Formica liogaster
| Formica liogaster | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Formicini |
| Genus: | Formica |
| Species: | F. liogaster |
| Binomial name | |
| Formica liogaster Chang & He, 2002 | |
Identification
Chang and He (2002) - Similar to Formica candida, but F. liogaster lacking hair and pubescence on 1 - 3 gastral tergites; mesonotum straight in profile, superior border significantly higher than pronotum.
Distribution
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Palaearctic Region: China (type locality).
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |
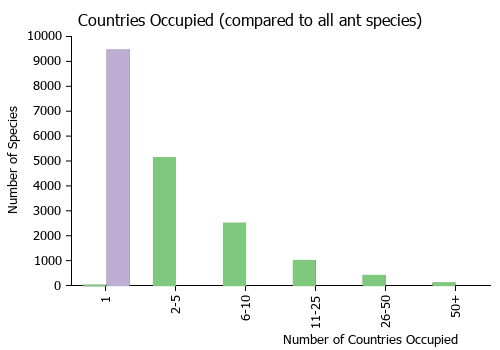
|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |

|
Biology
Castes
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- liogaster. Formica liogaster Chang & He, 2002a: 54, figs. 11, 12, 59 (w.) CHINA.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Type Material
Holotype worker, No 99 - 152, 22-VI-1999, Haiyuan, 1720 m, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, coll. CHANG Yourde. Paratypes 8 workers, No 99 - 196, same as holotype. Deposited in Ningxia Agricultural College collection.
References
- Chang, Y.-D.; He, D.-H. 2002a. Taxonomic study of genus Formica L. from Northwest China with descriptions of nine new species and four new records (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Zoological Research. 23:49-60. (page 54, worker described)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.