Strumigenys eggersi
| Strumigenys eggersi | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Myrmicinae |
| Tribe: | Attini |
| Genus: | Strumigenys |
| Species: | S. eggersi |
| Binomial name | |
| Strumigenys eggersi Emery, 1890 | |
An unusual Strumigenys in its tolerance for its tolerance of relatively dry conditions. Strumigenys eggersi can inhabit a wide range of habitats, e.g., forests, thickets, gardens.
| At a Glance | • Invasive |
Identification
Bolton (2000) - A member of the gundlachi-complex in the Strumigenys gundlachi group. Among the species closest related to Strumigenys gundlachi, eggersi is isolated by the characters in its description. It separates from Strumigenys denticulata, with which it shares the characters of extreme reduction or absence of postpetiolar appendages, by its shorter mandibles (MI 58 - 65 as opposed to MI 72 - 85 in denticulata), presence of a pair of standing hairs anteriorly on the pronotum, and more strongly sculptured gaster. Pyramica eggersi and P. gundlachi are the only species of the gundlachi-group to have been recorded from the U.S.A., where they are apparently restricted to Florida (Brown, 1960a; D. R. Smith, 1979; Deyrup, Johnson, et al., 1989).
Longino (Ants of Costa Rica) - Mandibles in full-face view linear, elongate and narrow; leading edge of scape with freely projecting hairs; inner margin of mandible without a tooth or distinctly enlarged denticle at or near the midlength; labral lobes short, trigger hairs at apices of lobes long; apical fork of mandible small, with two tiny intercalary denticles; mandibles straight, with weakly convex inner borders, each bearing 4-8 minute denticles on distal 1/3 to 1/2; spongiform appendages of petiole and postpetiole obsolete; first gastral tergum superficially reticulate-punctulate and opaque in front, becoming indefinitely shagreened and weakly shining behind.
Keys including this Species
- Key to Nearctic Strumigenys (as Pyramica)
- Key to Neotropical Strumigenys (as Pyramica)
- Key to Strumigenys of Hispaniola
- Key to US Strumigenys species
Distribution
A common species in Florida, where it has been introduced, as far north as Union County. Pest status: none. First published Florida record: Brown 1960. (Deyrup, Davis & Cover, 2000.)
Latitudinal Distribution Pattern
Latitudinal Range: 25.019° to -31.632389°.
| North Temperate |
North Subtropical |
Tropical | South Subtropical |
South Temperate |
- Source: AntMaps
Distribution based on Regional Taxon Lists
Indo-Australian Region: Philippines, Singapore.
Nearctic Region: United States.
Neotropical Region: Argentina, Barbados, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Greater Antilles, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Lesser Antilles (type locality), Mexico, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Saint Lucia, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela.
Distribution based on AntMaps
Distribution based on AntWeb specimens
Check data from AntWeb
Countries Occupied
| Number of countries occupied by this species based on AntWiki Regional Taxon Lists. In general, fewer countries occupied indicates a narrower range, while more countries indicates a more widespread species. |

|
Estimated Abundance
| Relative abundance based on number of AntMaps records per species (this species within the purple bar). Fewer records (to the left) indicates a less abundant/encountered species while more records (to the right) indicates more abundant/encountered species. |
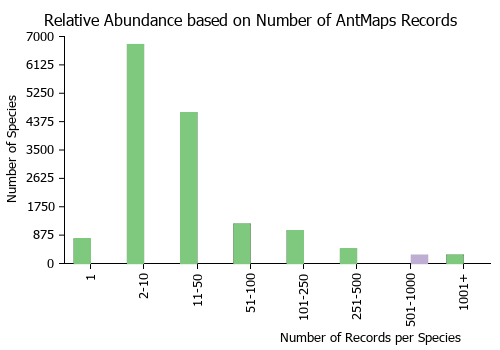
|
Biology
Deyrup (1997) - Among the snap-trap ants this is an unusually drought-tolerant species that also thrives in disturbed conditions. The queens are often relatively abundant, giving the impression that this species lives in small colonies that produce many new queens that can found new colonies. This would be a useful adaptation for living in frequently disturbed habitats, where occupied nest sites are often destroyed and new ones created.
Atchison & Lucky (2022) found that this species, as expected, does not remove seeds.
Regional Information
Caribbean
Brown (1960) - Weber found specimens in a compost heap in the Botanical Garden at Roseau, Dominica, and in an island of vegetation growing in the Pitch Lake of Trinidad; also on Trinidad, he took a sample from low-growing epiphytes in second-growth forest. Kempf sifted specimens from humus in Sao Paulo. Indications are that this species can stand more dryness than many dacetines, and its presence in many culture areas suggests that it is spreading rapidly through nursery stock transport and other human commerce.
Costa Rica
Longino (Ants of Costa Rica) - In Costa Rica this species appears rare, although my collecting has not emphasized dry and/or synanthropic habitats. I have encountered it in Winkler samples from Finca La Pacifica (riparian forest in seasonally dry region), and La Selva Biological Station (lowland rainforest).
Florida (USA)
Deyrup, Davis & Cover (2000) - In Florida this species is found in both moist and dry woods, as well as shaded yards and gardens. Nests are in leaf litter, or in hollow twigs or nuts in the litter. The species Strumigenys eggersi and Strumigenys emmae are the only dacetine ants that are commonly found in dry and mesic habitats of south and central Florida. There is little evidence that native dacetines were ever common in these areas, but if these two exotics continue their northward expansion we may be able to get some idea of their effect on native ants, since we have records of hundreds of litter samples from north Florida. These species are probably more or less specialized predators on entomobryiid Collembola. If they have not had an impact by reducing or replacing the populations of native predators of Collembola in south Florida, they must be a novel predator of the Collembola themselves in this area.
Philippines
General (2017) reports this species from an urban university campus in the Philippines, possibly introduced by trade in potted ornamental plants. He also notes that there is an unconfirmed report of its presence in Singapore (D. Booher, personal communication). The distribution of this species in the Philippines and its ecological impact there are unknown.
Castes
Worker
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Worker. Specimen code casent0103845. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by ABS, Lake Placid, FL, USA. |
   
| |
| Worker. Specimen code casent0178118. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by ALWC, Alex L. Wild Collection. |
Queen
Images from AntWeb
   
| |
| Queen (alate/dealate). Specimen code casent0103843. Photographer April Nobile, uploaded by California Academy of Sciences. | Owned by ABS, Lake Placid, FL, USA. |
Nomenclature
The following information is derived from Barry Bolton's Online Catalogue of the Ants of the World.
- eggersi. Strumigenys eggersi Emery, 1890b: 69, pl. 7, fig. 9 (w.q.) ANTILLES. Combination in S. (Pyramica): Brown, 1948e: 110; in Pyramica: Bolton, 1999: 1673; in Strumigenys: Baroni Urbani & De Andrade, 2007: 119. See also: Brown, 1960b: 46; Bolton, 2000: 184.
Unless otherwise noted the text for the remainder of this section is reported from the publication that includes the original description.
Description
Worker
Bolton (2000) - TL 1.6 - 2.0, HL 0.40 - 0.45, HW 0.32 - 0.37, CI 81 - 86, ML 0.23 - 0.28, MI 58 - 65, SL 0.20 - 0.24, SI 58 - 64, PW 0.20 - 0.23, AL 0.40 - 0.46 (20 measured). Characters of gundlachi complex; see also notes under Strumigenys gundlachi. Inner margin of mandible feebly convex, with 4 - 8 preapical small denticles on the distal one-third to one-half of the length. Dorsum of pronotum with a single pair of erect hairs (as well as the humeral pair), located on anterior half, usually between the humeral pair. Pair of mesonotal erect hairs short and stiff. On postpetiole ventral spongiform appendage vestigial to absent; lateral lobe absent or at most represented by a narrow marginal non-spongiform carina. First gastral tergite strongly reticulate to reticulate-punctate basally; this sculpture may cover the entire sclerite or tend to diminish in intensity posteriorly.
Type Material
Bolton (2000) - Syntype workers and queens, ANTILLES IS: St Thomas I . (Eggers) (Naturhistorisches Museum Wien, Vienna, Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo, National Museum of Natural History) [examined].
References
- Albuquerque, E., Prado, L., Andrade-Silva, J., Siqueira, E., Sampaio, K., Alves, D., Brandão, C., Andrade, P., Feitosa, R., Koch, E., Delabie, J., Fernandes, I., Baccaro, F., Souza, J., Almeida, R., Silva, R. 2021. Ants of the State of Pará, Brazil: a historical and comprehensive dataset of a key biodiversity hotspot in the Amazon Basin. Zootaxa 5001, 1–83 (doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5001.1.1).
- Atchison, R. A., Lucky, A. 2022. Diversity and resilience of seed-removing ant species in Longleaf Sandhill to frequent fire. Diversity 14, 1012 (doi:10.3390/d14121012).
- Baroni Urbani, C. & De Andrade, M.L. 2007. The ant tribe Dacetini: limits and constituent genera, with descriptions of new species. Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale “G. Doria” 99: 1-191.
- Bolton, B. 1999. Ant genera of the tribe Dacetonini (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Journal of Natural History. 33:1639-1689. (page 1673, Combination in Pyramica)
- Bolton, B. 2000. The ant tribe Dacetini. Mem. Am. Entomol. Inst. 65: 1-1028 (page 184, redescription of worker)
- Brown, W. L., Jr. 1948. A preliminary generic revision of the higher Dacetini (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Transactions of the American Entomological Society. 74: 101-129. (page 110, Combination in S. (Pyramica))
- Brown, W. L., Jr. 1960c [1959]. The neotropical species of the ant genus Strumigenys Fr. Smith: group of gundlachi (Roger). Psyche (Camb.) 66: 37-52 (page 46, redescription of worker, queen)
- Brown, W. L., Jr. 1962c. The neotropical species of the ant genus Strumigenys Fr. Smith: synopsis and keys to the species. Psyche. 69:238-267.
- Conceição-Neto, R., França, E.C.B., Feitosa, R.M., Queiroz, J.M. 2021. Revisiting the ideas of trees as templates and the competition paradigm in pairwise analyses of ground-dwelling ant species occurrences in a tropical forest. Revista Brasileira de Entomologia 65, e20200026 (doi:10.1590/1806-9665-rbent-2020-0026).
- Deyrup, M. 1997. Dacetine ants of the Bahamas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bahamas J. Sci. 5:2-6.
- Deyrup, M., Davis, L. & Cover, S. 2000. Exotic ants in Florida. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 126, 293-325.
- Deyrup, M.; Johnson, C.; Davis, L. 1997. Notes on the ant Eurhopalothrix floridana, with a description of the male (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Entomol. News 108: 183-189 (page 3, see also)
- Deyrup, M.A., Carlin, N., Trager, J., Umphrey, G. 1988. A review of the ants of the Florida Keys. Florida Entomologist 71: 163-176.
- Emery, C. 1890c. Studii sulle formiche della fauna neotropica. Bullettino della Società Entomologica Italiana 22:38-80. (page 69, worker, queen described)
- Franco, W., Ladino, N., Delabie, J.H.C., Dejean, A., Orivel, J., Fichaux, M., Groc, S., Leponce, M., Feitosa, R.M. 2019. First checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of French Guiana. Zootaxa 4674, 509–543 (doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4674.5.2).
- General, D.E.M. 2017. First Philippine record of the Neotropical ant Strumigenys eggersi
Emery (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Philippine Entomologist 31: 73-78.
- General, D.E.M., Buenavente, P.A.C., Rodriguez, L.J.V. 2020. A preliminary survey of nocturnal ants, with novel modifications for collecting nocturnal arboreal ants. Halteres 11: 1-12 (doi:10.5281/ZENODO.3707151).
- Hamer, M.T., Turner, C.R. 2024. Strumigenys emmae (Emery, 1890) (Myrmicinae) new to Britain, with an updated key to the known Strumigenys of the West Palaearctic. Zootaxa 5415(4), 570–576 (doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5415.4.6).
- Herrera, H.W., Baert, L., Dekoninck, W., Causton, C.E., Sevilla, C.R., Pozo, P., Hendrickx, F. 2020. Distribution and habitat preferences of Galápagos ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Belgian Journal of Entomology, 93: 1–60.
- Lubertazzi, D. 2019. The ants of Hispaniola. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology, 162(2), 59-210 (doi:10.3099/mcz-43.1).
- MacGown, J.A., Booher, D., Richter, H., Wetterer, J.K., Hill, J.G. 2021. An updated list of ants of Alabama (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with new state records. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 147: 961-981 (doi:10.3157/061.147.0409).
- MacGown, J.A., Wetterer, J.K. 2013. Distribution and biological notes of Strumigenys margaritae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Dacetini). Terrestrial Arthropod Reviews 6, 247–255 (doi:10.1163/18749836-06001066).
- Meurgey, F. 2020. Challenging the Wallacean shortfall: A total assessment of insect diversity on Guadeloupe (French West Indies), a checklist and bibliography. Insecta Mundi 786: 1–183.
- Nielsen, A., Atchison, R., Lucky, A. 2020. Effects of the invasive Little Fire Ant (Wasmannia auropunctata) on ant community composition on UF Campus. University of Florida | Journal of Undergraduate Research | Volume 22
- [[Media:Silva, T.S.R.D., Chaul, J.C.M. et al. 2022. Lectotype designation and redescription of four commonly collected Neotropical species of Strumigenys (10.5852@ejt.2022.798.1673).pdf|Silva, T.S.R.D., Chaul, J.C.M., Feitosa, R.M. 2022. Lectotype designation and redescription of four commonly collected Neotropical species of Strumigenys (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). European Journal of Taxonomy, 798(1), 103–126 (Template:Doi.org).]]
- Varela-Hernández, F., Medel-Zosayas, B., Martínez-Luque, E.O., Jones, R.W., De la Mora, A. 2020. Biodiversity in central Mexico: Assessment of ants in a convergent region. Southwestern Entomologist 454: 673-686.
- Wang, W.Y., Soh, E.J.Y., Yong, G.W.J., Wong, M.K.L., Benoit Guénard, Economo, E.P., Yamane, S. 2022. Remarkable diversity in a little red dot: a comprehensive checklist of known ant species in Singapore (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with notes on ecology and taxonomy. Asian Myrmecology 15: e015006 (doi:10.20362/am.015006).
References based on Global Ant Biodiversity Informatics
- Achury R., and A.V. Suarez. 2017. Richness and composition of ground-dwelling ants in tropical rainforest and surrounding landscapes in the Colombian Inter-Andean valley. Neotropical Entomology https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-017-0565-4
- Basset Y., L. Cizek, P. Cuenoud, R. K. Didham, F. Guilhaumon, O. Missa, V. Novotny, F. Odegaards, T. Roslin, J. Schmidl et al. 2012. Arthropod diversity in a tropical forest. Science 338(6113): 1481-1484.
- Bezdeckova K., P. Bedecka, and I. Machar. 2015. A checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of Peru. Zootaxa 4020 (1): 101–133.
- Boer P. 2019. Ants of Curacao, species list. Accessed on January 22 2019 at http://www.nlmieren.nl/websitepages/SPECIES%20LIST%20CURACAO.html
- Bolton, B. 2000. The Ant Tribe Dacetini. Memoirs of the American Entomological Institute 65
- Branstetter M. G. and L. Sáenz. 2012. Las hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) de Guatemala. Pp. 221-268 in: Cano E. B. and J. C. Schuster. (eds.) 2012. Biodiversidad de Guatemala. Volumen 2. Guatemala: Universidad del Valle de Guatemala, iv + 328 pp
- Brown W. L. Jr. 1960. The neotropical species of the ant genus Strumigenys Fr. Smith: group of gundlachi (Roger). Psyche (Cambridge) 66: 37-52.
- Brown W. L. Jr. 1962. The neotropical species of the ant genus Strumigenys Fr. Smith: synopsis and keys to the species. Psyche (Cambridge) 69: 238-267.
- Chacon de Ulloa P., A. M. Osorio-Garica, R. Achury, and C. Bermudez-Rivas. 2012. Hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) del Bosque seco tropical (Bs-T) de la cuenca alta del rio Cauca, Colombia. Biota Colombiana 13(2): 165-181.
- Dattilo W. et al. 2019. MEXICO ANTS: incidence and abundance along the Nearctic-Neotropical interface. Ecology https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2944
- Del Toro, I., M. Vázquez, W.P. Mackay, P. Rojas and R. Zapata-Mata. Hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) de Tabasco: explorando la diversidad de la mirmecofauna en las selvas tropicales de baja altitud. Dugesiana 16(1):1-14.
- Deyrup M. 1997. Dacetine ants of the Bahamas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bahamas Journal of Science 5(1): 2-6.
- Deyrup M., L. Davis, and S. Buckner. 1998. Composition of the ant fauna of three Bahamian islands. Proceedings of the seventh symposium on the natural history of the Bahamas. 23-32. Bahamian Field Station, San Salvador, Bahamas
- Dias N. D. S., R. Zanetti, M. S. Santos, M. F. Gomes, V. Peñaflor, S. M. F. Broglio, and J. H. C. Delabie. 2012. The impact of coffee and pasture agriculture on predatory and omnivorous leaf-litter ants. Journal of Insect Science 13:29. Available online: http://www.insectscience.org/13.29
- Dias N. S., R. Zanetti, M. S. Santos, J. Louzada, and J. H. C. Delabie. 2008. Interaction between forest fragments and adjacent coffee and pasture agroecosystems: responses of the ant communities (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Iheringia, Sér. Zool., Porto Alegre, 98(1): 136-142.
- Emery C. 1890. Studii sulle formiche della fauna neotropica. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 22: 38-8
- Fernandes, P.R. XXXX. Los hormigas del suelo en Mexico: Diversidad, distribucion e importancia (Hymenoptera: Formicidae).
- Fernández F., E. E. Palacio, W. P. MacKay, and E. S. MacKay. 1996. Introducción al estudio de las hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) de Colombia. Pp. 349-412 in: Andrade M. G., G. Amat García, and F. Fernández. (eds.) 1996. Insectos de Colombia. Estudios escogidos. Bogotá: Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales, 541 pp
- Fernández F., and E. E. Palacio. 1995. Hormigas de Colombia IV: nuevos registros de géneros y especies. Caldasia 17: 587-596.
- Fernández, F. and S. Sendoya. 2004. Lista de las hormigas neotropicales. Biota Colombiana Volume 5, Number 1.
- Fichaux M., B. Bechade, J. Donald, A. Weyna, J. H. C. Delabie, J. Murienne, C. Baraloto, and J. Orivel. 2019. Habitats shape taxonomic and functional composition of Neotropical ant assemblages. Oecologia 189(2): 501-513.
- Field Museum Collection, Chicago, Illinois (C. Moreau)
- Fontanla Rizo J.L. 1997. Lista preliminar de las hormigas de Cuba. Cocuyo 6: 18-21.
- Fontenla J. L., and J. Alfonso-Simonetti. 2018. Classification of Cuban ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) into functional groups. Poeyana Revista Cubana de Zoologia 506: 21-30.
- Fontenla Rizo J. L. 1997. Lista preliminar de las hormigas de Cuba (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Cocuyo 6: 18-21.
- Franco W., N. Ladino, J. H. C. Delabie, A. Dejean, J. Orivel, M. Fichaux, S. Groc, M. Leponce, and R. M. Feitosa. 2019. First checklist of the ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of French Guiana. Zootaxa 4674(5): 509-543.
- Galkowski C. 2016. New data on the ants from the Guadeloupe (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Bull. Soc. Linn. Bordeaux 151, 44(1): 25-36.
- Gomes D. S., F. S. Almeida, A. B. Vargas, and J. M. Queiroz. 2013. Resposta da assembleia de formigas na interface solo-serapilheira a um gradiente de alteração ambiental. Iheringia, Série Zoologia, Porto Alegre, 103(2):104-109
- Kempf W. W. 1958. The ants of the tribe Dacetini in the State of Sao Paulo, Brazil, with the description of a new species of Strumigenys. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Studia Entomologica (n.s.)1: 553-560.
- Kempf W. W. 1961. A survey of the ants of the soil fauna in Surinam (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Studia Entomologica 4: 481-524.
- Kempf, W.W. 1972. Catalago abreviado das formigas da regiao Neotropical (Hym. Formicidae) Studia Entomologica 15(1-4).
- Lattke, J.E. & Goitía, W. 1997. El género Strumigenys en Venezuela. Caldasia 19: 367-396.
- Longino J. T. 2013. Ants of Nicargua. Consulted on 18 Jan 2013. https://sites.google.com/site/longinollama/reports/ants-of-nicaragua
- Longino J. T. L., and M. G. Branstetter. 2018. The truncated bell: an enigmatic but pervasive elevational diversity pattern in Middle American ants. Ecography 41: 1-12.
- Longino J. et al. ADMAC project. Accessed on March 24th 2017 at https://sites.google.com/site/admacsite/
- Maes, J.-M. and W.P. MacKay. 1993. Catalogo de las hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) de Nicaragua. Revista Nicaraguense de Entomologia 23.
- Marinho C. G. S., R. Zanetti, J. H. C. Delabie, M. N. Schlindwein, and L. de S. Ramos. 2002. Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) Diversity in Eucalyptus (Myrtaceae) Plantations and Cerrado Litter in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Neotropical Entomology 31(2): 187-195.
- Mirmecofauna de la reserva ecologica de San Felipe Bacalar
- Morrison L. W. 1998. A review of Bahamian ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) biogeography. Journal of Biogeography 25: 561-571.
- Munhae C. B., Z. A. F. N. Bueno, M. S. C. Morini, and R. R. Silva. 2009. Composition of the Ant Fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Public Squares in Southern Brazil. Sociobiology 53(2B): 455-472.
- Olson D. M. 1991. A comparison of the efficacy of litter sifting and pitfall traps for sampling leaf litter ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in a tropical wet forest, Costa Rica. Biotropica 23(2): 166-172.
- Pacheco, R., R.R. Silva, M.S. de C. Morini, C.R.F. Brandao. 2009. A Comparison of the Leaf-Litter Ant Fauna in a Secondary Atlantic Forest with an Adjacent Pine Plantation in Southeastern Brazil. Neotropical Entomology 38(1):055-065
- Perez-Gelabert D. E. 2008. Arthropods of Hispaniola (Dominican Republic and Haiti): A checklist and bibliography. Zootaxa 1831:1-530.
- Pires de Prado L., R. M. Feitosa, S. Pinzon Triana, J. A. Munoz Gutierrez, G. X. Rousseau, R. Alves Silva, G. M. Siqueira, C. L. Caldas dos Santos, F. Veras Silva, T. Sanches Ranzani da Silva, A. Casadei-Ferreira, R. Rosa da Silva, and J. Andrade-Silva. 2019. An overview of the ant fauna (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the state of Maranhao, Brazil. Pap. Avulsos Zool. 59: e20195938.
- Portuondo E. F., and J. L. Reyes. 2002. Mirmecofauna de los macizos montañosos de Sierra Maestra y Nipe-Sagua-Baracoa. Cocuyo 12: 10-13
- Portuondo Ferrer E., and J. L. Fernández Triana. 2005. Species of hymenopterans (bees, wasps, and ants) recorded in Alejandro de Humboldt National Park, from literature records, revision of the collection at BIOECO, and collections before and during the rapid inventory, 12-22 February 2004. In Fong G., A., D. Maceira F., W. S. Alverson, y/and T. Wachter, eds. 2005. Cuba: Parque Nacional Alejandro de Humboldt. Rapid Biological Inventories Report 14. The Field Museum, Chicago.
- Portuondo Ferrer, E. and J. Fernandez Triana. Biodiversidad del orden Hymenoptera en Los Macizos Montanosos de Cuba Oriental. Boletin S.E.A. 35:121-136.
- Ramos L. S., R. Z. B. Filho, J. H. C. Delabie, S. Lacau, M. F. S. dos Santos, I. C. do Nascimento, and C. G. S. Marinho. 2003. Ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the leaf-litter in cerrado stricto sensu areas in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Lundiana 4(2): 95-102.
- Ramos L. de S., C. G. S. Marinho, R. Zanetti, and J. H. C. Delabie. 2003. Impacto de iscas formicidas granuladas sobre a mirmecofauna não-alvo em eucaliptais segundo duas formas de aplicacação / Impact of formicid granulated baits on non-target ants in eucalyptus plantations according to two forms of application. Neotropical Entomology 32(2): 231-237.
- Ramos L. de S., R. Zanetti, C. G. S. Marinho, J. H. C. Delabie, M. N. Schlindwein, and R. P. Almado. 2004. Impact of mechanical and chemical weedings of Eucalyptus grandis undergrowth on an ant community (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Rev. Árvore 28(1): 139-146.
- Reyes, J. L. "Inventario de la colección de hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) del Centro Oriental de Ecosistemas y Biodiversidad, Santiago de Cuba, Cuba." Boletín de la Sociedad Aragonesa 36 (2005): 279-283.
- Rosa da Silva R. 1999. Formigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) do oeste de Santa Catarina: historico das coletas e lista atualizada das especies do Estado de Santa Catarina. Biotemas 12(2): 75-100.
- Rosa da Silva R., and B. Cortes Lopes. 1997. Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from Atlantic rainforest at Santa Catarina Island, Brazil: two years of sampling. Rev. Biol. Trop. 45(4): 1641-1648.
- Rosumek, F.B., M.A. Ulyssea, B.C. Lopes, J. Steiner. 2008. Formigas de solo e de bromélias em uma área de Mata Atlântica, Ilha de Santa Catarina, sul do Brasil: Levantamento de espécies e novos registros. Revista Biotemas 21(4):81-89.
- Salazar F., and D. A. Donoso. 2013. New ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) records for Ecuador deposited at the Carl Rettenmeyer ant collection in the QCAZ Museum. Boletín Tecnico 11, Serie Zoológica 8-9: 151 177.
- Salinas P. J. 2010. Catalogue of the ants of the Táchira State, Venezuela, with notes on their biodiversity, biogeography and ecology (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Amblyioponinae, Ponerinae, Proceratiinae, Myrmicinae, Ecitoninae, Formicinae, Pseudomyrmecinae, Dolichoderinae). Boletín de la SEA 47: 315-328.
- Santos M. P. C. J., A. F. Carrano-Moreira, and J. B. Torres. 2012. Diversity of soil ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in dense Atlantic Forest and sugarcane plantationsin the County of Igarassu-PE. Revista Brasileira de Ciências Agrárias 7(4): 648-656.
- Santos M. S., J. N. C. Louzada, N. Dias, R. Zanetti, J. H. C. Delabie, and I. C. Nascimento. 2006. Litter ants richness (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in remnants of a semi-deciduous forest in the Atlantic rain forest, Alto do Rio Grande region, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Iheringia, Sér. Zool., Porto Alegre, 96(1): 95-101.
- Santschi F. 1930. Quelques fourmis de Cuba et du Brésil. Bulletin. Société Entomologique d'Egypte. 14: 75-83.
- Santschi F. 1931. Fourmis de Cuba et de Panama. Revista de Entomologia (Rio de Janeiro). 1: 265-282.
- Silva T. S. R., and R. M. Feitosa. 2019. Using controlled vocabularies in anatomical terminology: A case study with Strumigenys (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Arthropod Structure and Development 52: 1-26.
- Silvestre R., C. R. F. Brandão, and R. R. Silva da 2003. Grupos funcionales de hormigas: el caso de los gremios del cerrado. Pp. 113-148 in: Fernández, F. (ed.) 2003. Introducción a las hormigas de la región Neotropical. Bogotá: Instituto de Investigación de Recursos Biológicos Alexander von Humboldt, xxvi + 424 pp.
- Silvestre R., M. F. Demetrio, and J. H. C. Delabie. 2012. Community Structure of Leaf-Litter Ants in a Neotropical Dry Forest: A Biogeographic Approach to Explain Betadiversity. Psyche doi:10.1155/2012/306925
- Siqueira de Castro F., A. B. Gontijo, P. de Tarso Amorim Castro, and S. Pontes Ribeiro. 2012. Annual and Seasonal Changes in the Structure of Litter-Dwelling Ant Assemblages (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Atlantic Semideciduous Forests. Psyche doi:10.1155/2012/959715
- Siqueira de Castro F., A. B. Gontijo, W. Duarte da Rocha, and S. Pontes Ribeiro. 2011. As comunidades de formigas de serapilheira nas florestas semidecíduas do Parque Estadual do Rio Doce, Minas Gerais. MG.BIOTA, Belo Horizonte 3(5): 5-24.
- Smith M. A., W. Hallwachs, D. H. Janzen. 2014. Diversity and phylogenetic community structure of ants along a Costa Rican elevational gradient. Ecography 37(8): 720-731.
- Smith M. R. 1937. The ants of Puerto Rico. Journal of Agriculture of the University of Puerto Rico 20: 819-875.
- Soares S. A., D. Lange, and W. F. Antoniali Junior. 2006. Communities of Epigaeic ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in an area of reforestation and in native forest. Sociobiology 49(3): 251-263.
- Soares S. A., W. F. Antoniali Junior, and S. E. Lima-Junior. 2010. Diversidade de formigas epigéicas (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) em dois ambientes no Centro-Oeste do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Entomologia 54(1): 7681.
- Suguituru S. S., D. R. de Souza, C. de Bortoli Munhae, R. Pacheco, and M. S. de Castro Morini. 2011. Diversidade e riqueza de formigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) em remanescentes de Mata Atlântica na Bacia Hidrográfica do Alto Tietê, SP. Biota Neotrop. 13(2): 141-152.
- Suguituru S. S., M. Santina de Castro Morini, R. M. Feitosa, and R. Rosa da Silva. 2015. Formigas do Alto Tiete. Canal 6 Editora 458 pages
- Torres, Juan A. and Roy R. Snelling. 1997. Biogeography of Puerto Rican ants: a non-equilibrium case?. Biodiversity and Conservation 6:1103-1121.
- Ulyssea M. A., C. R. F. Brandao. 2013. Catalogue of Dacetini and Solenopsidini ant type specimens (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, Myrmicinae) deposited in the Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo, Brazil. Papies Avulsos de Zoologia 53(14): 187-209.
- Vittar, F., and F. Cuezzo. "Hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) de la provincia de Santa Fe, Argentina." Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina (versión On-line ISSN 1851-7471) 67, no. 1-2 (2008).
- Vásquez-Bolaños M. 2011. Lista de especies de hormigas (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) para México. Dugesiana 18: 95-133
- Wang W. Y., and S. Yamane. 2017. First record of a New World ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), Strumigenys eggersi Emery, 1890 in the Old World. BioInvasions Records 6: in Press.
- Weber N. A. 1952. Biological notes on Dacetini (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). American Museum Novitates 1554: 1-7.
- Weber N. A. 1952. Biological notes on Dacetini (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). American Museum Novitates 1554: 1-7.
- Wetterer J. K. 2018. Geographic Distributions of Strumigenys gundlachi and Strumigenys eggersi (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Transactions of the American Entomological Society 144(1): 131-141.
- Wheeler W. M. 1905. The ants of the Bahamas, with a list of the known West Indian species. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 21: 79-135.
- Wheeler W. M. 1908. The ants of Porto Rico and the Virgin Islands. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 24: 117-158.
- Wheeler W. M. 1922. The ants of Trinidad. American Museum Novitates 45: 1-16.
- da Silva, R.R., C.R.F. Brandao, and R. Silvestre. 2004. Similarity Between Cerrado Localities in Central and Southeastern Brazil Based on the Dry Season Bait Visitors Ant Fauna. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment 39(3):191-199.



