. Environmental Entomology 20(10): 1-11.
- Braman C. A., and B. T. Forschler. 2018. Survey of Formicidae attracted to protein baits on Georgia’s Barrier Island dunes. Southeastern Naturalist 17(4): 645-653.
- Colby, D. and D. Prowell. 2006. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Wet Longleaf Pine Savannas in Louisiana. Florida Entomologist 89(2):266-269
- Dash S. T. and L. M. Hooper-Bui. 2008. Species diversity of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Louisiana. Conservation Biology and Biodiversity. 101: 1056-1066
- Del Toro, I. 2010. PERSONAL COMMUNICATION. MUSEUM RECORDS COLLATED BY ISRAEL DEL TORO
- Deyrup M., C. Johnson, G. C. Wheeler, J. Wheeler. 1989. A preliminary list of the ants of Florida. Florida Entomologist 72: 91-101
- Deyrup M., L. Deyrup, and J. Carrel. 2013. Ant Species in the Diet of a Florida Population of Eastern Narrow-Mouthed Toads, Gastrophryne carolinensis. Southeastern Naturalist 12(2): 367-378.
- Deyrup, M. 2003. An updated list of Florida ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Florida Entomologist 86(1):43-48.
- Deyrup, M. and J. Trager. 1986. Ants of the Archbold Biological Station, Highlands County, Florida (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Florida Entomologist 69(1):206-228
- Epperson, D.M. and C.R. Allen. 2010. Red Imported Fire Ant Impacts on Upland Arthropods in Southern Mississippi. American Midland Naturalist, 163(1):54-63.
- Feener D.H.,Jr. 1987. Response of Pheidole morrisi to two species of enemy ants, and a general model of defense behavior in Pheidole. Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 60: 569-575.
- Forster J.A. 2005. The Ants (hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Alabama. Master of Science, Auburn University. 242 pages.
- General D.M. & Thompson L.C. 2008. New Distributional Records of Ants in Arkansas for 2008. Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science. 63: 182-184
- Glancey B. M., Wojcik D. P., Craig C. H. and Mitchell J. A. 1976. Ants of Mobile County, AL, as monitored by bait transects. Journal of the Georgia Entomological Society 11: 191-197
- Glancey, B.M., Wojcik, D.P., Craig, C.H. and Mitchell, J.A. 1976. Ants of Mobile County, AL, as monitored by bait transects. Journal of the Georgia Entomological Society 11(3):191-197
- Graham J.H., H.H. Hughie, S. Jones, K. Wrinn, A.J. Krzysik, J.J. Duda, D.C. Freeman, J.M. Emlen, J.C. Zak, D.A. Kovacic, C. Chamberlin-Graham, H. Balbach. 2004. Habitat disturbance and the diversity and abundance of ants (Formicidae) in the Southeastern Fall-Line Sandhills. 15pp. Journal of Insect Science. 4: 30
- Graham, J.H., A.J. Krzysik, D.A. Kovacic, J.J. Duda, D.C. Freeman, J.M. Emlen, J.C. Zak, W.R. Long, M.P. Wallace, C. Chamberlin-Graham, J.P. Nutter and H.E. Balbach. 2008. Ant Community Composition across a Gradient of Disturbed Military Landscapes at Fort Benning, Georgia. Southeastern Naturalist 7(3):429-448
- Guénard B., K. A. Mccaffrey, A. Lucky, and R. R. Dunn. 2012. Ants of North Carolina: an updated list (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Zootaxa 3552: 1-36.
- Hess C. G. 1958. The ants of Dallas County, Texas, and their nesting sites; with particular reference to soil texture as an ecological factor. Field and Laboratory 26: 3-72.
- Ipser R. M. 2004. Native and exotic ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Georgia: Ecological Relationships with implications for development of biologically-based management strategies. Doctor of Philosophy thesis, University of Georgia. 165 pages.
- Jeanne R. J. 1979. A latitudinal gradient in rates of ant predation. Ecology 60(6): 1211-1224.
- Johnson C. 1986. A north Florida ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Insecta Mundi 1: 243-246
- Jusino-Atresino R., and S. A. Phillips, Jr. 1992. New ant records for Taylor Co., Texas. The Southern Naturalist 34(4): 430-433.
- King J. R. 2007. Patterns of co-occurrence and body size overlap among ants in Florida's upland ecosystems. Ann. Zool. Fennici. 44: 189-201
- Klotz, J.H., J.R. Mangold, K.M. Vail, L.R. Davis Jr., R.S. Patterson. 1995. A survey of the urban pest ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Peninsular Florida. Florida Entomologist 78(1):109-118
- LeBrun E. G., R. M. Plowes, and L. E. Gilbert. 2015. Imported fire ants near the edge of their range: disturbance and moisture determine prevalence and impact of an invasive social insect. Journal of Animal Ecology,81: 884–895.
- MacGown J. A. 2015. Report on the ants collected on Spring Island, Beaufort County, South Carolina. A report submitted to Spring Island Nature Preserve, May 2015. Mississippi Entomological Museum Report #2015-01. 8 pp
- MacGown J. A., J. G. Hill, R. L. Brown, T. L. Schiefer, J. G. Lewis. 2012. Ant diversity at Noxubee National Wildlife Refuge in Oktibbeha, Noxubee, and Winston Counties, Mississippi. Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station Bulletin 1197: 1-30
- MacGown J. A., J. G. Hill, and M. Deyrup. 2009. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Little Ohoopee River Dunes, Emanuel County, Georgia. J. Entomol. Sci. 44(3): 193-197.
- MacGown J. A., J. G. Hill, and R. L. Brown. 2010. Native and exotic ant in Mississippi state parks. Proceedings: Imported Fire Ant Conference, Charleston, South Carolina, March 24-26, 2008: 74-80.
- MacGown J. A., and R. L. Brown. 2006. Survey of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Tombigbee National Forest in Mississippi. Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 79(4):325-340.
- MacGown, J. and J.G. Hill. Ants collected at Palestinean Gardens, George County Mississippi.
- MacGown, J.A and J.A. Forster. 2005. A preliminary list of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Alabama, U.S.A. Entomological News 116(2):61-74
- MacGown, J.A. and R.L. Brown. 2006. Survey of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Tombigbee National Forest in Mississippi. Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 79(4):325-340.
- MacGown, J.A., J.G. Hill, R.L. Brown and T.L. 2009. Ant Diversity at Noxubee National Wildlife Refuge in Oktibbeha, Noxubee, and Winston Counties, Mississippi Report #2009-01. Schiefer. 2009.
- McDonald D. L., D. R. Hoffpauir, and J. L. Cook. 2016. Survey yields seven new Texas county records and documents further spread of Red Imported Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta Buren. Southwestern Entomologist, 41(4): 913-920.
- Menozzi C. 1932. Formiche del Nord America raccolte dal Prof. F. Silvestri. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Zoologia Generale e Agraria della Reale Scuola Superiore d'Agricoltura. Portici. 26: 310-312.
- Moody J. V., and O. F. Francke. 1982. The Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Western Texas Part 1: Subfamily Myrmicinae. Graduate Studies Texas Tech University 27: 80 pp.
- O'Keefe S. T., J. L. Cook, T. Dudek, D. F. Wunneburger, M. D. Guzman, R. N. Coulson, and S. B. Vinson. 2000. The Distribution of Texas Ants. The Southwestern Entomologist 22: 1-92.
- Oyama L., J. R. King, and D. G. Jenkins. 2018. Diversity and distribution of Solenopsis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) thief ants belowground. Myrmecological News 27: 47-57.
- Parys K. A., M. L. Gimmel, and S. J. Johnson. 2013. Checklist of Insects Associated with Salvinia minima Baker in Louisiana, USA. Check List 9(6): 14881495.
- Roeder K. A., and D. V. Roeder. 2017. The Pheidole (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Oklahoma: new species records and distributional notes. Check List 13(2): 2071.
- Smith M. R. 1934. A list of the ants of South Carolina. Journal of the New York Entomological Society 42: 353-361.
- Smith M. R. 1934. Dates on which the immature or mature sexual phases of ants have been observed (Hymen.: Formicoidea) (continued from page 251). Entomological News 45: 264-267.
- Smith M. R. 1936. A list of the ants of Texas. Journal of the New York Entomological Society 44: 155-170.
- Van Pelt A. F. 1948. A Preliminary Key to the Worker Ants of Alachua County, Florida. The Florida Entomologist 30(4): 57-67
- Van Pelt A., and J. B. Gentry. 1985. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Savannah River Plant, South Carolina. Dept. Energy, Savannah River Ecology Lab., Aiken, SC., Report SRO-NERP-14, 56 p.
- Wheeler W. M. 1908. The ants of Texas, New Mexico and Arizona. (Part I.). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 24: 399-485.
- Wheeler W. M. 1913. Ants collected in Georgia by Dr. J. C. Bradley and Mr. W. T. Davis. Psyche (Cambridge) 20: 112-117.
- Wheeler, G.C. and J. Wheeler. 1985. A checklist of Texas ants. Prairie Naturalist 17:49-64.
- Whitcomb W. H., H. A. Denmark, A. P. Bhatkar, and G. L. Greene. 1972. Preliminary studies on the ants of Florida soybean fields. Florida Entomologist 55: 129-142.
- Wilson, E.O. 2003. Pheidole in the New World: A Dominant, Hyperdiverse Genus. Harvard University Press