Carebara atoma
| Carebara atoma | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Myrmicinae |
| Tribe: | Crematogastrini |
| Genus: | Carebara |
| Species: | C. atoma |
| Binomial name | |
| Carebara atoma (Emery, 1900) | |
Heterick & Kitching (2022) collected this species in leaf litter within a lowland dipterocarp forest in Brunei.
Identification
Keys including this Species
Distribution
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: -5.12033° to -19.11833°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Australasian Region: Australia.
Indo-Australian Region: Brunei Darussalam, Fiji, Micronesia (Federated States of), New Guinea, Palau, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Wallis and Futuna Islands.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |

|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |

|
Biology
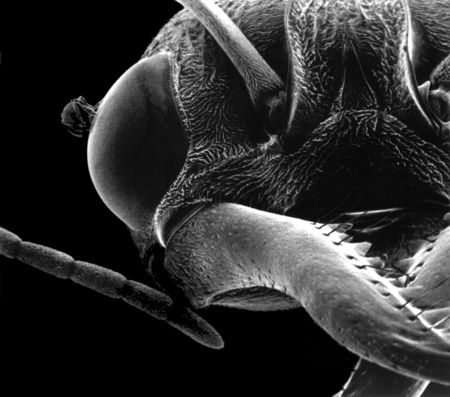
Myrmecia brevinoda, one of the largest ants, together with one of the smallest, Carebara atoma, photographed using an electron microscope. One of the reasons ants are so successful is because of their great morphological diversity. This diversity also extends to their life history and ecology. These two species differ so greatly that they would likely not even recognise each other when they meet in northern Queensland, Australia, where they both occur. They would pass by without a second thought and certainly wouldn't realise that they are cousins!
Castes
Images from AntWeb
 
| |
| Worker. Specimen code casent0101462. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by MNHN, Paris, France. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- atoma. Oligomyrmex atomus Emery, 1900c: 328, pl. 8, fig. 30 (s.w.) NEW GUINEA (Papua New Guinea).
- Type-material: syntype major and minor workers (numbers not stated).
- Type-localities: Papua New Guinea (“Nova-Guinea, Colonia Germanica”): Hansemann Mts (L. Biró), Papua New Guinea: Tamara I. (L. Biró), Papua New Guinea: Beliao I. (L. Biró).
- Type-depositories: HNHM, MSNG.
- Mann, 1919: 331 (q.).
- Combination in O. (Oligomyrmex): Emery, 1924d: 217;
- combination in Carebara: Fernández, 2004a: 235.
- Status as species: Mann, 1919: 331; Emery, 1924d: 217; Wheeler, W.M. 1935g: 27; Chapman & Capco, 1951: 156; Ettershank, 1966: 123; Wilson & Taylor, 1967: 60; Taylor, 1976a: 86; Taylor, 1991b: 606; Dlussky, 1994: 54; Bolton, 1995b: 299; Wetterer, 2002: 128; Wetterer & Vargo, 2003: 416; Clouse, 2007b: 245; Sarnat & Economo, 2012: 74; Sarnat, et al. 2013: 71.
- Distribution: Australia, Fiji Is, Micronesia, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Is, Tonga.
Type Material
- Oligomyrmex atomus Emery, 1900: Syntype, workers, Hansemann Mountain, Tamara Island and Beliao Island, Papua New Guinea, Museo Civico di Storia Naturale, Genoa.
Description
References
- Clouse, R. M. 2007. The Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Micronesia. Micronesica. 39(2): 171–296.
- Emery, C. 1900b. Formicidarum species novae vel minus cognitae in collectione Musaei Nationalis Hungarici quas in Nova-Guinea, colonia germanica, collegit L. Biró. Publicatio secunda. Természetr. Füz. 23: 310-338 (page 328, pl. 8, fig. 30 soldier, worker described)
- Fernández, F. 2004a. The American species of the myrmicine ant genus Carebara Westwood (Hymentoptera: Formicidae). Caldasia 26(1): 191-238 (page 235, Combination in Carebara)
- Heterick, B.E., Kitching, R.L. 2022. The ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of a one-hectare plot of lowland dipterocarp forest. Entomologist’s Monthly Magazine 158(4), 261–272 (doi:10.31184/m00138908.1584.4153).
- Mann, W. M. 1919. The ants of the British Solomon Islands. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 63: 273-391 (page 331, queen described)
- Taylor, R. W. 1991b. Nomenclature and distribution of some Australasian ants of the Myrmicinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Mem. Qld. Mus. 30: 599-614 (page 606, see also)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- CSIRO Collection
- Clouse R. M. 2007. The ants of Micronesia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Micronesica. 39: 171-295.
- Clouse, R.M. 2007. The ants of Micronesia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Micronesica 39(2): 171-295.
- Dlussky G.M. 1994. Zoogeography of southwestern Oceania. Zhivotnoe naselenie ostrovov Iugo-Zapadnoi Okeanii ekologo-geograficheskie issledovanii 48-93.
- Emery C. 1900. Formicidarum species novae vel minus cognitae in collectione Musaei Nationalis Hungarici quas in Nova-Guinea, colonia germanica, collegit L. Biró. Publicatio secunda. Természetrajzi Füzetek 23: 310-338.
- Greenslade P.J.M. and Greenslade Penelope. 1977. Some Effects of Vegetation Cover and Disturbance on a Tropical Ant Fauna. Insectes Sociaux 24(2): 163-182
- Greenslade P.J.M. and P. Greenslade. 1977. Some effects of vegetation cover and disturbance on a tropical ant fauna. Insectes Sociaux 24(2): 163-182.
- Janda M., G. D. Alpert, M. L. Borowiec, E. P. Economo, P. Klimes, E. Sarnat, and S. O. Shattuck. 2011. Cheklist of ants described and recorded from New Guinea and associated islands. Available on http://www.newguineants.org/. Accessed on 24th Feb. 2011.
- Kami K.S., and S. E. Miller. 1998. Samoan insects and related arthropods: checklist and bibliography. Bishop Museum Technical Report 13, pp 121.
- Kami KS & Miller SE. 1998. Samoan insects and related arthropods: checklist and bibliography. Bishop Museum Technical Report No. 13.
- Lucky A., L. E. Alonso, E. Sarnat, and J. Hulr. 2015. Ants and scolytine beetles. In: Richards, S.J. and N. Whitmore (editors) 2015. A rapid biodiversity assessment of Papua New Guinea's Hindenburg Wall region. Wildlife Conservation Society Papua New Guinea Program. Goroka, PNG.
- Mann W. M. 1919. The ants of the British Solomon Islands. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology 63:273-391.
- Mann, W.M. 1919. The ants of the British Solomon Islands. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology of Harvard College 63: 273-391
- Sarnat Eli M. 2009. The Ants [Hymenoptera: Formicdiae] of Fiji: Systematics, Biogeography and Conservation of an Island Arc Fauna. 80-252
- Snelling R. R. 1998. Insect Part 1: The social Hymenoptera. In Mack A. L. (Ed.) A Biological Assessment of the Lakekamu Basin, Papua New Guinea, RAP 9. 189 ppages
- Taylor R. W. 1976. The ants of Rennell and Bellona Islands. Natural History of Rennell Island, British Solomon Islands 7: 73-90.
- Taylor R. W. 1991. Nomenclature and distribution of some Australasian ants of the Myrmicinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 30: 599-614.
- Viehmeyer H. 1912. Ameisen aus Deutsch Neuguinea gesammelt von Dr. O. Schlaginhaufen. Nebst einem Verzeichnisse der papuanischen Arten. Abhandlungen und Berichte des Königlichen Zoologischen und Anthropologische-Ethnographischen Museums zu Dresden 14: 1-26.
- Ward D. 2008. Ecological partitioning and invasive ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in a tropical rain forest ant community from Fiji. Pacific Science 62(4): 473-482.
- Ward, Darren and Beggs, Jacqueline. 2007. Coexistence, habitat patterns and the assembly of ant communities in the Yasawa islands, Fiji. Ant Oecologica. 32:215-223.
- Wetterer, James K. 2002. Ants of Tonga. Pacific Science. 56.2: 125-135.
- Wetterer, James K. and Vargo, Donald Vargo L. 2003. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Samoa. Pacific Science. 57(4):409-419.
- Wheeler W.M. 1935. Check list of the ants of Oceania. Occasional Papers of the Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum 11(11):1-56.
- Wheeler, William Morton.1935.Checklist of the Ants of Oceania.Occasional Papers 11(11): 3-56
- Wilson E. O.; Taylor, R. W. 1967. The ants of Polynesia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Pacific Insects Monograph 14:1-109.
- Wilson E.O., and G.L. Hunt. 1967. Ant fauna of Futuna and Wallis islands, stepping stones to Polynesia. Pacific Insects 9(4): 563-584.
- Wilson EO & Hunt GL. 1967. Ant fauna of Futuna and Wallis Islands, stepping stones to Polynesia. Pacific Insects 9.4: 563-584.
- Wilson EO, Hunt GL. 1967. Ant fauna of Futuna and Wallis Islands, stepping stones to Polynesia. Pacific Insects 9.4: 563-584.
- Wilson EO, Taylor RW. 1967. The ants of Polynesia. Pacific Insects Monograph 14:1-109.
- Wilson, Edward O. and George L. Hunt. 1967. Ant Fauna of Futuna and Wallis Islands, Stepping Stones To Polynesia. Pacific Insects. 9(4):563-584.
- Wilson, Edward O. and Hunt, George L. Jr. 1967. Ant Fauna of Futuna and Wallis Islands, Stepping Stones to Polynesia. Pacific Insects. 9(4):563-584