Pheidole maculifrons
| Pheidole maculifrons | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Myrmicinae |
| Tribe: | Attini |
| Genus: | Pheidole |
| Species: | P. maculifrons |
| Binomial name | |
| Pheidole maculifrons Wheeler, W.M., 1929 | |
Identification
Wheeler (1929) - This species seems to be most closely related to Pheidole hortensis of Java, but is evidently quite distinct and unlike any of the species hitherto described from the Philippines or any of several undescribed species from those islands in my collection.
Distribution
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Indo-Australian Region: Philippines (type locality).
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
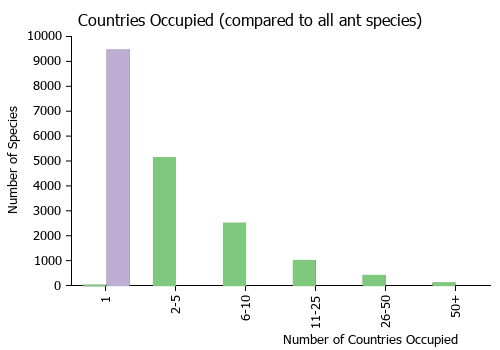
|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |

|
Biology
Castes
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- maculifrons. Pheidole maculifrons Wheeler, W.M. 1929g: 42, fig. 5 (s.) PHILIPPINES.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Soldier. Length nearly 2 mm.
Head subrectangular, about 1 1/4- times as long as broad, as broad in front as behind, with feebly and evenly convex sides and medially rather deeply excised posterior border; front and occipital corners convex, the latter somewhat turned upward, leaving a distinct concavity between them and the swollen front. Occipital groove deep and very short, continued forward only to this cavity. Eyes well-developed, convex, about as long as their distance from the anterior corners of the head. Mandibles convex, with two coarse apical teeth. Clypeus short and rather fiat, the anterior border sinuate in the middle and on each side. Frontal area deeply impressed; frontal groove obsolete; frontal carinae more than half as long as the antennal scapes, widely diverging posteriorly. Antennae slender; scapes curved, reaching nearly to the middle of the sides of the head; funicular joints 2-7 subequal, distinctly broader than long, together shorter than the club, the two basal joints of which are as long as the terminal joint, the latter with a long and distinct point. Thorax small, decidedly shorter than the head, the pro-and mesonotum voluminous and convex, together forming a projecting, hemispherical mass in profile; seen from above the pronotum is twice as broad as long, transverse, with large, bluntly angular humeri; promesonotal suture distinct. Mesonotum feebly convex, descending rather abruptly to the epinotum, without transverse groove or toms. Epinotum very small and low, scarcely more than half as high as the pronotum, higher than long, with the base horizontal and somewhat shorter than the steep declivity and two acute teeth as long as broad at their bases, directed upward and somewhat backward. Petiolar node anteroposteriorly compressed, its upper border entire and distinctly pointed or acuminate in the middle. Postpetiole small, transverse, more than twice as broad as long, produced and bluntly angulate on each side; in profile its dorsal surface is very convex but not quite as high as the petiolar node. Gaster elliptical, about as large as the head. Femora and tibiae somewhat incrassated.
Shining; mandibles and clypeus smooth, the former with a few scattered punctures; anterior two-thirds of head longitudinally rugose, the rugae slender, widely separated on the front, more numerous on the sides, the interrugal spaces smooth and flat; posterior third of head loosely and somewhat transversely reticulate-rugose. Remainder of body smooth and shining, except the mesopleurae, which are finely and densely punctate.
Hairs yellow, coarse, moderately long and abundant on the body, much shorter and oblique or subappressed on the appendages. Pale castaneous brown; mandibles, clypeus, front, cheeks, mesonotum, mesopleurae, sides and anterior portion of pronotum, antennae and legs ivory yellow; clypeus and front spotted with brown; borders of mandibles black.
Type Material
A single specimen from Los Banos, Luzon Island, Philippines.
References
- Baltazar, C.R. 1966. A catalogue of Philippine Hymenoptera (with a bibliography, 1758-1963). Pacific Insects Monographs 8: 1-488. (page 256, listed)
- Wheeler, W. M. 1929h. Ants collected by Professor F. Silvestri in Formosa, the Malay Peninsula and the Philippines. Boll. Lab. Zool. Gen. Agrar. R. Sc. Super. Agric. 24: 27-64 (page 42, fig. 5 soldier described)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Chapman, J. W., and Capco, S. R. 1951. Check list of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Asia. Monogr. Inst. Sci. Technol. Manila 1: 1-327

