Lepisiota capensis
| Lepisiota capensis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Plagiolepidini |
| Genus: | Lepisiota |
| Species: | L. capensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Lepisiota capensis (Mayr, 1862) | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| At a Glance | • Limited invasive |
Identification
Distribution
Wachkoo et al. (2021) - The nominal form of L. capensis does not occur naturally in India, despite its implied presence by the use of the name L. capensis reported by Bingham (1903). The species referred to in the latter paper, with abundant yellowish erect setae is clearly not L. capensis, which has sparse dark (brown or black) erect setae (see Mayr 1862, 1865; Arnold 1920) and is distributed in southern Africa (not from the Himalayas through to Northeastern Africa).
Bingham’s (1903) report was apparently based on an erroneous reporting of the presence of L. capensis with whitish setae in India and Sri Lanka (then Ceylon) by Forel (1892, 1894), and the attribution of dense pilosity to L. capensis served only to perpetuate this error until today (Peter Hawkes & F. Hita Garcia, pers. comm.).
The Indian material currently and in the past attributed to L. capensis in fact represents a very different species, now known to be Lepisiota mayri.
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 32.812778° to -34.76667°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Afrotropical Region: Botswana, Comoros, Democratic Republic of Congo, Eritrea, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Africa (type locality).
Malagasy Region: Madagascar.
Palaearctic Region: Canary Islands, China.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |

|
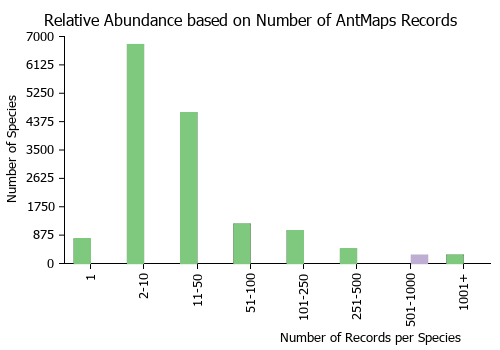
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |
|
Biology
Association with Other Organisms
 Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Associate data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- This species is a host for the encyrtid wasp Anagyrus lopezi (a parasite) (Universal Chalcidoidea Database) (associate).
- This species is a host for the cricket Myrmophilellus meneliki (a myrmecophile) in Ethiopia (Reichensperger, 1913).
- This species is a prey for the syrphid fly Paramixogaster acantholepidis (a predator) (Quevillon, 2018).
Castes
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- capensis. Acantholepis capensis Mayr, 1862: 699 (w.) SOUTH AFRICA. Mayr, 1865: 57 (m.); Emery, 1877b: 366 (q.); Wheeler, G.C. & Wheeler, J. 1980: 542 (l.). Combination in Lepisiota: Xu, 1994c: 233. Current subspecies: nominal plus acholli, anceps, guineensis, issore, junodi, laevis, lunaris, minuta, simplex, simplicoides, specularis, subopaciceps, thoth. See also: Bingham, 1903: 316; Arnold, 1920a: 568.
Description
Karyotype
- See additional details at the Ant Chromosome Database.
 Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
Explore: Show all Karyotype data or Search these data. See also a list of all data tables or learn how data is managed.
- 2n = 18 (India) (Imai et al., 1984) (as Acantholepis lunaris).
References
- Arnold, G. 1920a. A monograph of the Formicidae of South Africa. Part IV. Myrmicinae. Ann. S. Afr. Mus. 14: 403-578 (page 568, see also)
- Bingham, C. T. 1903. The fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Hymenoptera, Vol. II. Ants and Cuckoo-wasps. London: Taylor and Francis, 506 pp. (page 316, see also)
- Borowiec, L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Devenish, A.J.M., Newton, R.J., Bridle, J.R., Gomez, C., Midgley, J.J., Sumner, S. 2021. Contrasting responses of native ant communities to invasion by an ant invader, Linepithema humile. Biological Invasions 23, 2553–2571 (doi:10.1007/s10530-021-02522-7).
- Dias, R.K.S., Kosgamage, K.R.K.A. 2013. Occurrence and species diversity of ground-dwelling worker ants (Family: Formicidae) in selected lands in the dry zone of Sri Lanka. Journal of Science of the University of Kelaniya Sri Lanka 7: 55-72 (doi:10.4038/josuk.v7i0.6233).
- Dias, R.K.S., Rajapaksa, R.P.K.C. 2017. Geographic records of subfamilies, genera and species of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the four climatic zones of Sri Lanka: A review. Journal of Science of the University of Kelaniya Sri Lanka 11, 23-45. (doi:10.4038/josuk.v11i2.7999).
- Emery, C. 1877a. Catalogo delle formiche esistenti nelle collezioni del Museo Civico di Genova. Parte prima. Formiche provenienti dal Viaggio dei signori Antinori, Beccari e Issel nel Mar Rosso e nel paese dei Bogos. [part]. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. 9: 363-368 (page 366, queen described)
- Guillem, R., Bensusan, K. 2022. Thee new exotic species of ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) for Madeira, with comments on its myrmecofauna. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 91: 321–333 (doi:10.3897/jhr.91.81624).
- Liu, C., Fischer, G., Hita Garcia, F., Yamane, S., Liu, Q., Peng, Y.Q., Economo, E.P., Guénard, B., Pierce, N.E. 2020. Ants of the Hengduan Mountains: a new altitudinal survey and updated checklist for Yunnan Province highlight an understudied insect biodiversity hotspot. ZooKeys 978, 1–171 (doi:10.3897/zookeys.978.55767).
- Mayr, G. 1862. Myrmecologische Studien. Verh. K-K. Zool.-Bot. Ges. Wien 12: 649-776 (page 699, worker described)
- Mayr, G. 1865. Formicidae. In: Reise der Österreichischen Fregatte "Novara" um die Erde in den Jahren 1857, 1858, 1859. Zoologischer Theil. Bd. II. Abt. 1. Wien: K. Gerold's Sohn, 119 pp. (page 57, male described)
- Rasheed, S.B., Ali, M., Zaidi, F., Noreen, S. 2020. Diversity of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in residential area of Tarbela, Swabi: New recrds from Pakistan. The Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences 31: 617-624 (doi:10.36899/japs.2021.2.0250).
- Taylor, B., Agoinon, N., Sinzogan, A., Adandonon, A., Kouaguou, Y. N., Bello, S., Wargui, R., Anato, F., Ouagoussounon, I., Houngbo, H., Tchibozo, S., Todjihounde, R., Vayssieres, J.F. 2018. Records of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from the Republic of Benin, with particular reference to the mango farm ecosystem. Journal of Insect Biodiversity 8(1): 6-29 (doi:10.12976/jib/2018.08.1.2).
- Wachkoo, A.A., Bharti, H., Akbar, S.A. 2021. Taxonomic review of the ant genus Lepisiota Santschi, 1926 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae) from India. Bonn Zoological Bulletin 70(2): 227–245 (doi:10.20363/BZB-2021.70.2.227).
- Wheeler, G. C.; Wheeler, J. 1980. Supplementary studies on ant larvae: Ponerinae, Myrmicinae and Formicinae. Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 106: 527-545 (page 542, larva described)
- Xu, Z. 1994c. A taxonomic study of the ant genus Lepisiota Santschi from southwestern China (Hymenoptera Formicidae Formicinae). J. Southwest For. Coll. 14: 232-237 (page 233, Combination in Lepisiota)
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Bernard F. 1950. Contribution à l'étude de l'Aïr. Hyménoptères Formicidae. Mém. Inst. Fr. Afr. Noire 10: 284-294.
- Bernard F. 1977. Trois fourmis nouvelles du Sahara (Hym. Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société Entomologique de France 82: 29-32.
- Bernard F., and H. Cagniant. 1963. Capture au Hoggar de trois Acantholepis nouveaux pour ce massif avec observations sur leurs modes de vie (Hym. Formicidae). Bulletin de la Société Entomologique de France 67: 161-164.
- Bernard, F., and H. Cagniant. "Capture au Hoggar de trois Acantholepis nouveaux pour ce massif avec observations sur leurs modes de vie (Hym. Formicidae)." Bulletin de la Société Entomologique de France 67 (1963): 161-164.
- Bharti H., Y. P. Sharma, M. Bharti, and M. Pfeiffer. 2013. Ant species richness, endemicity and functional groups, along an elevational gradient in the Himalayas. Asian Myrmecology 5: 79-101.
- Borowiec L. 2014. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus (Wroclaw) 25(1-2): 1-340.
- Cheng D., Z. Chen, and S. Zhou. 2015. An analysis on the ant fauna of Jinzhongshan Nature Reserve in Gunagxi, China. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 33(3): 129.137.
- Dad J. M., S. A. Akbar, H. Bharti, and A. A. Wachkoo. 2019. Community structure and ant species diversity across select sites ofWestern Ghats, India. Acta Ecologica Sinica 39: 219–228.
- Dean W. R. J., and J. S. Turner. 1991. Ants nesting under stones in the semi-arid Karoo, South Africa: predator avoidance or temperature benefits? Journal of Arid Environments 21: 59-69.
- Diame L., B. Taylor, R. Blatrix, J. F. Vayssieres, J. Y. Rey, I. Grechi, and K. Diarra. 2017. A preliminary checklist of the ant (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) fauna of Senegal. Journal of Insect Biodiversity 5(15): 1-16.
- Dias R. K. S. 2002. Current knowledge on ants of Sri Lanka. ANeT Newsletter 4: 17- 21.
- Dias R. K. S. 2006. Current taxonomic status of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Sri Lanka. The Fauna of Sri Lanka: 43-52. Bambaradeniya, C.N.B. (Editor), 2006. Fauna of Sri Lanka: Status of Taxonomy, Research and Conservation. The World Conservation Union, Colombo, Sri Lanka & Government of Sri Lanka. viii + 308pp.
- Dias R. K. S., K. R. K. A. Kosgamage, and H. A. W. S. Peiris. 2012. The Taxonomy and Conservation Status of Ants (Order: Hymenoptera, Family: Formicidae) in Sri Lanka. In: The National Red List 2012 of Sri Lanka; Conservation Status of the Fauna and Flora. Weerakoon, D.K. & S. Wijesundara Eds., Ministry of Environment, Colombo, Sri Lanka. p11-19.
- Dias R. K. S., and K. R. K. Anuradha Kosgamage. 2012. Occurrence and species diversity of ground-dwelling worker ants (Family: Formicidae) in selected lands in the dry zone of Sri Lanka. J. Sci. Univ. Kelaniya 7: 55-72.
- Dias R. K. S., and R. P. K. C. Rajapaksa. 2016. Geographic records of subfamilies, genera and species of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the four climatic zones of Sri Lanka: a review. J. Sci. Univ. Kelaniya 11(2): 23-45.
- Dias, R.K.S. 2006. Overview of ant research in Sri Lanka: 2000-2004. ANeT Newsletter 8:7-10
- Emery C. 1895. Voyage de M. E. Simon dans l'Afrique australe (janvier-avril 1893). 3e mémoire. Formicides. Annales de la Société Entomologique de France 64: 15-56.
- Emery, C.. "Catalogo delle formiche esistenti nelle collezioni del Museo Civico di Genova. Parte prima. Formiche provenienti dal Viaggio dei signori Antinori, Beccari e Issel nel Mar Rosso e nel paese dei Bogos. [concl.]." Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 9 (1877): 363-381.
- Emery, C.. "Viaggio ad Assab nel Mar Rosso dei Signori G. Doria ed O. Beccari con il R. Avviso "Esploratore" dal 16 novembre 1879 al 26 febbraio 1880. I. Formiche." Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 16 (1881): 525-535.
- Finzi B. 1939. Materiali zoologici dell'Eritrea raccolti da G. Müller durante la spedizione dell'Istituto Sieroterapico Milanese e conservati al Museo di Trieste. Parte III. Hymenoptera: Formicidae. Atti del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Trieste 14: 153-168.
- Forel A. 1894. Les Formicides de l'Empire des Indes et de Ceylan. Part IV. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 8: 396-420.
- Forel A. 1901. Einige neue Ameisen aus Südbrasilien, Java, Natal und Mossamedes. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft. 10: 297-311.
- Forel A. 1901. Einige neue Ameisen aus Südbrasilien, Java, Natal und Mossamedes. Mitt. Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 10: 297-311.
- Forel A. 1903. Einige neue Ameisen aus Sud-Angola. Pp 559-564, in: Baum, H. Kunene-Sambesi-Expedition, 1903. Berlin: Verlag des Kolonial-Wirtschaftlichen Komitees, 593pp.
- Forel A. 1904. Note sur les fourmis du Musée Zoologique de l'Académie Impériale des Sciences à St. Pétersbourg. Ezheg. Zool. Muz. 8: 368-388.
- Forel A. 1907. Ameisen von Madagaskar, den Comoren und Ostafrika. Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse. Reise in Ostafrika 2: 75-92.
- Forel A. 1909. Fourmis du Musée de Bruxelles. Fourmis de Benguela récoltées par M. Creighton Wellman, et fourmis du Congo récoltées par MM. Luja, Kohl et Laurent. Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 53: 51-73.
- Forel A. 1910. Ameisen aus der Kolonie Erythräa. Gesammelt von Prof. Dr. K. Escherich (nebst einigen in West-Abessinien von Herrn A. Ilg gesammelten Ameisen). Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Systematik, Geographie und Biologie der Tiere 29: 243-274.
- Forel A. 1910. Zoologische und anthropologische Ergebnisse einer Forschungsreise im westlichen und zentralen Südafrika ausgeführt in den Jahren 1903-1905 von Dr. Leonhard Schultze. Vierter Band. Systematik und Tiergeographie. D) Formicidae. Denkschriften der Medizinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena 16: 1-30.
- Forel A. 1913. Formicides du Congo Belge récoltés par MM. Bequaert, Luja, etc. Revue Zoologique Africaine (Brussels). 2: 306-351.
- Forel A. 1914. Formicides d'Afrique et d'Amérique nouveaux ou peu connus. Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles 50: 211-288.
- French K., and R. E. Major. 2001. Effect of an exotic Acacia (Fabaceae) on ant assemblages in South African fynbos. Austral Ecology 26: 303310.
- Garcia F.H., Wiesel E. and Fischer G. 2013.The Ants of Kenya (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)Faunal Overview, First Species Checklist, Bibliography, Accounts for All Genera, and Discussion on Taxonomy and Zoogeography. Journal of East African Natural History, 101(2): 127-222
- Guénard B., and R. R. Dunn. 2012. A checklist of the ants of China. Zootaxa 3558: 1-77.
- IZIKO South Africa Museum Collection
- Imai H. T., C. Baroni Urbani, M. Kubota, G. P. Sharma, M. H. Narasimhanna, B. C. Das, A. K. Sharma, A. Sharma, G. B. Deodikar, V. G. Vaidya, and M. R. Rajasekarasetty. 1984. Karyological survey of Indian ants. Japanese Journal of Genetics 59: 1-32.
- Koen J. H., and W. Breytenbach. 1988. Ant species richness of fynbos and forest ecosystems in the Southern Cape. South Afr. Tydskr. Dierk. 23(3): 184-188.
- Kouakou L. M. M., K. Yeo, K. Ouattara, W. Dekoninck, T. Delsinne, and S. Konate. 2018. Investigating urban ant community (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in port cities and in major towns along the border in Côte d’Ivoire: a rapid assessment to detect potential introduced invasive ant species. Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences 36(1): 5793-5811.
- Kouakou L. M. M., W. Dekoninck, M. Kone, T. Delsinne, K. Yeo, K. Ouattara, and S. Konate. 2018. Diversity and distribution of introduced and potentially invasive ant species from the three main ecoregions of Côte d’Ivoire (West Africa). Belgian Journal of Zoology 148 (1): 83–103.
- Lach, L. 2008. Argentine ants displace floral arthropods in a biodiversity hotspot. Diversity and Distributions 14:281-290
- Li Q., B. D. Hoffmann, Z. X. Lu, and Y. Q. Chen. 2017. Ants show that the conservation potential of afforestation efforts in Chinese valley-type savanna is dependent upon the afforestation method. Journal of Insect Conservation DOI 10.1007/s10841-017-0005-0
- Li Q., Z. Lu, Z. Wei, M. Yanyan, and F. Ping. 2015. Communities of ground-dwelling ants in different plantation forest in arid-hot valleys of Jinsha river, Yunnan Province, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 51(8): 134-142.
- Li Z.h. 2006. List of Chinese Insects. Volume 4. Sun Yat-sen University Press
- Lu Z., B. D. Hoffmann, and Y. Chen. 2016. Can reforested and plantation habitats effectively conserve SW China’s ant biodiversity? Biodivers. Conserv. DOI 10.1007/s10531-016-1090-1
- Lu Z., K. Li, N. Zhang, and Y. Chen. 2017. Diversity and indicator species of leaf-litter ants in Eucalyptus grandis plantations and secondary natural forests. Forest Research 29(4): 576-580
- Lu Z., Y. Chen, Q. Li, S. Wang, C. Liu, and W. Zhang. 2012. Effect of population of Kerria yunnanensis on diversity of ground dwelling ant. Acta Ecologica Sinica 32(19): 6195-6202.
- Lévieux J. 1977. La nutrition des fourmis tropicales: V- Elements de synthèse. Les modes d'exploitation de la biocenose. Insectes Sociaux 24(3): 235-260.
- Madl M. 2019. Notes on the ant fauna of Eritrea (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Formicidae): type specimens deposited in the Natural History Museum Vienna (Austria) and a preliminary checklist. Ann. Naturhist. Mus. Wien, B 121: 9-18.
- Mathew R. 2003. On Formicidae (Insecta: Hymenoptera) of Nongkhyllem Wild Life Sanctuary, Ri-Bhoi District, Meghalaya. Records of the Zoological Survey of India 101:195-207.
- Mathew R., and R. N. Tiwari. 2000. Insecta: Hymenoptera: Formicidae. Pp. 251-409 in: Director; Zoological Survey of India (ed.) 2000. Fauna of of Meghalaya. Part 7. [State Fauna Series 4.] Insecta 2000. Calcutta: Zoological Survey of India, 621 pp.
- Pajni H. R., and R. K. Suri. 1978. First report on the Formicid fauna (Hymenoptera) of Chandigarh. Res. Bull. (Science) Punjab University 29: 5-12.
- Rajan P. D., M. Zacharias, and T. M. Mustak Ali. 2006. Insecta: Hymenoptera: Formicidae. Fauna of Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Wildlife Sanctuary (Karnataka). Conservation Area Series, Zool. Surv. India.i-iv,27: 153-188.
- Ran H., and S. Y. Zhou. 2012. Checklist of chinese ants: formicomorph subfamilies (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) II. Journal of Guangxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 30(4): 81-91.
- Santschi F. 1914. Formicides de l'Afrique occidentale et australe du voyage de Mr. le Professeur F. Silvestri. Bollettino del Laboratorio di Zoologia Generale e Agraria della Reale Scuola Superiore d'Agricoltura. Portici 8: 309-385.
- Santschi, F.. "Résultats de la Mission scientifique suisse en Angola, 1928-1929. Formicides de l'Angola." Revue Suisse de Zoologie 37 (1930): 53-81.
- Song Y., Z. Xu, C. Li, N. Zhang, L. Zhang, H. Jiang, and F. Mo. 2013. An Analysis on the Ant Fauna of the Nangun river Nature Reserve in Yunnan, China. Forest Research 26(6): 773-780.
- Taylor B. 1978. Ants of the Nigerian Forest Zone (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). II. Formicinae, Dolichoderinae. Cocoa Research Institute of Nigeria Research Bulletin 5: 1-57.
- Taylor B., and S. F. Adedoyin. 1978. The abundance and interspecific relations of common ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) on cocoa farms in western Nigeria. Bull. Ent. Res. 68: 105-121.
- Wheeler W. M. 1922. Ants of the American Museum Congo expedition. A contribution to the myrmecology of Africa. VIII. A synonymic list of the ants of the Ethiopian region. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 45: 711-1004
- Wu Z. W., X. D. Bi, X. He, Z. X. Lu, L. J. Wei, and Y. Q Chen. 2015. Impact of continuous fire disturbance on ground-dwelling ant communities in arid-hot valleys of Panzhihua, Sichuan. Journal of Yunnan University 37(3): 467-474.
- Xu Z., Zeng G., Liu T.-Y. and He Y.-F.. 1999. [A study on communities of Formicidae ants in different subtypes of vegetation in Xishuangbanna District of China.] Zoological Research 20: 118-125
- Pages using DynamicPageList3 parser function
- Limited invasive
- Need species key
- North subtropical
- Tropical
- South subtropical
- Encyrtid wasp Associate
- Host of Anagyrus lopezi
- Cricket Associate
- Host of Myrmophilellus meneliki
- Syrphid fly Associate
- Host of Paramixogaster acantholepidis
- Karyotype
- Species
- Extant species
- Formicidae
- Formicinae
- Plagiolepidini
- Lepisiota
- Lepisiota capensis
- Formicinae species
- Plagiolepidini species
- Lepisiota species
- Need Overview
- Need Body Text


